A metropolitan area encompasses a densely populated urban core along with its surrounding suburbs and exurbs, forming an interconnected economic and social region. These areas are characterized by significant infrastructure, cultural institutions, and diverse employment opportunities that drive growth and innovation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how metropolitan areas impact your daily life and regional development.
Table of Comparison
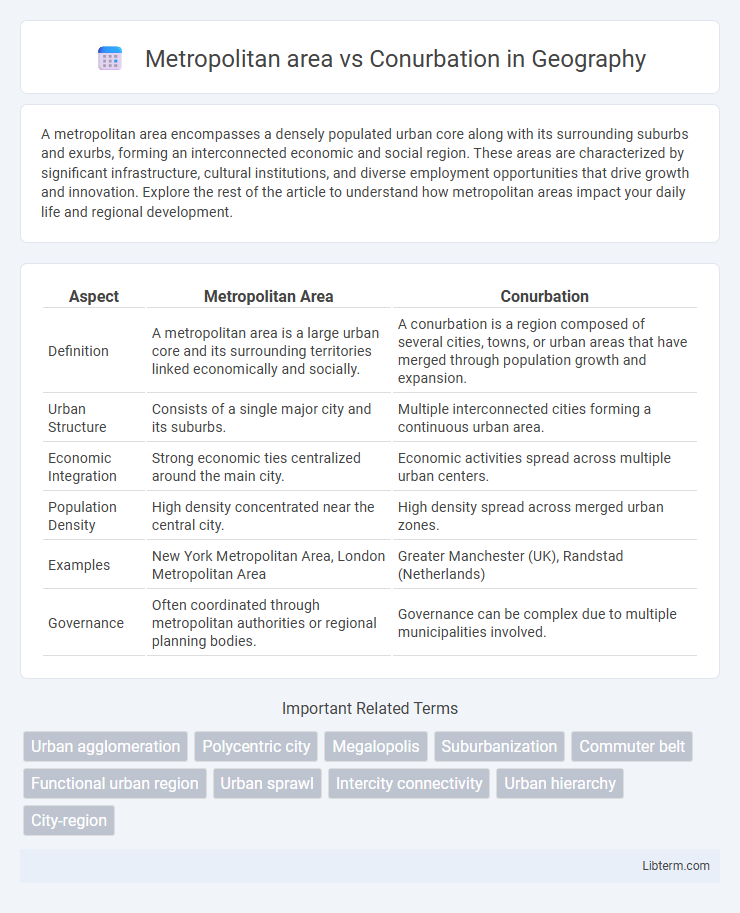
| Aspect | Metropolitan Area | Conurbation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A metropolitan area is a large urban core and its surrounding territories linked economically and socially. | A conurbation is a region composed of several cities, towns, or urban areas that have merged through population growth and expansion. |
| Urban Structure | Consists of a single major city and its suburbs. | Multiple interconnected cities forming a continuous urban area. |
| Economic Integration | Strong economic ties centralized around the main city. | Economic activities spread across multiple urban centers. |
| Population Density | High density concentrated near the central city. | High density spread across merged urban zones. |
| Examples | New York Metropolitan Area, London Metropolitan Area | Greater Manchester (UK), Randstad (Netherlands) |
| Governance | Often coordinated through metropolitan authorities or regional planning bodies. | Governance can be complex due to multiple municipalities involved. |
Definition of Metropolitan Area
A metropolitan area is a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure, and housing. It typically includes multiple jurisdictions such as cities, towns, and suburbs that are socially and economically connected. Unlike a conurbation, which refers specifically to a continuous urban area formed by the merging of several cities or towns, a metropolitan area encompasses both urban and rural zones tied together by commuting patterns and economic integration.
Definition of Conurbation
A conurbation is a large urban area formed by the merging of multiple cities, towns, or metropolitan areas through continuous development and population growth. Unlike a metropolitan area, which typically centers around a single large city and its suburbs, a conurbation represents a polycentric region with interconnected urban centers. This spatial phenomenon highlights extensive urban sprawl and integrated infrastructure across previously distinct municipalities.
Historical Development of Urban Areas
Metropolitan areas historically emerged from the expansion of a central city and its surrounding suburbs, driven by industrialization and economic growth during the 19th and 20th centuries. Conurbations developed as multiple urban centers expanded and merged together, reflecting patterns of urban sprawl and regional integration without a singular dominant city. The evolution of transportation infrastructure and trade networks played a crucial role in shaping both metropolitan areas and conurbations throughout history.
Key Characteristics: Metropolitan Areas
Metropolitan areas encompass a core city and its surrounding suburbs, characterized by high population density, significant economic activity, and integrated infrastructure systems such as transportation and utilities. These areas often serve as major hubs for business, culture, and government, supporting diverse industries and extensive residential communities. The metropolitan region's spatial continuity and functional interdependence distinguish it from loosely connected urban clusters found in conurbations.
Key Characteristics: Conurbations
Conurbations are extensive urban areas formed by the continuous merging of multiple cities or towns, resulting in a densely populated region with interconnected infrastructure and economic activities. Unlike metropolitan areas, which usually revolve around a single core city, conurbations encompass several urban centers that grow together without clear boundaries. The key characteristics of conurbations include complex governance structures, diverse cultural and economic hubs, and significant transportation networks facilitating regional integration.
Examples Around the World
Metropolitan areas like New York City and Tokyo encompass a central city and its surrounding suburbs, functioning as a single economic and social unit with integrated infrastructure and governance. Conurbations such as the Ruhr in Germany and the Greater Tokyo Area consist of multiple adjacent cities and towns that have merged through urban sprawl, creating extensive continuous urban regions without a single dominant city center. Examples highlight that metropolitan areas focus on a hub city and its periphery, whereas conurbations represent the fusion of several independent urban centers.
Governance and Administrative Differences
Metropolitan areas typically function under a centralized governance structure with a single metropolitan authority overseeing urban planning, transportation, and public services within defined administrative boundaries. Conurbations, formed by the merging of multiple cities or towns, often lack unified governance and instead operate through a coalition of independent local governments that coordinate policy-making and service delivery. This fragmented administration in conurbations can lead to challenges in regional planning, infrastructure development, and consistent regulatory enforcement compared to the more streamlined governance of metropolitan areas.
Economic Impact and Demographics
A metropolitan area typically encompasses a single large city and its surrounding suburbs, driving significant economic impact through concentrated industries, business hubs, and a dense labor market with diverse demographics characterized by urban populations. In contrast, a conurbation consists of multiple interconnected cities or urban areas that merge to form an extensive economic zone, fostering regional economic integration, diverse employment sectors, and complex demographic patterns with varied cultural and social dynamics. Both entities contribute to regional growth but differ in scale and complexity regarding infrastructure, labor mobility, and economic diversification.
Urban Planning Challenges
Metropolitan areas face urban planning challenges related to managing diverse land uses, transportation networks, and population density within a typically centralized governance structure. Conurbations, formed by the merging of multiple urban centers, encounter complex coordination issues across different municipalities, leading to difficulties in harmonizing infrastructure development and public services. Both require strategic planning to address sprawl, congestion, and environmental sustainability, but conurbations demand more integrated regional policies due to their fragmented administrative landscapes.
Future Trends in Urban Expansion
Metropolitan areas are projected to expand through satellite cities and improved transportation networks, fostering economic hubs with integrated infrastructure. Conurbations will likely experience intensified urban sprawl, blending multiple municipalities into continuous urban landscapes dominated by housing and commercial development. Smart city technologies and sustainable planning will play crucial roles in managing growth, reducing congestion, and enhancing liveability in both forms of urban expansion.
Metropolitan area Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com