Herbs are natural plants valued for their aromatic, culinary, and medicinal properties, enriching both flavors and wellness routines. Incorporating fresh or dried herbs into your meals can boost nutritional benefits while enhancing taste profiles. Discover the diverse uses and benefits of herbs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
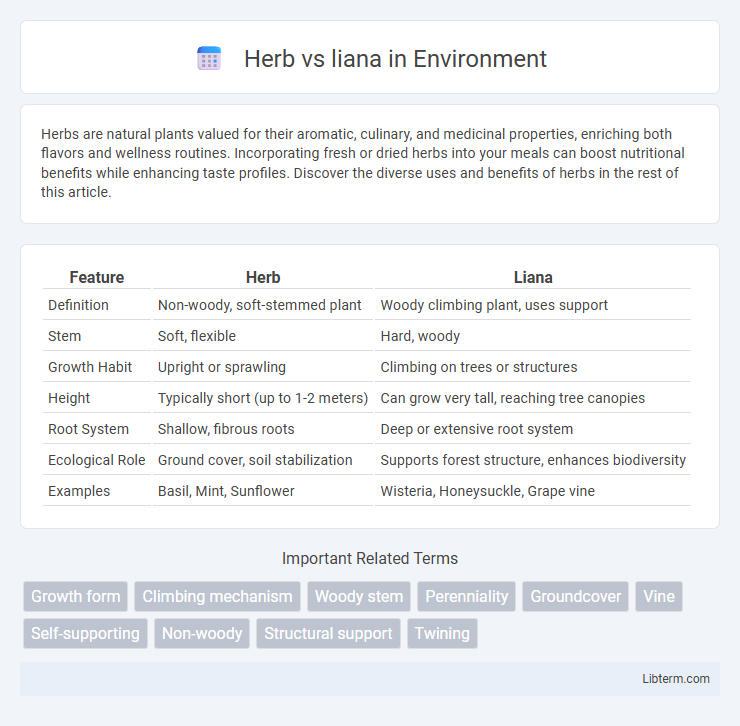
| Feature | Herb | Liana |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-woody, soft-stemmed plant | Woody climbing plant, uses support |
| Stem | Soft, flexible | Hard, woody |
| Growth Habit | Upright or sprawling | Climbing on trees or structures |
| Height | Typically short (up to 1-2 meters) | Can grow very tall, reaching tree canopies |
| Root System | Shallow, fibrous roots | Deep or extensive root system |
| Ecological Role | Ground cover, soil stabilization | Supports forest structure, enhances biodiversity |
| Examples | Basil, Mint, Sunflower | Wisteria, Honeysuckle, Grape vine |
Introduction to Herbs and Lianas
Herbs are non-woody, soft-stemmed plants that typically complete their life cycle within a single season, often used for culinary, medicinal, and aromatic purposes. Lianas are woody climbing plants found predominantly in tropical forests, using trees for structural support as they ascend toward sunlight. Both herbs and lianas play crucial ecological roles, with herbs contributing to ground-level biodiversity and lianas influencing forest dynamics and canopy structure.
Defining Herbs: Key Characteristics
Herbs are non-woody plants distinguished by their soft, green stems and relatively short lifespan, typically surviving less than two years. They play a crucial role in cooking, medicine, and aromatherapy due to their aromatic leaves and flowers rich in essential oils. Unlike lianas, which are long, woody climbers relying on support structures, herbs grow independently and lack persistent woody tissue.
Understanding Lianas: Features and Growth
Lianas are woody climbing plants characterized by their long, flexible stems that rely on trees for support to reach sunlight in dense forests. Unlike herbs, which have soft, non-woody stems and grow independently, lianas develop thick, lignified tissues enabling them to span large distances and access canopy light efficiently. Their growth strategy enhances forest biodiversity by connecting different tree species and creating complex habitats.
Morphological Differences Between Herbs and Lianas
Herbs exhibit soft, non-woody stems that typically die back at the end of the growing season, whereas lianas possess woody, climbing stems that provide structural support for ascending trees. The root structures differ, with herbs developing fibrous roots suitable for shallow soil layers, while lianas often develop deep and extensive root systems to anchor and absorb nutrients. Leaf morphology in herbs is generally simple and broad to maximize photosynthesis near the ground, contrasting with lianas that frequently have tougher, compound leaves adapted for climbing environments.
Ecological Roles of Herbs vs Lianas
Herbs contribute significantly to soil stabilization and nutrient cycling in ecosystems by rapidly decomposing and enriching the soil with organic matter. Lianas enhance forest structure complexity by connecting tree canopies, facilitating animal movement, and influencing light penetration to the understory. Both plant types play crucial but distinct roles in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem functionality.
Growth Patterns and Lifespans
Herbs typically exhibit rapid growth with shorter lifespans, often completing their life cycle within a single growing season or a few years. Lianas, woody climbing plants predominantly found in tropical forests, demonstrate slower growth rates but can live for several decades due to their strong, persistent stems. The growth pattern of lianas involves climbing on trees to reach sunlight, contrasting with herbs that grow independently from the ground.
Adaptations and Survival Strategies
Herbs exhibit rapid growth and short life cycles, enabling them to quickly exploit resources and environments with seasonal fluctuations. Lianas possess specialized climbing adaptations such as twining stems and adhesive rootlets to access sunlight in dense forests, reducing competition for light at ground level. These survival strategies allow herbs to thrive in open spaces while lianas dominate vertical forest niches.
Distribution and Habitat Preferences
Herbs predominantly inhabit temperate and tropical regions, thriving in diverse habitats ranging from grasslands and forests to disturbed soils and wetlands. Lianas are primarily found in tropical rainforests, where they climb trees to access sunlight in dense canopies. The distribution of herbs is broader and more varied, while lianas have a specialized preference for humid, densely vegetated environments.
Economic and Medicinal Importance
Herbs are widely used in the pharmaceutical industry for their potent medicinal compounds, contributing significantly to the development of drugs and natural remedies. Lianas, while less commonly utilized, provide valuable economic resources such as materials for furniture, handicrafts, and traditional medicine in tropical regions. Both herbs and lianas play essential roles in local economies by supporting herbal medicine markets and sustainable harvesting practices.
Summary: Choosing Between Herb and Liana
Herbs are non-woody plants that complete their life cycle quickly, often used for culinary and medicinal purposes, while lianas are woody climbing plants found primarily in tropical forests, providing structural support to trees. The choice between herb and liana depends on space availability, growth habits, and the desired ecological role, with herbs suited for compact gardens and lianas ideal for vertical growth and biodiversity enhancement. Selecting the appropriate plant type optimizes environmental benefits and practical uses in landscaping or agriculture.
Herb Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com