Political ecology explores the complex relationship between political, economic, and social factors with environmental issues and changes. Understanding how power dynamics, resource distribution, and policy decisions impact ecosystems is crucial for developing sustainable solutions. Dive deeper into the role of political ecology and how it shapes your environment by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
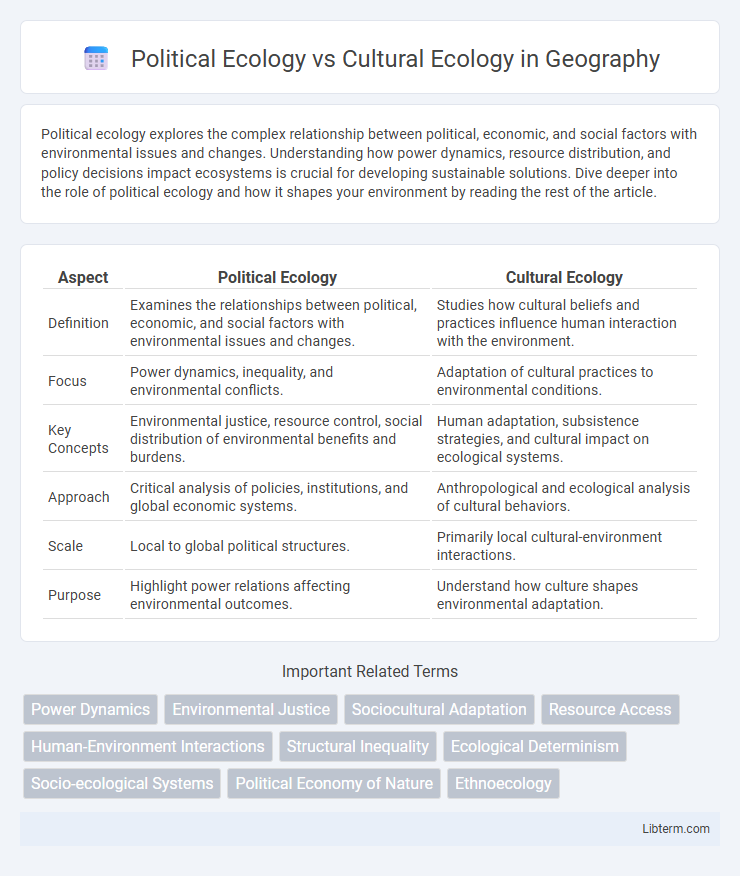
| Aspect | Political Ecology | Cultural Ecology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Examines the relationships between political, economic, and social factors with environmental issues and changes. | Studies how cultural beliefs and practices influence human interaction with the environment. |
| Focus | Power dynamics, inequality, and environmental conflicts. | Adaptation of cultural practices to environmental conditions. |
| Key Concepts | Environmental justice, resource control, social distribution of environmental benefits and burdens. | Human adaptation, subsistence strategies, and cultural impact on ecological systems. |
| Approach | Critical analysis of policies, institutions, and global economic systems. | Anthropological and ecological analysis of cultural behaviors. |
| Scale | Local to global political structures. | Primarily local cultural-environment interactions. |
| Purpose | Highlight power relations affecting environmental outcomes. | Understand how culture shapes environmental adaptation. |
Introduction to Political Ecology and Cultural Ecology
Political ecology examines the intricate relationships between political, economic, and social factors affecting environmental issues and resource management, highlighting power dynamics and inequality. Cultural ecology focuses on how cultural beliefs and practices influence human interactions with the environment, emphasizing adaptation and sustainable resource use within specific cultural contexts. Both frameworks offer valuable perspectives for understanding human-environment interactions but differ in their emphasis on power structures versus cultural adaptations.
Defining Political Ecology: Key Concepts
Political ecology examines power dynamics and economic structures influencing environmental issues, emphasizing conflicts over resource access and control. It integrates social, political, and economic factors to analyze environmental degradation and its impact on marginalized communities. Key concepts include environmental justice, capitalist exploitation, and the role of state policies in shaping ecological outcomes.
Understanding Cultural Ecology: Core Principles
Cultural ecology examines the dynamic relationship between human societies and their environments through the lens of cultural practices, technology, and adaptation strategies. Central to this field are concepts such as cultural adaptation, environmental determinism, and the role of social structures in shaping human-environment interactions. This approach contrasts with political ecology by emphasizing local knowledge systems and cultural factors in understanding ecological changes rather than focusing primarily on power relations and economic influences.
Historical Development of Political and Cultural Ecology
Political ecology emerged in the 1970s as a critical response to the limitations of cultural ecology, highlighting the influence of power dynamics, economic factors, and colonial histories on environmental issues. Cultural ecology, developed primarily through the work of Julian Steward in the mid-20th century, emphasized the adaptive relationship between human cultures and their environments without adequately addressing social inequalities. The historical development of political ecology integrated interdisciplinary approaches from geography, anthropology, and environmental studies to reveal how political economy shapes ecological outcomes, contrasting with cultural ecology's focus on cultural adaptations and environmental determinism.
Theoretical Foundations and Influential Thinkers
Political Ecology centers on the power dynamics and socioeconomic inequalities influencing environmental issues, with foundational thinkers like Piers Blaikie and Michael Watts highlighting the role of political economy in resource access and environmental degradation. Cultural Ecology, pioneered by Julian Steward, emphasizes the adaptive strategies of human cultures in relation to their environments, focusing on the interaction between cultural practices and ecological systems. While Political Ecology critiques structural impacts and historical context of environmental problems, Cultural Ecology investigates how cultural adaptations shape human-environment relationships.
Methodological Approaches in Political and Cultural Ecology
Political ecology employs critical and interdisciplinary methodologies focusing on power relations, resource control, and environmental justice, often utilizing qualitative data, historical analysis, and case studies to reveal socio-political dynamics impacting ecological outcomes. Cultural ecology emphasizes ethnographic methods, participant observation, and ecological anthropology to understand how cultural practices and beliefs influence human-environment interactions at local and regional scales. Both approaches integrate spatial analysis and ecological data, but political ecology prioritizes structural critiques while cultural ecology centers on adaptive strategies and cultural meanings in environmental management.
Human-Environment Relations: Comparative Perspectives
Political ecology examines human-environment relations by emphasizing power dynamics, economic interests, and social conflicts that shape resource use and environmental policies. Cultural ecology focuses on how cultural beliefs, practices, and technologies enable societies to adapt sustainably to their environment over time. Comparative analysis highlights that political ecology foregrounds structural inequalities and environmental justice, while cultural ecology prioritizes adaptive strategies and local knowledge systems.
Case Studies: Political vs Cultural Approaches
Case studies in political ecology emphasize the power dynamics and economic structures influencing environmental issues, such as resource conflicts in the Amazon rainforest driven by corporate interests and indigenous resistance. Cultural ecology case studies focus on how cultural beliefs and practices shape human interactions with the environment, exemplified by traditional agricultural systems in Bali that promote sustainable water management. Comparing these approaches reveals political ecology's focus on structural inequalities, while cultural ecology highlights adaptive cultural strategies within local ecosystems.
Critiques and Limitations of Both Frameworks
Political ecology critiques highlight its tendency to overemphasize power dynamics and often overlook local ecological knowledge, leading to potential biases in environmental analysis. Cultural ecology faces limitations by sometimes downplaying the influence of political and economic structures on environmental outcomes, resulting in overly deterministic interpretations of cultural adaptation. Both frameworks struggle with balancing macro-level structural factors and micro-level cultural practices, which can hinder comprehensive environmental assessments.
Integrating Political and Cultural Ecology in Contemporary Research
Integrating political ecology and cultural ecology in contemporary research offers a comprehensive framework to analyze environmental issues by combining socio-political power dynamics with cultural beliefs and practices influencing human-environment interactions. This interdisciplinary approach facilitates understanding how political economy shapes resource access and management while recognizing cultural values and knowledge systems that guide ecological adaptations. Emphasizing such integration enhances policy-making by addressing both structural inequalities and cultural diversity in environmental governance.
Political Ecology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com