Sand sheets are flat, expansive surfaces dominated by fine sand particles, often found in arid and semi-arid environments where wind action redistributes sediment. These geological formations influence local ecosystems by shaping soil moisture retention and vegetation growth patterns. Discover how sand sheets impact your landscape and what this means for environmental management by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
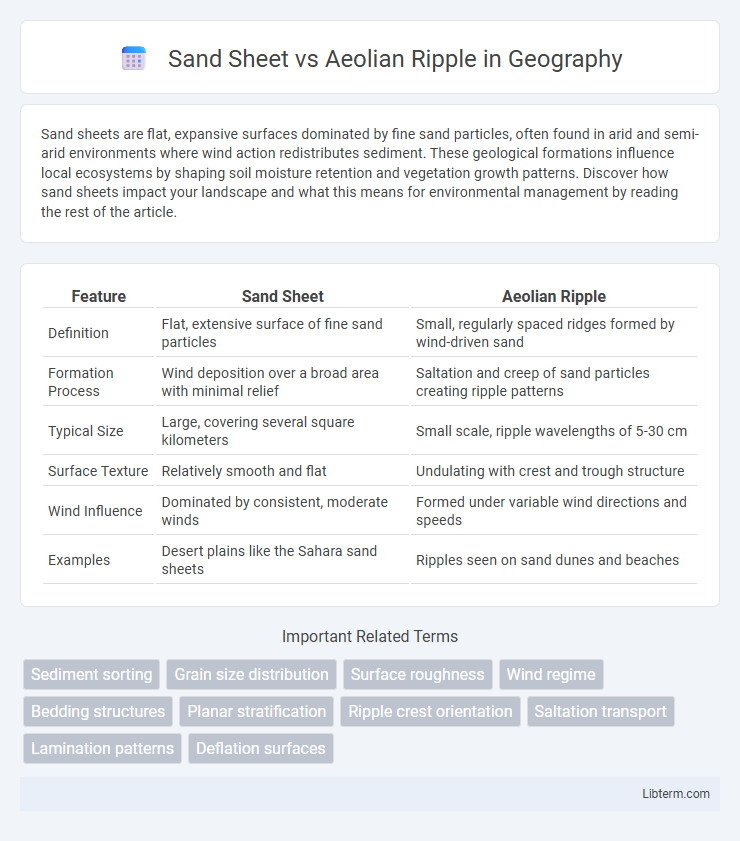
| Feature | Sand Sheet | Aeolian Ripple |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flat, extensive surface of fine sand particles | Small, regularly spaced ridges formed by wind-driven sand |
| Formation Process | Wind deposition over a broad area with minimal relief | Saltation and creep of sand particles creating ripple patterns |
| Typical Size | Large, covering several square kilometers | Small scale, ripple wavelengths of 5-30 cm |
| Surface Texture | Relatively smooth and flat | Undulating with crest and trough structure |
| Wind Influence | Dominated by consistent, moderate winds | Formed under variable wind directions and speeds |
| Examples | Desert plains like the Sahara sand sheets | Ripples seen on sand dunes and beaches |
Introduction to Sand Sheets and Aeolian Ripples
Sand sheets are expansive, flat deposits of fine to medium sand particles formed by wind action in arid and semi-arid environments, characterized by low relief and minimal surface texture variation. Aeolian ripples consist of small, regularly spaced bedforms created by the saltation and creep of sand grains, typically ranging from a few centimeters to tens of centimeters in wavelength and height. Both features result from wind-driven sediment transport but differ in scale, morphology, and formation processes, with sand sheets representing broader depositional surfaces and aeolian ripples indicating active sediment movement.
Defining Sand Sheets: Characteristics and Formation
Sand sheets are extensive, flat surfaces of fine to medium sand with little to no ripple or dune formation, typically found in desert basins and coastal regions. Their formation results from consistent wind patterns that distribute sand evenly, preventing the development of distinct ripple marks or dunes. The surface texture of sand sheets is characteristically smooth due to the lack of significant wind-induced sorting or sedimentary structures like those seen in aeolian ripples.
Understanding Aeolian Ripples: Key Features
Aeolian ripples are small-scale, wind-formed sedimentary structures characterized by their regular spacing of 5 to 20 centimeters and symmetric to slightly asymmetric cross-laminations. These ripples typically develop on sand sheets and consist of well-sorted, fine to medium sand grains that respond to optimal wind velocity, creating distinct ripple crests and troughs. Unlike sand sheets, which are relatively flat and homogenous, aeolian ripples display clear sediment sorting and surface roughness driven by saltation and creep processes.
Geological Processes Behind Sand Sheet Formation
Sand sheets form through the deposition of fine, well-sorted particles by wind in areas with limited vegetation and relatively low wind energy, leading to a flat, featureless surface. Aeolian ripples arise from the saltation of sand grains, where wind-driven grains hop and impact the surface, creating small, regularly spaced ridges. Unlike ripples, sand sheets result from slower sediment transport and accumulation, emphasizing the geological significance of wind velocity and sediment supply in their formation.
Mechanisms Driving Aeolian Ripple Development
Aeolian ripples develop through the saltation process, where wind-driven sand grains hop and collide, causing smaller grains to creep and settle into ridges. The periodic impact and shadowing effect of saltating grains promote sediment accumulation on ripple crests, resulting in regularly spaced, small-scale bedforms. In contrast, sand sheets lack such organized grain sorting, forming from uniform sand transport under consistent wind speeds without distinct ripple structures.
Physical Differences: Sand Sheets vs Aeolian Ripples
Sand sheets are extensive, flat depositional surfaces characterized by uniform, fine-grained sand with minimal surface texture, typically formed by the steady accumulation of wind-blown particles. Aeolian ripples exhibit small-scale, periodic undulations with well-defined crests and troughs, resulting from the saltation and creep of sand grains influenced by wind velocity and sand supply. The primary physical difference lies in sand sheets' smooth, featureless appearance compared to the distinct, regularly spaced ripple patterns of aeolian ripples.
Environmental Influence on Sand Sheet and Ripple Formation
Sand sheets form in environments with consistent but moderate wind strength, leading to relatively flat, extensive sand deposits with minimal ripple structures. Aeolian ripples develop under more variable wind conditions that create small-scale, regularly spaced ridges due to saltation and surface creep of sand grains. The interplay of factors such as wind velocity, sediment supply, and surface moisture critically influences the morphology and spatial distribution of both sand sheets and ripples in desert and coastal landscapes.
Role in Desert and Coastal Ecosystems
Sand sheets and aeolian ripples play distinct roles in desert and coastal ecosystems by influencing sediment transport and surface stability. Sand sheets, characterized by flat, wind-swept surfaces with minimal relief, facilitate the redistribution of fine particles across larger areas, aiding in soil formation and plant colonization. Aeolian ripples, with their small-scale, regularly spaced ridges, enhance microhabitat diversity by trapping moisture and organic matter, supporting microbial and vegetation communities critical for ecosystem resilience.
Methods for Identifying Sand Sheets and Aeolian Ripples
Sand sheets are identified through aerial imagery and sedimentary analysis revealing their flat, featureless surfaces composed of well-sorted, fine grains. Aeolian ripples are recognized by their distinctive small-scale, wave-like patterns visible both in field surveys and high-resolution drone mapping, characterized by consistent wavelength and amplitude. Grain size distribution and wind regime data further assist in distinguishing between the broadly dispersed sand sheets and the dynamic, regularly spaced ripples formed by saltation.
Importance and Applications in Geomorphology
Sand sheets offer critical insight into wind strength and sediment supply, serving as indicators of prevailing aeolian processes in arid environments. Aeolian ripples, with their characteristic spacing and orientation, provide valuable data on wind direction variability and near-surface airflow dynamics. Both features are essential in geomorphology for reconstructing paleoclimate conditions and guiding land management in desertification-prone regions.
Sand Sheet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com