Finding the perfect balance in a broad-niche market involves targeting a wide audience while maintaining enough specificity to stand out from competitors. This approach allows you to appeal to diverse customer needs without diluting your brand message. Explore this article to discover effective strategies for mastering your broad-niche market and maximizing your business potential.
Table of Comparison
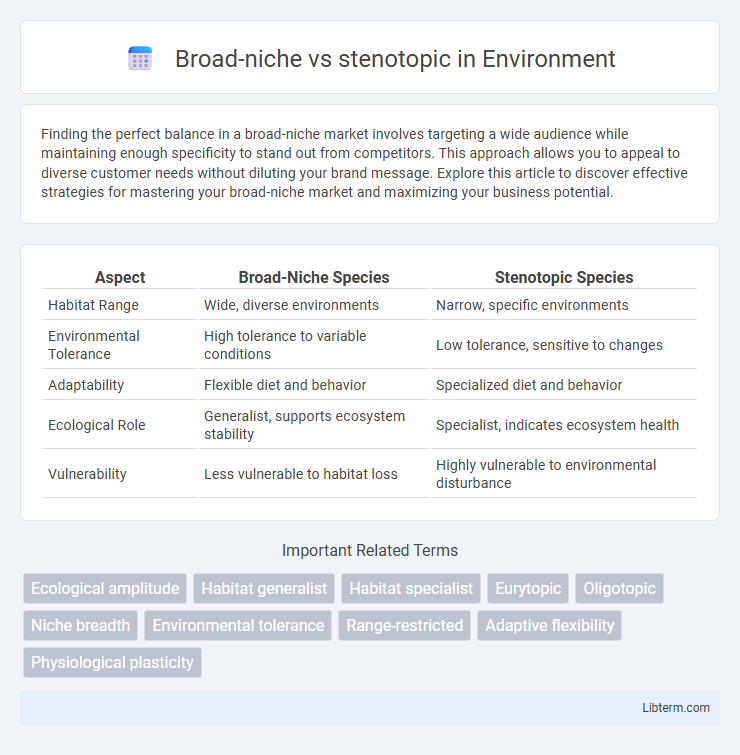
| Aspect | Broad-Niche Species | Stenotopic Species |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat Range | Wide, diverse environments | Narrow, specific environments |
| Environmental Tolerance | High tolerance to variable conditions | Low tolerance, sensitive to changes |
| Adaptability | Flexible diet and behavior | Specialized diet and behavior |
| Ecological Role | Generalist, supports ecosystem stability | Specialist, indicates ecosystem health |
| Vulnerability | Less vulnerable to habitat loss | Highly vulnerable to environmental disturbance |
Understanding Broad-Niche and Stenotopic Organisms
Broad-niche organisms thrive in diverse environments by utilizing a wide range of resources, exhibiting high ecological plasticity and adaptability. Stenotopic organisms are specialized species restricted to narrow ecological conditions, often with limited tolerance to environmental changes. Understanding these contrasting survival strategies provides insight into species distribution, habitat preference, and ecosystem resilience.
Defining Niche Breadth in Ecology
Niche breadth reflects the range of environmental conditions and resources a species can utilize, distinguishing broad-niche species that thrive in diverse habitats from stenotopic species restricted to specific conditions. Broad-niche species exhibit ecological flexibility, enabling adaptation across varied ecosystems, while stenotopic species show specialization that may increase vulnerability to environmental changes. Understanding niche breadth informs ecological resilience, species distribution modeling, and conservation strategies in dynamic habitats.
Characteristics of Broad-Niche Species
Broad-niche species exhibit high ecological tolerance, enabling them to thrive in diverse habitats and utilize a wide variety of resources. Their adaptability to fluctuating environmental conditions promotes resilience and widespread distribution across ecosystems. These species often have generalized dietary preferences and reproductive strategies that enhance their survival in multiple niches.
Traits of Stenotopic Species
Stenotopic species exhibit a narrow ecological niche, thriving only under specific environmental conditions such as precise temperature, humidity, or substrate types. These species often possess specialized physiological and behavioral adaptations that limit their tolerance to habitat variability. High sensitivity to environmental changes makes stenotopic organisms valuable bioindicators for ecosystem health and stability.
Adaptability and Survival Strategies
Broad-niche species exhibit high adaptability by exploiting diverse environments, enhancing survival through flexible diet, habitat use, and reproductive strategies. Stenotopic species demonstrate specialized survival tactics limited to narrow ecological niches, relying on precise environmental conditions and resources for survival. This specialization renders stenotopic organisms more vulnerable to habitat changes, while broad-niche species often thrive amid environmental fluctuations.
Ecological Roles and Interactions
Broad-niche species exhibit versatile ecological roles, interacting with a wide range of habitats and species, enhancing ecosystem resilience through diverse resource utilization. Stenotopic species occupy specialized niches, forming highly specific interactions that contribute to the stability of particular ecological communities. These contrasting niche strategies influence biodiversity patterns and ecosystem dynamics by balancing generalist adaptability with specialist precision.
Environmental Tolerance and Distribution
Broad-niche species exhibit high environmental tolerance, allowing them to thrive across diverse habitats and wide geographic distributions. Stenotopic species possess narrow environmental tolerance, restricting them to specific ecological conditions and limited ranges. This contrast in adaptability directly influences their potential for colonization and survival amid environmental fluctuations.
Evolutionary Implications of Niche Width
Broad-niche species possess flexible habitat preferences and resource use, promoting adaptability and resilience in fluctuating environments, which can drive evolutionary diversification and speciation. In contrast, stenotopic species exhibit specialized ecological tolerances, leading to narrower niche widths that enhance competitive advantage in stable environments but increase vulnerability to environmental changes. Evolutionarily, niche width influences species' survival strategies, genetic variation, and potential for adaptive radiation in response to ecological pressures.
Human Impact on Niche Specialization
Broad-niche species exhibit greater ecological flexibility, allowing them to exploit diverse habitats and resources, which enhances their resilience to human-induced environmental changes such as habitat fragmentation and pollution. In contrast, stenotopic species are highly specialized with narrow habitat requirements, making them more vulnerable to anthropogenic disturbances and often resulting in population declines or local extinctions. Human activities that alter ecosystem stability disproportionately threaten stenotopic organisms, emphasizing the need for targeted conservation strategies to preserve biodiversity.
Conservation Considerations for Broad-Niche and Stenotopic Species
Broad-niche species exhibit adaptability to a wide range of habitats, making their conservation management more flexible and focused on preserving diverse ecosystem services and connectivity across landscapes. Stenotopic species require highly specific environmental conditions, demanding targeted conservation strategies that protect their limited habitats from fragmentation, pollution, and climate change impacts. Prioritizing habitat integrity and microhabitat quality is critical for stenotopic species conservation, while broad-niche species benefit from maintaining overall ecosystem resilience and heterogeneity.
Broad-niche Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com