Prairies are expansive grasslands dominated by tall grasses, wildflowers, and a variety of wildlife, playing a crucial role in biodiversity and carbon sequestration. These ecosystems provide habitat for numerous species, support soil health, and act as natural buffers against climate change. Discover how prairies impact your environment and why their preservation is vital in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
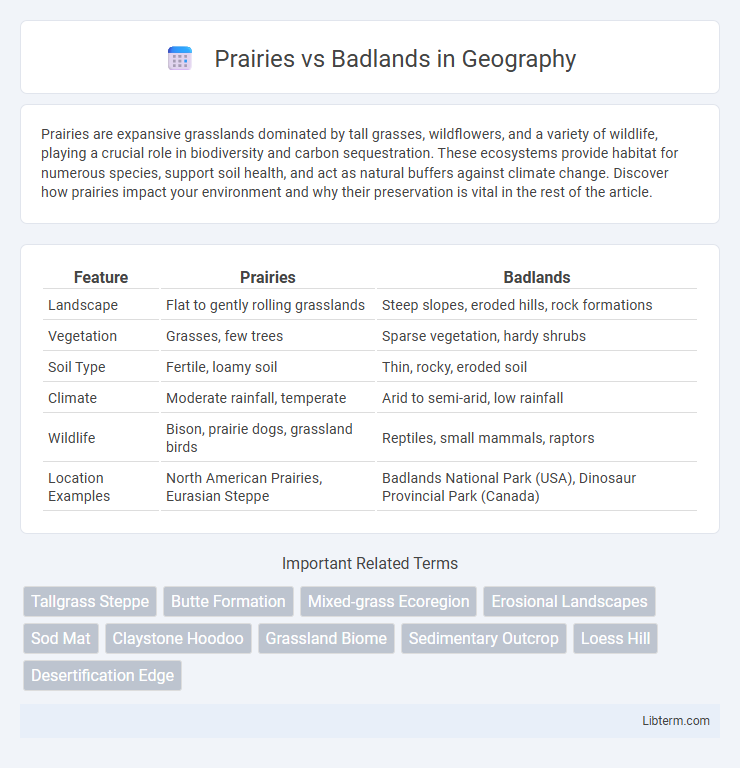
| Feature | Prairies | Badlands |
|---|---|---|
| Landscape | Flat to gently rolling grasslands | Steep slopes, eroded hills, rock formations |
| Vegetation | Grasses, few trees | Sparse vegetation, hardy shrubs |
| Soil Type | Fertile, loamy soil | Thin, rocky, eroded soil |
| Climate | Moderate rainfall, temperate | Arid to semi-arid, low rainfall |
| Wildlife | Bison, prairie dogs, grassland birds | Reptiles, small mammals, raptors |
| Location Examples | North American Prairies, Eurasian Steppe | Badlands National Park (USA), Dinosaur Provincial Park (Canada) |
Introduction: Understanding Prairies and Badlands
Prairies are vast, fertile grasslands characterized by rich soil and diverse plant species, primarily located in North America's central regions. Badlands, in contrast, are rugged terrains with heavily eroded clay and sedimentary rock formations, notable for their striking color layers and sparse vegetation. Understanding the ecological and geological differences between prairies and badlands reveals their unique roles in biodiversity and land use.
Geographical Distribution of Prairies and Badlands
Prairies predominantly span the central regions of North America, covering vast areas of the Great Plains from Canada to Texas, characterized by flat to gently rolling terrain and fertile soils. In contrast, Badlands are typically found in arid or semi-arid regions such as South Dakota's Badlands National Park and parts of Alberta, Canada, featuring rugged landscapes with steep slopes, minimal vegetation, and eroded rock formations. The distinct geographical distribution between prairies and badlands is influenced by differences in climate, soil composition, and erosional processes.
Geological Formation: Prairies vs Badlands
Prairies are characterized by flat to gently rolling landscapes formed primarily through sediment deposition from ancient seas and glaciation, resulting in rich soil layers ideal for grasslands. Badlands feature rugged terrains shaped by intense erosion of soft sedimentary rocks such as clay, shale, and sandstone, exposing colorful stratified layers and unique rock formations. The contrasting geological processes highlight prairies' stability and fertility versus badlands' dynamic erosion and exposed geological history.
Climate Differences Between Prairies and Badlands
Prairies experience a temperate climate characterized by moderate rainfall and distinct seasonal temperature variations, supporting lush grasslands and diverse flora. In contrast, Badlands have an arid to semi-arid climate with low precipitation, extreme temperature fluctuations, and sparse vegetation adapted to dry conditions. These climatic differences shape the unique ecosystems and geological formations found in each region.
Distinctive Flora and Fauna
Prairies feature vast expanses of grasses such as big bluestem and needlegrass, supporting herbivores like bison and pronghorn, while the Badlands are characterized by rugged terrain with sparse vegetation including sagebrush and cactus, sheltering species like bighorn sheep and rattlesnakes. The prairie ecosystem promotes a diverse bird population including meadowlarks and grasshopper sparrows, contrasting with the Badlands' unique reptiles and small mammals adapted to arid conditions. These differing plant and animal communities reflect adaptation to climate, soil, and topography, defining the distinct ecological identities of Prairies and Badlands.
Soil Composition and Land Use
Prairies feature deep, fertile mollisol soils rich in organic matter, making them ideal for agriculture and supporting diverse grassland ecosystems. Badlands consist of highly eroded, less fertile soils with high clay and silt content, limiting agricultural use and favoring sparse vegetation adapted to harsh conditions. Land use in prairies primarily includes crop production and grazing, while badlands are often preserved for conservation, recreation, and geological study.
Human Settlement and Cultural Significance
Prairies have supported extensive human settlement due to fertile soil and abundant water sources, fostering diverse agricultural communities and rich Indigenous cultures. In contrast, Badlands feature rugged terrain with sparse vegetation, limiting permanent settlements but serving as significant sites for paleontological research and Indigenous spiritual practices. Both landscapes hold unique cultural significance, with prairies reflecting agricultural heritage and badlands preserving ancient fossils and sacred landmarks.
Recreation and Tourism Opportunities
Prairies offer expansive hiking trails, bird-watching spots, and seasonal wildflower viewing that attract nature enthusiasts seeking tranquility and wide-open landscapes. Badlands feature rugged terrain ideal for adventurous activities like rock climbing, fossil hunting, and guided tours exploring unique geological formations and paleontological sites. Both regions provide diverse recreational experiences, with prairies appealing to low-impact outdoor activities and Badlands catering to adventure tourism and educational exploration.
Conservation Challenges and Efforts
Prairies face significant conservation challenges due to habitat fragmentation, invasive species, and agricultural development that threaten native plant and animal populations. Badlands are vulnerable to accelerated erosion, limited vegetation cover, and human activities such as mining and tourism that disrupt fragile ecosystems. Conservation efforts in prairies emphasize restoration projects, invasive species control, and protected area expansion, while badlands protection involves erosion control measures, habitat preservation, and sustainable land use planning.
Conclusion: Key Differences and Importance
Prairies are characterized by vast, fertile grasslands supporting diverse plant and animal life, while Badlands feature rugged terrain with eroded rock formations and sparse vegetation. The key differences lie in their ecosystems, soil composition, and water availability, which influence the biodiversity and land use of each region. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective conservation strategies and sustainable management of natural resources.
Prairies Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com