Conservancy efforts play a crucial role in protecting biodiversity and preserving natural habitats for future generations. These initiatives often involve sustainable practices, habitat restoration, and community engagement to ensure lasting environmental impact. Discover how your involvement can make a difference by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
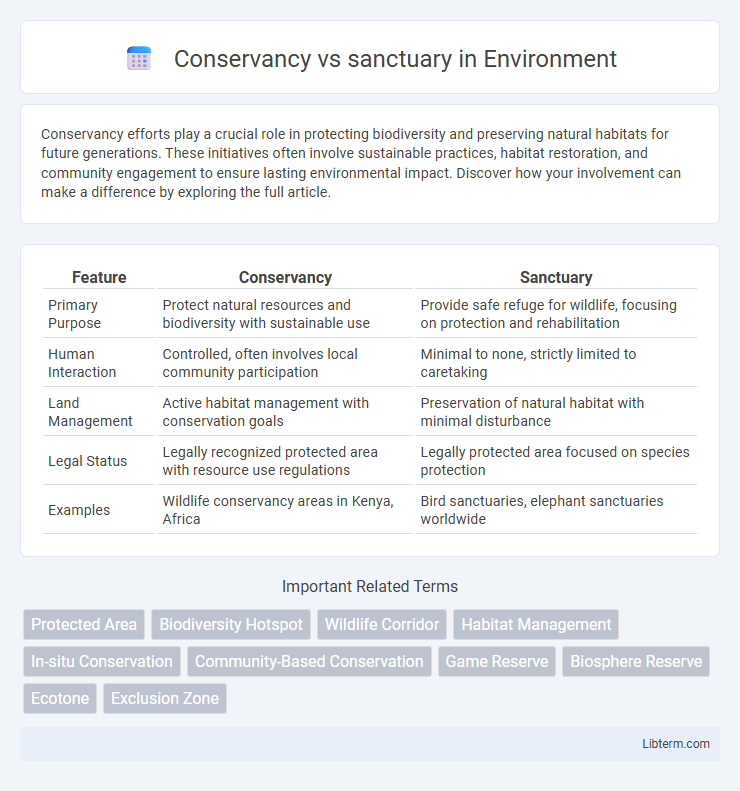
| Feature | Conservancy | Sanctuary |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Protect natural resources and biodiversity with sustainable use | Provide safe refuge for wildlife, focusing on protection and rehabilitation |
| Human Interaction | Controlled, often involves local community participation | Minimal to none, strictly limited to caretaking |
| Land Management | Active habitat management with conservation goals | Preservation of natural habitat with minimal disturbance |
| Legal Status | Legally recognized protected area with resource use regulations | Legally protected area focused on species protection |
| Examples | Wildlife conservancy areas in Kenya, Africa | Bird sanctuaries, elephant sanctuaries worldwide |
Introduction to Conservancy and Sanctuary
A conservancy is a designated area managed primarily for the protection and sustainable use of natural resources, often involving community participation and wildlife conservation efforts. A sanctuary refers to a protected space established to provide safe habitat specifically for endangered or vulnerable species, emphasizing strict preservation with limited human interference. Both conservancies and sanctuaries play critical roles in biodiversity conservation but differ in management approaches and conservation priorities.
Definition of Conservancy
A conservancy refers to a protected area managed for the conservation of wildlife, natural resources, and habitat restoration, often involving local community participation and sustainable use practices. Unlike a sanctuary, which strictly prohibits human activities to protect species, a conservancy balances ecological preservation with controlled human access and resource management. Key examples include Kenya's wildlife conservancies that integrate conservation goals with pastoral livelihoods to promote biodiversity and economic benefits.
Definition of Sanctuary
A sanctuary is a protected area designated for the conservation and safe refuge of wildlife, where animals live free from hunting, poaching, or habitat destruction. It provides a natural habitat with minimal human interference, ensuring the preservation of species and biodiversity. Unlike conservancies, which may involve sustainable use of resources and community management, sanctuaries emphasize strict protection and non-exploitative conservation practices.
Key Differences Between Conservancy and Sanctuary
A conservancy is a protected area managed for sustainable use of natural resources and community benefit, while a sanctuary strictly restricts human activities to preserve wildlife and habitats. Conservancies often involve local communities in conservation efforts and allow controlled resource use, whereas sanctuaries enforce stricter regulations to minimize human impact. Both are vital for biodiversity preservation, but their management objectives and levels of human interaction differ significantly.
Objectives and Purpose
A conservancy primarily focuses on the sustainable management and protection of natural resources while promoting community involvement and economic benefits such as eco-tourism. Sanctuaries are dedicated to providing a safe habitat for wildlife, emphasizing strict protection and minimal human interference to preserve biodiversity. Both aim to conserve species and ecosystems but differ in their approach to resource use and local community engagement.
Legal Framework and Governance
Conservancies operate under community-based legal frameworks that emphasize local governance, allowing indigenous or local populations to manage natural resources sustainably while adhering to national wildlife and land-use laws. Sanctuaries are typically governed by stricter state or federal regulations focused on habitat preservation and species protection, often limiting human activities and requiring formal management by governmental or authorized organizations. The legal distinctions between conservancies and sanctuaries impact enforcement mechanisms, stakeholder involvement, and permissible land uses within these protected areas.
Conservation Strategies Employed
Conservancies implement community-based conservation strategies that actively involve local populations in sustainable resource management and wildlife protection, promoting coexistence with natural habitats. Sanctuaries primarily focus on habitat preservation and strict protection measures to safeguard endangered species, often restricting human activities to minimize disturbances. Both strategies aim to enhance biodiversity, but conservancies emphasize participatory governance while sanctuaries rely on controlled environments to achieve conservation goals.
Community Involvement and Participation
Conservancies emphasize community involvement by integrating local stakeholders in decision-making and management, fostering sustainable resource use and biodiversity protection. Sanctuaries typically operate under strict protection regulations with limited public access, prioritizing habitat preservation over direct community participation. Community-led governance in conservancies enhances ecological outcomes while supporting livelihoods, contrasting with the more exclusionary approach of traditional sanctuaries.
Challenges Faced by Both Models
Conservancies and sanctuaries both face challenges related to habitat degradation, poaching, and human-wildlife conflicts, which threaten biodiversity and ecosystem stability. Conservancies often struggle with balancing community needs and wildlife conservation due to resource competition and insufficient funding. Sanctuaries encounter difficulties in maintaining genetic diversity and ensuring adequate space for species survival within confined protected areas.
Future Prospects and Recommendations
Conservancies and sanctuaries both play critical roles in biodiversity preservation, with future prospects centered on integrating technology-driven monitoring and community engagement to enhance habitat protection. Recommendations emphasize expanding collaborative frameworks between local stakeholders and governments to ensure sustainable funding and adaptive management practices. Prioritizing ecosystem connectivity and climate resilience within these protected areas will significantly improve long-term conservation outcomes.
Conservancy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com