Synthetic weed control involves the use of chemical herbicides to effectively eliminate unwanted plants in agricultural or garden settings. These herbicides target specific weed species while minimizing damage to crops, enhancing overall yield and land management. Explore the article to discover the best synthetic weed control methods and how they can benefit your cultivation practices.
Table of Comparison
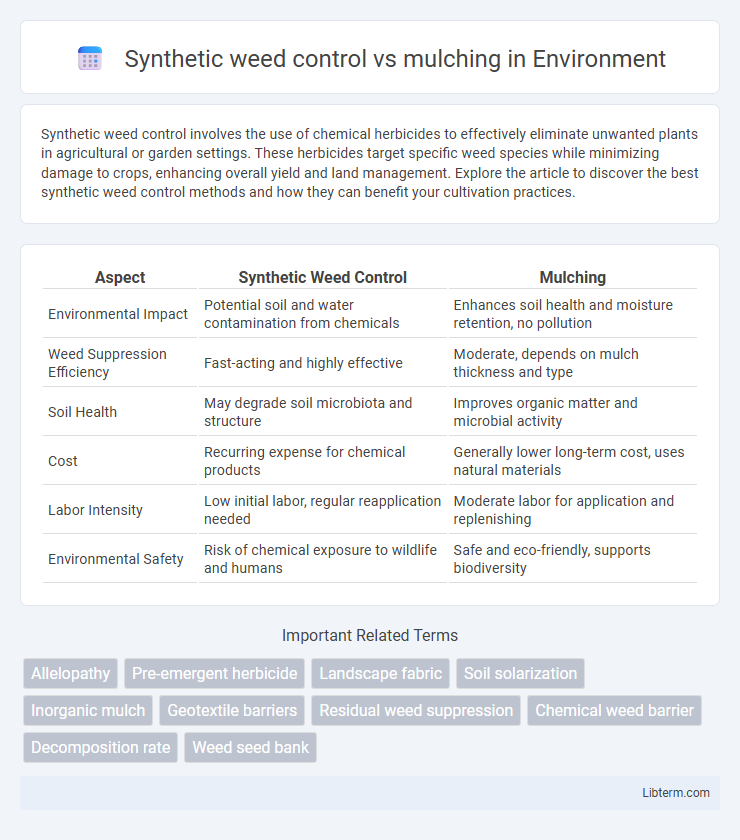
| Aspect | Synthetic Weed Control | Mulching |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Potential soil and water contamination from chemicals | Enhances soil health and moisture retention, no pollution |
| Weed Suppression Efficiency | Fast-acting and highly effective | Moderate, depends on mulch thickness and type |
| Soil Health | May degrade soil microbiota and structure | Improves organic matter and microbial activity |
| Cost | Recurring expense for chemical products | Generally lower long-term cost, uses natural materials |
| Labor Intensity | Low initial labor, regular reapplication needed | Moderate labor for application and replenishing |
| Environmental Safety | Risk of chemical exposure to wildlife and humans | Safe and eco-friendly, supports biodiversity |
Understanding Synthetic Weed Control
Synthetic weed control involves the application of chemical herbicides designed to target and eliminate specific weed species, providing rapid and effective weed management in agricultural and landscaping settings. These herbicides function by disrupting essential plant processes such as photosynthesis or cell division, resulting in controlled and selective weed suppression. Understanding the mode of action, environmental impact, and safety precautions associated with synthetic weed control is crucial for optimizing its efficacy and minimizing potential ecological harm.
What Is Mulching?
Mulching involves covering the soil surface with organic or inorganic materials like straw, wood chips, or plastic to suppress weed growth, retain soil moisture, and regulate temperature. This natural weed control method improves soil health by adding nutrients and enhancing microbial activity, unlike synthetic weed control which relies on chemical herbicides. Mulching also reduces erosion and runoff, promoting sustainable agricultural practices while minimizing environmental impact.
Effectiveness in Weed Suppression
Synthetic weed control uses herbicides that target and kill weeds at the root level, providing rapid and effective suppression over large areas. Mulching physically blocks sunlight and inhibits weed seed germination, offering a natural and environmentally friendly method but with slower onset and limited long-term control. Combining both methods can optimize weed suppression by delivering immediate control through chemicals and sustained prevention through mulch barriers.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Synthetic weed control relies heavily on chemical herbicides that can contaminate soil and water, posing significant risks to biodiversity and long-term ecosystem health. Mulching, using organic materials like straw or wood chips, enhances soil moisture retention and fertility while minimizing erosion and chemical runoff, promoting sustainable agricultural practices. The environmental footprint of mulching is considerably lower, supporting soil microbiota and reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to synthetic alternatives.
Cost Analysis: Synthetic vs Mulch
Synthetic weed control methods typically involve higher initial expenses due to the purchase of chemical herbicides and application equipment but often result in faster weed management. Mulching offers a cost-effective alternative with lower upfront costs, utilizing organic or synthetic materials that improve soil health and moisture retention while suppressing weeds. Over time, mulch can reduce long-term weed control expenses by enhancing soil fertility and reducing the frequency of intervention compared to synthetic herbicides.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Synthetic weed control involves laying down geotextile fabrics or plastic films that are durable and require minimal maintenance, effectively blocking sunlight to prevent weed growth. Mulching requires the consistent application and replenishment of organic or inorganic materials like wood chips or straw, demanding regular monitoring to maintain adequate coverage and weed suppression. Installation of synthetic barriers is typically more labor-intensive upfront, while mulching offers easier application but necessitates ongoing upkeep to remain effective.
Impact on Soil Health
Synthetic weed control often relies on chemical herbicides that can disrupt soil microbial communities and reduce biodiversity, leading to long-term degradation of soil health. Mulching improves soil structure by conserving moisture, enhancing organic matter content, and promoting beneficial microbial activity critical for nutrient cycling. Compared to synthetic methods, mulching supports sustainable soil fertility and reduces erosion, fostering a more resilient agricultural ecosystem.
Aesthetic Considerations
Synthetic weed control offers a clean, uniform look by preventing weed growth without disrupting soil appearance, maintaining a tidy landscape surface. Mulching enhances aesthetic appeal through natural textures and colors, adding depth and warmth to garden beds while simultaneously suppressing weeds. Combining both methods can balance the sleek, low-maintenance benefits of synthetic products with the organic visual charm of mulches.
Long-Term Benefits and Drawbacks
Synthetic weed control offers immediate and effective suppression of weeds but may lead to soil degradation and chemical resistance in the long term. Mulching enhances soil moisture retention, suppresses weed growth naturally, and improves soil fertility over time, promoting sustainable plant health. However, mulching requires more labor and may attract pests if not managed properly, contrasting with the convenience of synthetic herbicides.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Garden
Synthetic weed control offers rapid effectiveness against unwanted plants by using chemical herbicides, ideal for large-scale gardens requiring quick results. Mulching improves soil health and moisture retention while suppressing weeds naturally, making it suitable for sustainable and organic gardening practices. Gardeners should evaluate factors like garden size, environmental impact, and long-term soil quality when choosing between synthetic methods and mulching to maintain a healthy growing environment.
Synthetic weed control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com