Stenotopic species exhibit a narrow tolerance to environmental conditions, thriving only within specific habitats or climate ranges. This specialization makes them particularly sensitive to habitat changes and environmental disturbances. Explore the full article to understand how stenotopic organisms impact biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Table of Comparison
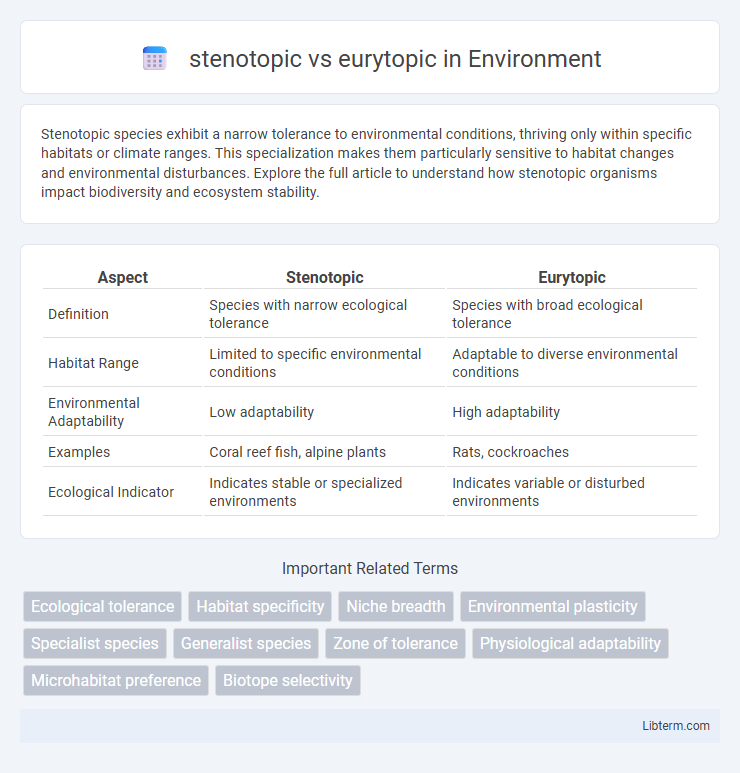
| Aspect | Stenotopic | Eurytopic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Species with narrow ecological tolerance | Species with broad ecological tolerance |
| Habitat Range | Limited to specific environmental conditions | Adaptable to diverse environmental conditions |
| Environmental Adaptability | Low adaptability | High adaptability |
| Examples | Coral reef fish, alpine plants | Rats, cockroaches |
| Ecological Indicator | Indicates stable or specialized environments | Indicates variable or disturbed environments |
Introduction to Stenotopic and Eurytopic Species
Stenotopic species thrive within narrow environmental conditions, exhibiting high specialization and limited tolerance to habitat variability. Eurytopic species display broad ecological amplitude, adapting to diverse habitats and fluctuating environmental factors. Understanding these distinctions is critical for ecological niche modeling and biodiversity conservation strategies.
Defining Stenotopic: Meaning and Examples
Stenotopic organisms exhibit a narrow range of environmental tolerance, thriving only under specific conditions such as particular temperature, humidity, or salinity levels. Examples include certain amphibians like the axolotl, which require stable aquatic habitats with precise water quality and temperature. These species' limited adaptability makes them highly sensitive to environmental changes, contrasting with eurytopic species that tolerate diverse habitats.
Understanding Eurytopic: Characteristics and Instances
Eurytopic species exhibit broad ecological tolerance, thriving in diverse environmental conditions such as varying temperature, humidity, and soil types. These organisms are commonly found in habitats ranging from forests and grasslands to urban areas, demonstrating adaptability that allows survival across multiple biotopes. Examples include generalist plants like dandelions and animals like raccoons, which can exploit wide-ranging resources and environments.
Physiological Adaptations of Stenotopic Organisms
Stenotopic organisms exhibit physiological adaptations that enable survival within narrow environmental ranges, such as specialized metabolic pathways to tolerate specific temperature or pH levels. These adaptations include enhanced osmoregulatory mechanisms and selective enzyme functionality that optimize performance under consistent habitat conditions. Such precise physiological traits limit their distribution but increase efficiency in stable, specialized niches.
Environmental Flexibility of Eurytopic Species
Eurytopic species exhibit high environmental flexibility, thriving across diverse habitats and varying ecological conditions due to their broad tolerance range. Their adaptability enables survival in fluctuating temperatures, moisture levels, and nutrient availabilities, which contrasts with stenotopic species that require narrowly specific environmental parameters. This plasticity in habitat preference supports ecosystem resilience and facilitates the colonization of disturbed or changing environments.
Ecological Roles and Niche Specialization
Stenotopic species exhibit narrow ecological niches, demonstrating high specialization in habitat requirements and resource use, often thriving in stable, specialized environments such as alpine or desert ecosystems. Eurytopic species possess broad ecological tolerances, allowing them to exploit diverse habitats and resources, which supports their role as generalists in various ecological communities. The differing niche specialization influences ecosystem dynamics, with stenotopic species contributing to biodiversity through unique niche occupation, while eurytopic species enhance resilience by maintaining ecological functions across fluctuating environmental conditions.
Habitat Preferences and Distribution Patterns
Stenotopic species exhibit narrow habitat preferences, thriving only within specific environmental conditions, which limits their distribution to localized or specialized ecosystems. In contrast, eurytopic species display broad habitat tolerance, enabling them to inhabit diverse environments and maintain widespread geographical distributions. This adaptability in eurytopic species enhances their resilience to environmental changes compared to stenotopic species, whose restricted niches increase vulnerability to habitat disturbances.
Evolutionary Implications of Stenotopy and Eurytopy
Stenotopic species exhibit narrow ecological niches, often evolving specialized adaptations that restrict them to stable, specific habitats, which may limit their ability to cope with environmental changes. Eurytopic species possess broad ecological tolerances, enabling them to inhabit diverse environments and adapt to fluctuating conditions, enhancing their evolutionary resilience and dispersal potential. The evolutionary implications of stenotopy versus eurytopy highlight trade-offs between specialization and adaptability, influencing species' survival and diversification in dynamic ecosystems.
Conservation Concerns and Vulnerabilities
Stenotopic species, which have narrow ecological tolerances and specialized habitat requirements, face higher conservation concerns due to their vulnerability to habitat loss and environmental changes. Eurytopic species, with broad ecological ranges, exhibit greater resilience and adaptability, reducing their immediate conservation risk but potentially impacting ecosystem dynamics. Protecting stenotopic species demands targeted habitat preservation and monitoring to mitigate threats from climate change and human activities.
Comparing Stenotopic vs Eurytopic Responses to Environmental Change
Stenotopic species exhibit narrow ecological tolerance, responding negatively to environmental changes such as temperature fluctuations and habitat alterations, often resulting in localized distribution and higher vulnerability. Eurytopic species demonstrate broad ecological tolerance, adapting to diverse environmental conditions by modifying behavior, physiological processes, or habitat preferences, which supports their widespread distribution and resilience. Comparing their responses highlights the importance of niche breadth in predicting species survival under environmental stressors, guiding conservation strategies for habitat management.
stenotopic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com