Rapid urbanization transforms societies by concentrating populations in cities, driving economic growth and innovation while posing challenges like overcrowding and environmental strain. Managing urban expansion requires sustainable planning and efficient infrastructure to enhance quality of life. Explore the full article to understand how urbanization shapes your world and future.
Table of Comparison
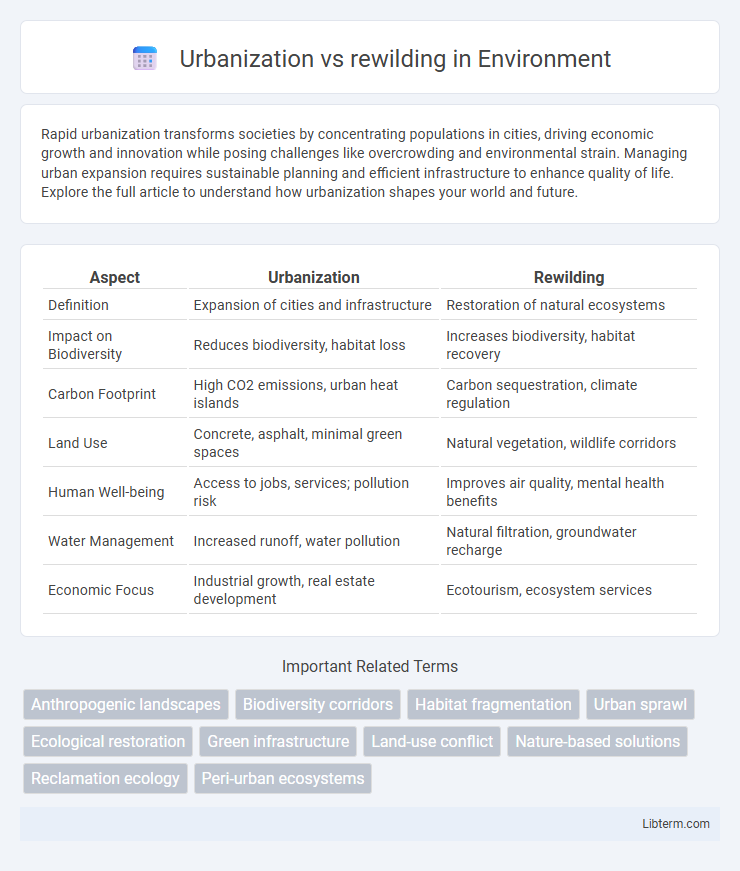
| Aspect | Urbanization | Rewilding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expansion of cities and infrastructure | Restoration of natural ecosystems |
| Impact on Biodiversity | Reduces biodiversity, habitat loss | Increases biodiversity, habitat recovery |
| Carbon Footprint | High CO2 emissions, urban heat islands | Carbon sequestration, climate regulation |
| Land Use | Concrete, asphalt, minimal green spaces | Natural vegetation, wildlife corridors |
| Human Well-being | Access to jobs, services; pollution risk | Improves air quality, mental health benefits |
| Water Management | Increased runoff, water pollution | Natural filtration, groundwater recharge |
| Economic Focus | Industrial growth, real estate development | Ecotourism, ecosystem services |
Defining Urbanization and Rewilding
Urbanization refers to the process by which rural areas transform into urban centers characterized by increased population density, infrastructure development, and industrial growth. Rewilding involves restoring natural ecosystems by reintroducing native species, allowing landscapes to regenerate, and promoting biodiversity. These contrasting concepts highlight the shift between expanding human settlements and efforts to conserve or restore natural environments.
Historical Context: Urban Growth and Natural Decline
Urbanization accelerated rapidly during the Industrial Revolution, leading to significant expansion of cities and a corresponding decline in natural habitats. Historical land use changes, driven by population growth and economic development, caused widespread deforestation and fragmentation of ecosystems. These transformations historically reduced biodiversity and disrupted ecological balance, prompting modern efforts to promote rewilding as a strategy to restore natural landscapes and enhance urban resilience.
Environmental Impacts of Urbanization
Urbanization drastically alters natural habitats, leading to significant biodiversity loss and increased carbon emissions due to deforestation and infrastructure development. Impervious surfaces like concrete and asphalt exacerbate urban heat islands, disrupt water cycles, and reduce groundwater recharge. These environmental impacts contribute to climate change, habitat fragmentation, and the decline of ecosystem services critical for human and wildlife survival.
Rewilding: Concepts and Key Practices
Rewilding emphasizes restoring natural ecosystems by reintroducing native species, promoting biodiversity, and allowing ecological processes to unfold with minimal human intervention. Key practices include habitat restoration, removal of invasive species, and creating wildlife corridors to reconnect fragmented landscapes. This approach counteracts urbanization's environmental impacts by enhancing ecosystem resilience and supporting sustainable wildlife populations.
Socioeconomic Effects of Urban Expansion
Urban expansion accelerates economic growth by creating job opportunities, increasing infrastructure development, and attracting investments, yet it often exacerbates social inequalities through displacement and rising living costs. Rewilding initiatives counteract these negative effects by restoring natural habitats, improving public health, and fostering eco-tourism that supports local economies. Integrating green spaces within urban areas enhances residents' quality of life and promotes sustainable urban development.
Biodiversity Loss vs. Restoration Efforts
Urbanization drives significant biodiversity loss by fragmenting habitats and reducing species populations, leading to ecosystem imbalance and extinction risks. Rewilding projects focus on restoration efforts by reintroducing native species, restoring natural processes, and expanding green corridors to enhance habitat connectivity. These initiatives promote ecosystem resilience, increase biodiversity, and counteract the detrimental effects of urban expansion.
Urban Green Spaces and Rewilding Initiatives
Urban green spaces play a crucial role in balancing urbanization by providing habitats for native wildlife and enhancing biodiversity within cities. Rewilding initiatives aim to restore natural ecosystems by reintroducing native plant species and wildlife, promoting ecological resilience amid expanding urban development. Integrating rewilding projects into urban green spaces supports sustainable city planning and improves air quality, mental health, and climate change mitigation.
Policy Approaches: Balancing Development and Conservation
Effective policy approaches to balancing urbanization and rewilding prioritize integrated land-use planning that supports sustainable development while conserving natural habitats. Incentives for green infrastructure, habitat restoration, and wildlife corridors promote biodiversity within expanding urban areas. Regulatory frameworks that enforce zoning laws and environmental impact assessments ensure urban growth does not compromise ecological integrity or rewilding goals.
Case Studies: Successful Urban Rewilding Projects
Urban rewilding projects such as London's Green Grid and New York City's High Line showcase successful integration of natural habitats within highly urbanized environments, promoting biodiversity and community engagement. In Berlin, urban rewilding initiatives in Tempelhofer Feld have transformed former industrial spaces into thriving ecosystems, enhancing urban resilience and air quality. These case studies demonstrate that urbanization and rewilding can coexist by prioritizing green infrastructure and ecological restoration in city planning.
Future Perspectives: Harmonizing Cities and Nature
Future perspectives on urbanization and rewilding emphasize the integration of green infrastructure and biodiversity corridors within metropolitan areas to create sustainable ecosystems. Advances in urban planning prioritize the restoration of native habitats alongside smart city technologies, promoting ecological balance and enhanced quality of life. Collaborative policies involving governments, ecologists, and communities aim to harmonize urban growth with nature conservation for resilient, adaptive cities.
Urbanization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com