Loess, a fine-grained, wind-blown sediment, differs significantly from sand dunes, which consist of coarser sand particles shaped by wind into ridges or mounds. Understanding the formation, composition, and environmental impact of both loess deposits and sand dunes is crucial for appreciating soil fertility and desert ecosystems. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these fascinating geological features influence your surroundings.
Table of Comparison
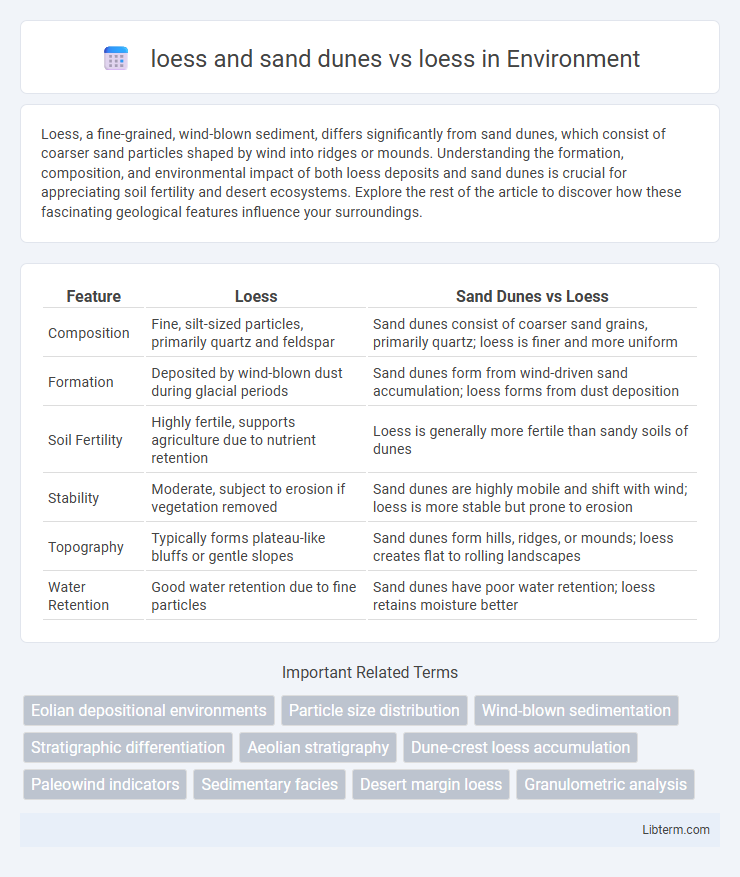
| Feature | Loess | Sand Dunes vs Loess |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Fine, silt-sized particles, primarily quartz and feldspar | Sand dunes consist of coarser sand grains, primarily quartz; loess is finer and more uniform |
| Formation | Deposited by wind-blown dust during glacial periods | Sand dunes form from wind-driven sand accumulation; loess forms from dust deposition |
| Soil Fertility | Highly fertile, supports agriculture due to nutrient retention | Loess is generally more fertile than sandy soils of dunes |
| Stability | Moderate, subject to erosion if vegetation removed | Sand dunes are highly mobile and shift with wind; loess is more stable but prone to erosion |
| Topography | Typically forms plateau-like bluffs or gentle slopes | Sand dunes form hills, ridges, or mounds; loess creates flat to rolling landscapes |
| Water Retention | Good water retention due to fine particles | Sand dunes have poor water retention; loess retains moisture better |
Introduction to Loess and Sand Dunes
Loess is a fine-grained, wind-deposited sediment primarily composed of silt-sized particles that create fertile soils, whereas sand dunes consist of coarser sand grains shaped by wind into dynamic landforms. Loess deposits are generally stable and support extensive agricultural activity, while sand dunes are more mobile and found in arid or coastal environments. Understanding the distinct sediment characteristics and depositional processes is crucial for studying soil formation, erosion patterns, and landscape evolution.
Loess Deposits: Formation and Characteristics
Loess deposits form primarily through the accumulation of wind-blown silt particles, creating thick, homogeneous layers with high porosity and fertility, unlike sand dunes composed mainly of coarser sand grains shaped by wind into shifting ridges. Loess is typically deposited in periglacial regions during glacial periods, characterized by its dust-like texture and mineral richness, which supports robust agricultural use. These deposits exhibit unique properties such as high moisture retention and susceptibility to erosion, influencing soil management and landscape development.
Sand Dunes: Types and Geomorphology
Sand dunes, classified into crescentic, linear, star, dome, and parabolic types, exhibit diverse geomorphological features shaped by wind patterns and sediment supply. Unlike loess, which consists of fine, windblown silt deposits forming fertile, stable landscapes, sand dunes are dynamic landforms characterized by loose sand grains that shift with changing wind directions. Their morphology is influenced by local topography, vegetation cover, and climatic conditions, resulting in varied dune shapes and size distributions across arid and coastal environments.
Differences Between Loess and Sand Dunes
Loess consists of fine, silt-sized particles primarily composed of quartz and feldspar, deposited by wind over large areas, forming fertile, stable soils. Sand dunes are accumulations of coarser, sand-sized grains typically shaped by wind into ridges or mounds, often found in deserts and coastal regions with loose, dry sand. Unlike loess, which is homogenous and supports agriculture, sand dunes are dynamic, with constantly shifting grains that inhibit plant growth.
Geological Processes Behind Loess vs Sand Dune Formation
Loess forms primarily through the accumulation of fine, wind-blown silt and clay particles originating from glacial outwash plains and arid regions, where minimal vegetation allows prolonged suspension and deposition. In contrast, sand dunes develop from the migration and accumulation of coarser sand grains driven by consistent wind patterns in deserts or coastal areas, where sediment supply and aerodynamic sorting are key factors. The particle size, source material, and transport mechanisms distinctly influence the geological processes shaping loess deposits versus sand dunes.
Soil Composition: Loess vs Sand Dunes
Loess consists predominantly of silt-sized particles composed of quartz, feldspar, and calcite, creating a fine, fertile soil with high porosity and good water retention. Sand dunes are primarily composed of coarse, well-sorted quartz sand grains that exhibit low nutrient content and high permeability, resulting in poor water retention. Soil composition in loess supports rich vegetation, whereas sand dunes often present challenging conditions for plant growth due to their coarse texture and rapid drainage.
Ecological Impacts: Loess Versus Sand Dunes
Loess and sand dunes both influence ecosystems differently due to their distinct compositions and stability. Loess, composed of fine silt-sized particles, supports fertile soils that promote diverse vegetation and stabilize habitats, whereas sand dunes, made of coarser sand, often create arid, shifting environments with specialized flora and fauna adapted to dynamic conditions. The ecological impact of loess includes enhanced soil fertility and water retention, while sand dunes primarily affect biodiversity through habitat suppression and limited nutrient availability.
Human Interaction with Loess and Sand Dunes
Human interaction with loess and sand dunes varies significantly due to their distinct physical properties and ecological roles. Loess, a highly fertile and easily tillable soil composed of wind-blown silt, has supported intensive agriculture and settlement since ancient times, particularly in regions like the Chinese Loess Plateau and the Mississippi Valley. In contrast, sand dunes, characterized by loose, shifting sand and poor nutrient content, face challenges from human activities such as off-road driving and construction, which can destabilize dunes and necessitate conservation efforts to prevent erosion and habitat loss.
Global Distribution of Loess and Sand Dune Landscapes
Loess is predominantly found in extensive inland regions such as the Eurasian Steppe and parts of North America, covering areas with fertile, silty soils formed from wind-deposited fine particles. Sand dunes, composed of coarser sand grains, are widespread in arid and semi-arid environments including the Sahara Desert, Arabian Peninsula, and coastal regions worldwide, shaped by persistent wind activity in dry climates. The global distribution of loess landscapes contrasts with that of sand dunes, where loess deposits favor temperate zones with seasonal wind patterns, while sand dunes thrive in deserts and coastal zones with abundant loose sand and minimal vegetation.
Comparative Importance in Environmental Science
Loess, composed primarily of fine silt particles, plays a critical role in soil fertility and agricultural productivity due to its nutrient-rich composition and water retention capabilities, whereas sand dunes, dominated by coarse, loose sand grains, are vital in shaping desert ecosystems and acting as natural barriers against wind erosion. In environmental science, loess deposits provide valuable records of past climatic conditions through their stratification, contrasting with sand dunes that illustrate dynamic wind patterns and landscape evolution. Both loess and sand dunes influence biodiversity and land stability, but loess significantly impacts long-term soil formation and carbon sequestration, highlighting its comparative importance in understanding terrestrial environmental processes.
loess and sand dunes Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com