Alkaline mine drainage occurs when water interacts with minerals in mining sites, leading to elevated pH levels and the release of harmful substances into nearby ecosystems. Managing this issue requires careful monitoring and treatment to protect water quality and aquatic life from potential toxicity. Discover effective strategies and insights to mitigate alkaline mine drainage by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
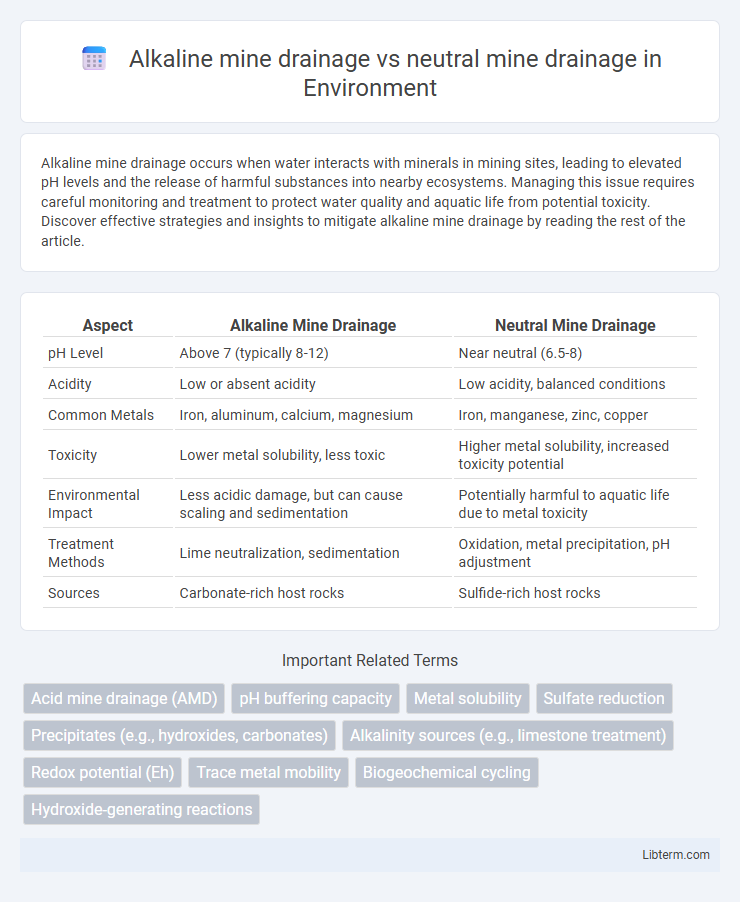
| Aspect | Alkaline Mine Drainage | Neutral Mine Drainage |
|---|---|---|
| pH Level | Above 7 (typically 8-12) | Near neutral (6.5-8) |
| Acidity | Low or absent acidity | Low acidity, balanced conditions |
| Common Metals | Iron, aluminum, calcium, magnesium | Iron, manganese, zinc, copper |
| Toxicity | Lower metal solubility, less toxic | Higher metal solubility, increased toxicity potential |
| Environmental Impact | Less acidic damage, but can cause scaling and sedimentation | Potentially harmful to aquatic life due to metal toxicity |
| Treatment Methods | Lime neutralization, sedimentation | Oxidation, metal precipitation, pH adjustment |
| Sources | Carbonate-rich host rocks | Sulfide-rich host rocks |
Introduction to Mine Drainage
Alkaline mine drainage (AMD) typically contains high concentrations of bicarbonates, calcium, and magnesium, which neutralize acidity and result in pH levels above 7, reducing environmental harm. In contrast, neutral mine drainage often arises from weathered sulfide minerals and maintains near-neutral pH without significant acid generation but may still carry elevated metal concentrations. Understanding the chemical differences between alkaline and neutral mine drainage is crucial for designing effective treatment and remediation strategies in mining-impacted environments.
What is Alkaline Mine Drainage?
Alkaline mine drainage (AMD) occurs when mining activities expose mineral deposits that interact with water and oxygen, producing water with a pH typically above 7 due to the presence of alkaline substances such as calcium carbonate or magnesium minerals. This type of drainage often results from mining operations in areas rich in carbonate minerals, which neutralize acidity and limit the release of harmful metals. Understanding the chemical composition and pH differences between alkaline mine drainage and neutral mine drainage is crucial for developing effective environmental management and remediation strategies in mining regions.
What is Neutral Mine Drainage?
Neutral mine drainage refers to water discharged from mining activities that has a near-neutral pH level, typically between 6 and 8, minimizing its acidity impact on the environment. Unlike acidic or alkaline mine drainage, neutral mine drainage contains lower concentrations of dissolved metals and sulfates, reducing its potential toxicity to aquatic life. Effective management of neutral mine drainage is essential to prevent metal contamination and maintain water quality in surrounding ecosystems.
Causes of Alkaline Mine Drainage
Alkaline mine drainage is primarily caused by the oxidation of sulfide minerals in the presence of carbonate minerals, which neutralize acid and result in elevated pH levels. This process often occurs in mining areas with high concentrations of minerals such as calcite and dolomite that buffer acidity, leading to alkaline water conditions. In contrast, neutral mine drainage occurs when the acid generated by sulfide oxidation is balanced by natural buffering capacity, maintaining a near-neutral pH.
Causes of Neutral Mine Drainage
Neutral mine drainage primarily results from the oxidation of sulfide minerals such as pyrite and chalcopyrite when exposed to oxygen and water, but the presence of carbonate minerals like calcite neutralizes acidity, maintaining near-neutral pH levels. The buffering capacity of carbonate-rich host rocks or mine tailings plays a critical role in mitigating acid generation, distinguishing neutral mine drainage from alkaline or acidic variants. Microbial activity influencing sulfide oxidation rates and the geochemical interactions between surface water and reactive minerals further contribute to the formation of neutral mine drainage conditions.
Chemical Characteristics: Alkaline vs Neutral Drainage
Alkaline mine drainage typically exhibits high pH values above 7 due to the presence of carbonate and hydroxide minerals, resulting in elevated concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate ions. Neutral mine drainage maintains a pH close to 7, often caused by the buffering capacity of carbonate minerals, with metal concentrations generally lower than acidic drainage and varying metal mobility. Chemical characteristics of alkaline drainage promote precipitation of metals as stable carbonates or hydroxides, whereas neutral drainage allows for moderate metal solubility depending on site-specific geochemistry.
Environmental Impacts of Alkaline Drainage
Alkaline mine drainage typically exhibits elevated pH levels and high concentrations of metals such as calcium, magnesium, and sometimes trace heavy metals, which can alter aquatic ecosystems by increasing water hardness and toxicity. The increased alkalinity can inhibit the solubility of certain metals, reducing their mobility but potentially leading to bioaccumulation in sediments and aquatic organisms. Environmental impacts include disruption of native species, changes in nutrient cycling, and potential harm to downstream water quality due to sediment contamination and altered chemical equilibria.
Environmental Impacts of Neutral Drainage
Neutral mine drainage typically exhibits near-neutral pH levels, resulting in lower solubility and mobility of heavy metals compared to acidic alkaline mine drainage, which reduces toxic metal contamination in surrounding ecosystems. The environmental impacts of neutral drainage primarily involve the alteration of water chemistry, which can affect aquatic life due to elevated concentrations of sulfates and neutral salts, potentially disrupting biodiversity. Although less harmful than acidic drainage, neutral mine drainage requires monitoring to prevent the accumulation of metals such as iron and manganese that may precipitate and smother habitats.
Treatment and Remediation Strategies
Treatment of alkaline mine drainage often involves passive systems like constructed wetlands and limestone drains that promote metal precipitation and neutralize pH naturally, whereas neutral mine drainage typically requires active treatments such as chemical precipitation with lime or other alkalis to remove metals. Remediation strategies for alkaline drainage focus on maintaining or enhancing natural buffering capacity and preventing metal mobilization, while neutral drainage remediation prioritizes precise control of pH and metal concentrations through engineered treatment plants. Both types benefit from source control practices, but alkaline mine drainage allows for more cost-effective, low-maintenance passive systems compared to the energy-intensive active treatment needed for neutral mine drainage.
Comparative Summary: Alkaline vs Neutral Mine Drainage
Alkaline mine drainage typically features higher pH levels, often above 7, due to the presence of carbonate minerals that neutralize acidity, while neutral mine drainage maintains a pH close to 7 without significant acid or base presence. Alkaline drainage commonly contains elevated concentrations of calcium, magnesium, and bicarbonate ions, contrasting with neutral mine drainage which exhibits lower mineralization and less metal solubility. Both types influence environmental impact differently; alkaline drainage tends to precipitate metals reducing toxicity, whereas neutral drainage may allow more metal mobility, affecting water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
Alkaline mine drainage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com