Effective pollution control involves implementing strategies to reduce contaminants in air, water, and soil, thereby protecting ecosystems and human health. Technologies like air scrubbers, wastewater treatment, and waste recycling play a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical pollution control methods and how You can contribute to a cleaner planet.
Table of Comparison
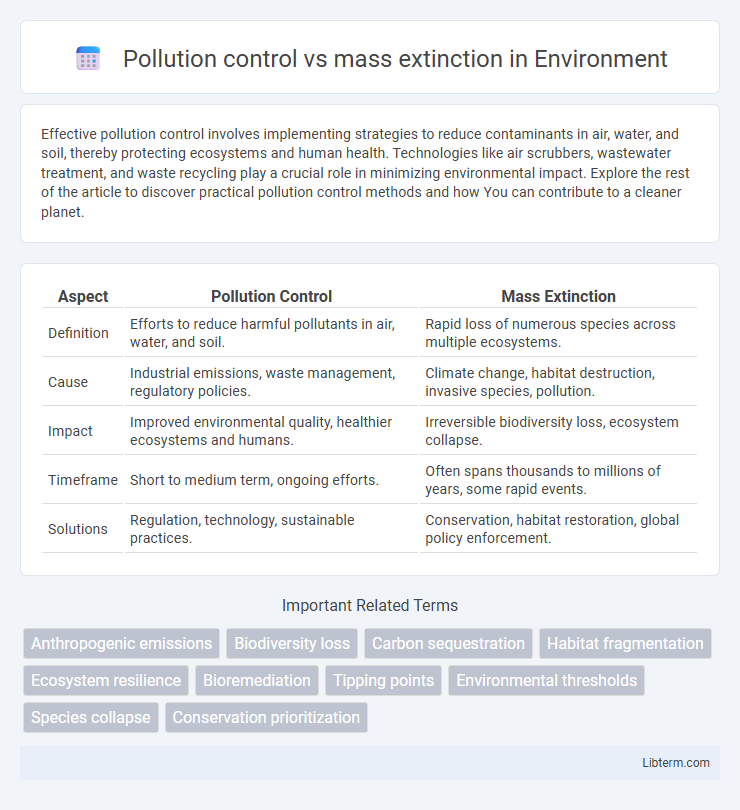
| Aspect | Pollution Control | Mass Extinction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Efforts to reduce harmful pollutants in air, water, and soil. | Rapid loss of numerous species across multiple ecosystems. |
| Cause | Industrial emissions, waste management, regulatory policies. | Climate change, habitat destruction, invasive species, pollution. |
| Impact | Improved environmental quality, healthier ecosystems and humans. | Irreversible biodiversity loss, ecosystem collapse. |
| Timeframe | Short to medium term, ongoing efforts. | Often spans thousands to millions of years, some rapid events. |
| Solutions | Regulation, technology, sustainable practices. | Conservation, habitat restoration, global policy enforcement. |
Understanding Pollution Control: An Overview
Pollution control employs advanced technologies and regulatory frameworks to reduce harmful emissions and contaminants affecting air, water, and soil quality. Effective pollution management minimizes the risk of habitat degradation and species loss, playing a crucial role in preventing mass extinction events. Integrating pollution control strategies with biodiversity conservation efforts ensures the protection of ecosystems and sustains global ecological balance.
The Rising Threat of Mass Extinction
The rising threat of mass extinction is driven by increasing pollution levels, including toxic chemicals, plastic debris, and airborne contaminants that devastate ecosystems worldwide. Pollution control measures are critical in mitigating habitat destruction, preserving biodiversity, and preventing irreversible species loss. Effective regulation of pollutants, along with habitat restoration efforts, can slow the accelerating rate of extinction and maintain ecological balance.
How Pollution Drives Species Loss
Pollution introduces toxic substances into ecosystems that disrupt food chains and degrade habitats, causing physiological stress and reproductive failures in sensitive species. Contaminants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and plastic microfibers accumulate in organisms, leading to bioaccumulation and biomagnification, which compromise survival rates and genetic diversity. This ongoing environmental degradation accelerates species loss and contributes significantly to the current mass extinction crisis by reducing biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Pollution Control Measures: Global Strategies
Global strategies for pollution control include enforcing stringent air and water quality standards, promoting the use of renewable energy sources, and implementing waste management systems to reduce contamination. International agreements such as the Paris Agreement and the Convention on Biological Diversity play crucial roles in coordinating efforts among countries to reduce pollutants that contribute to habitat degradation and species loss. Advanced technologies like carbon capture, bioremediation, and pollution-tracking sensors are increasingly utilized to monitor and mitigate environmental damage, directly supporting biodiversity conservation and preventing mass extinction events.
Mass Extinction Events: Historical Lessons
Mass extinction events, such as the Permian-Triassic and Cretaceous-Paleogene extinctions, demonstrate the catastrophic impact of rapid environmental changes on global biodiversity. Geological and fossil records reveal that massive shifts in atmospheric composition, ocean chemistry, and climate exacerbated species die-offs, underscoring the critical need for effective pollution control to prevent analogous outcomes. Understanding these historical lessons highlights how anthropogenic emissions of greenhouse gases, heavy metals, and persistent organic pollutants can trigger similar cascading ecosystem collapses if left unmitigated.
Connecting Biodiversity Loss to Industrial Pollution
Industrial pollution significantly accelerates biodiversity loss by contaminating ecosystems with toxic chemicals, heavy metals, and greenhouse gases that disrupt species habitats and reproductive cycles. Effective pollution control measures, including stricter emission regulations and waste management, are crucial to mitigating habitat degradation and preventing mass extinction events. Scientific studies link elevated pollution levels to declines in population diversity, highlighting the urgent need for integrated environmental policies to preserve global biodiversity.
Innovations in Pollution Reduction Technologies
Innovations in pollution reduction technologies play a crucial role in mitigating mass extinction by minimizing harmful emissions and preserving biodiversity. Advanced filtration systems, bioremediation techniques, and real-time air quality monitoring are significantly reducing toxic pollutants that threaten ecosystems. These technological advancements enable industries to balance growth with environmental protection, directly combating the drivers of species loss.
Pollution Regulation Policies and Their Impact on Ecosystems
Pollution regulation policies such as the Clean Air Act and the European Union's REACH framework have significantly reduced harmful emissions, improving air and water quality which directly benefits ecosystems. Effective pollution control mitigates habitat degradation and loss of biodiversity by limiting toxic substances that contribute to species decline and mass extinction events. Strengthening enforcement and updating regulations with scientific insights are crucial for sustaining ecosystem resilience against ongoing environmental threats.
The Role of Community Involvement in Pollution Prevention
Community involvement plays a crucial role in pollution prevention by fostering local stewardship and enhancing the effectiveness of pollution control measures. Active participation of residents in monitoring pollution sources, advocating for sustainable practices, and supporting regulatory policies significantly reduces environmental contaminants that contribute to mass extinction. Empowered communities can drive behavioral changes and hold industries accountable, ultimately safeguarding biodiversity and ecosystem health.
A Sustainable Future: Balancing Pollution Control and Biodiversity Conservation
Pollution control is essential in mitigating harmful emissions and waste that threaten ecosystems, directly supporting biodiversity conservation efforts aimed at preventing mass extinction. Implementing sustainable practices such as reducing industrial pollutants, promoting renewable energy, and enforcing environmental regulations helps maintain ecosystem resilience and species survival. Balancing these efforts fosters a harmonious relationship between human development and the natural world, ensuring a sustainable future for all living organisms.
Pollution control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com