The Bird's Foot Delta, formed by the Mississippi River, is a distinctive landscape characterized by multiple river channels that extend into the Gulf of Mexico, creating a rich and dynamic ecosystem. Its unique shape results from sediment deposition, which continually reshapes the delta, impacting local wildlife and human settlements. Explore the rest of the article to discover how this natural marvel influences environmental and economic factors in the region.
Table of Comparison
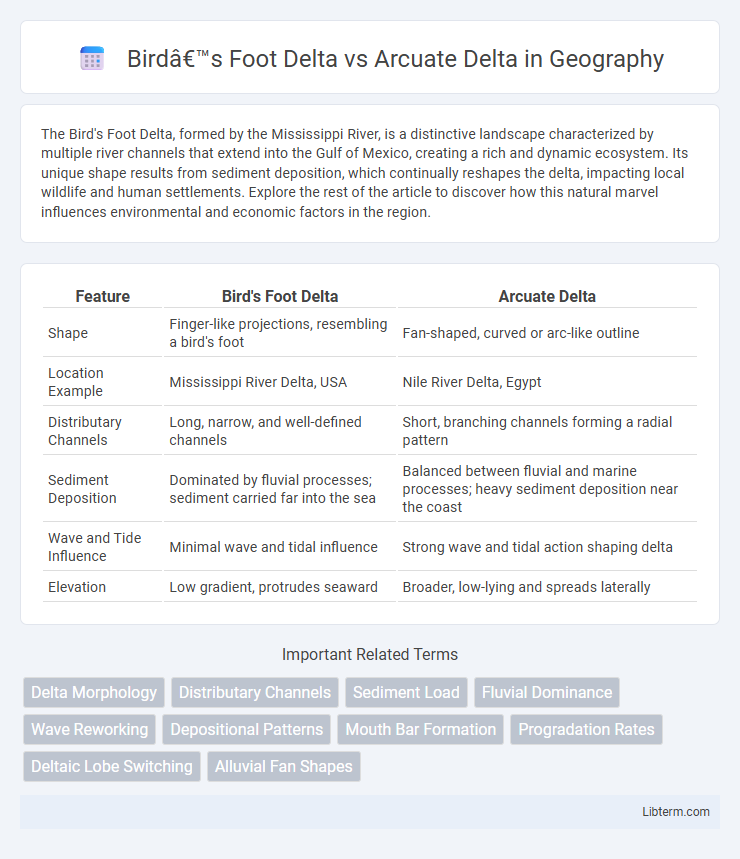
| Feature | Bird's Foot Delta | Arcuate Delta |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Finger-like projections, resembling a bird's foot | Fan-shaped, curved or arc-like outline |
| Location Example | Mississippi River Delta, USA | Nile River Delta, Egypt |
| Distributary Channels | Long, narrow, and well-defined channels | Short, branching channels forming a radial pattern |
| Sediment Deposition | Dominated by fluvial processes; sediment carried far into the sea | Balanced between fluvial and marine processes; heavy sediment deposition near the coast |
| Wave and Tide Influence | Minimal wave and tidal influence | Strong wave and tidal action shaping delta |
| Elevation | Low gradient, protrudes seaward | Broader, low-lying and spreads laterally |
Introduction to River Deltas
Bird's Foot Delta and Arcuate Delta represent distinctive river delta formations shaped by sediment deposition at river mouths. Bird's Foot Delta, exemplified by the Mississippi River Delta, is characterized by elongated distributary channels resembling a bird's foot, resulting from dominant river flow over wave action. In contrast, the Arcuate Delta, such as the Nile Delta, features a fan-shaped, curved outline formed by strong wave and tidal influences redistributing sediments evenly along the coastline.
Defining Bird’s Foot Delta
Bird's Foot Delta is characterized by its distinct protruding distributary channels that extend far into the body of water, resembling the toes of a bird's foot, typically formed where strong river flow dominates over wave and tidal forces, such as the Mississippi River Delta. In contrast, an Arcuate Delta features a rounded, bow-shaped shoreline where wave action redistributes sediments evenly along the coast, commonly seen in the Nile Delta. The key defining feature of Bird's Foot Delta lies in its elongated, finger-like projections driven by sediment deposition through multiple river branches branching out into a gulf or sea.
Key Features of Bird’s Foot Delta
The Bird's Foot Delta, exemplified by the Mississippi River Delta, is distinguished by its elongated distributary channels that extend far into the sea, creating a pattern resembling a bird's foot. This delta type features a high sediment supply and strong river currents that outpace wave and tidal influences, resulting in a protruding, channel-dominated structure. Unlike the arcuate delta, which has a fan-shaped and smooth coastline formed by balanced wave action, the Bird's Foot Delta maintains narrow, finger-like projections due to dominant fluvial processes.
Defining Arcuate Delta
Arcuate deltas are fan-shaped landforms characterized by a convex seaward edge formed by the deposition of sediments where a river meets a body of water, such as a sea or lake, allowing sediment to spread widely and create a broad, curved shoreline. Bird's Foot deltas, in contrast, extend elongated distributary channels seaward, resembling bird's claws, typically forming in regions with strong river flow exceeding wave and tidal influences. The defining feature of an arcuate delta is its outwardly curved, arcuate shape resulting from a balanced process of sediment deposition and wave action that evenly distributes sediments along the delta front.
Key Features of Arcuate Delta
The arcuate delta features a broad, fan-shaped appearance with smooth, rounded contours formed by evenly distributed sediment deposition along its shoreline. It typically develops where the river's sediment load interacts with moderate tidal currents and wave action that gently redistribute sediments, resulting in a convex seaward edge. Key examples include the Nile Delta and the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, characterized by extensive fertile soils and complex distributary networks.
Sediment Deposition Patterns
Bird's Foot Deltas exhibit elongated distributary channels that extend sediment deposits far into the basin, creating finger-like projections primarily composed of coarse sediments. Arcuate Deltas feature a more convex, arc-shaped frontier where sediment deposition occurs uniformly along the shoreline, resulting in broad, fan-shaped sediment layers dominated by finer particles. The contrasting hydrodynamic conditions and sediment load influence the distinct deposition patterns, with Bird's Foot Deltas forming in river-dominated environments and Arcuate Deltas in wave-dominated coastal settings.
Hydrodynamic Conditions and Influences
Bird's Foot Delta forms under weak wave and tidal energy with strong river discharge, allowing sediment to extend into the sea as elongated distributary channels. Arcuate Delta develops where wave action dominates, redistributing sediments along the coast and creating a smooth, convex shoreline. Hydrodynamic conditions such as river flow velocity and wave energy critically influence delta morphology, affecting sediment deposition patterns and channel formation.
Ecological and Environmental Impact
Bird's Foot Deltas, like the Mississippi River Delta, create extensive wetlands that provide critical habitats for diverse species but are vulnerable to subsidence and sea-level rise, increasing flood risk and habitat loss. Arcuate Deltas, such as the Nile Delta, support fertile agricultural lands due to their nutrient-rich sediments but face threats from reduced sediment supply and human activities causing coastline erosion and salinization. Both delta types play vital roles in carbon sequestration and biodiversity, yet their ecological balance is increasingly disrupted by climate change and anthropogenic impacts.
Real-World Examples: Mississippi vs Nile River
The Bird's Foot Delta of the Mississippi River extends into the Gulf of Mexico with narrow, finger-like distributaries formed by high sediment deposition and strong river currents. In contrast, the Nile River's Arcuate Delta fans out in a broad, curved shape along the Mediterranean coast due to slower sediment deposition and wave-dominated processes. These real-world examples highlight how sediment load, water flow, and coastal dynamics shape distinct deltaic forms critical for navigation, agriculture, and ecosystem diversity.
Summary: Comparative Analysis and Key Takeaways
Bird's Foot Delta, exemplified by the Mississippi River, features multiple narrow distributaries extending into the sea, promoting sediment deposition over a vast area. Arcuate Delta, such as the Nile Delta, presents a fan-shaped outline with smooth, curved margins formed by a balance of river sediment supply and wave action. Key distinctions include Bird's Foot's dominance by river processes versus Arcuate's wave-influenced shape, impacting sediment distribution, ecosystem diversity, and delta evolution patterns.
Bird’s Foot Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com