A primate city dominates a country's urban hierarchy by significantly out-sizing other cities in population, economy, and influence. This urban center often concentrates political power, cultural institutions, and economic activities, shaping national development patterns. Explore the rest of the article to understand how primate cities impact your country's growth and urban planning.
Table of Comparison
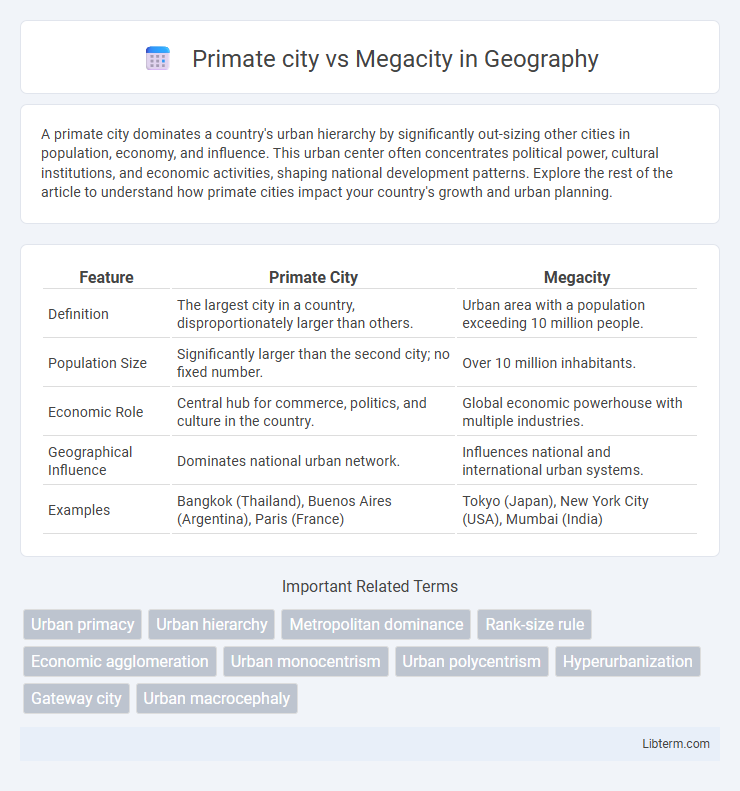
| Feature | Primate City | Megacity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The largest city in a country, disproportionately larger than others. | Urban area with a population exceeding 10 million people. |
| Population Size | Significantly larger than the second city; no fixed number. | Over 10 million inhabitants. |
| Economic Role | Central hub for commerce, politics, and culture in the country. | Global economic powerhouse with multiple industries. |
| Geographical Influence | Dominates national urban network. | Influences national and international urban systems. |
| Examples | Bangkok (Thailand), Buenos Aires (Argentina), Paris (France) | Tokyo (Japan), New York City (USA), Mumbai (India) |
Introduction to Primate Cities and Megacities
Primate cities dominate their nation's urban hierarchy by possessing more than twice the population size of the next largest city, serving as economic, political, and cultural hubs. Megacities, defined as urban areas with populations exceeding 10 million, showcase intense urbanization and complex infrastructure demands. Both urban forms illustrate contrasting patterns of population concentration influencing national development strategies and resource allocation.
Defining Primate Cities
Primate cities are defined as the largest city in a country or region that disproportionately dominates the political, economic, and cultural landscape, often exceeding the size of the next largest cities by a significant margin. Unlike megacities, which are primarily characterized by a population exceeding 10 million residents, primate cities emphasize their dominance within a national urban hierarchy rather than just population size. Examples of primate cities include Bangkok in Thailand and Paris in France, where urban primacy leads to centralization of resources and influence.
What Constitutes a Megacity?
A megacity is defined by its population size, typically exceeding 10 million residents, making it one of the largest urban areas worldwide. Unlike a primate city, which dominates a country's urban hierarchy by political, economic, and cultural influence, a megacity's significance derives primarily from its massive population and extensive infrastructure. Examples of megacities include Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai, where high-density living coexists with vast economic activities and complex metropolitan governance.
Key Differences Between Primate Cities and Megacities
Primate cities are urban areas that dominate a country's economic, political, and cultural activities, typically being more than twice the size of the next largest city, such as Bangkok in Thailand, while megacities are defined by their population size, often exceeding 10 million inhabitants, like Tokyo or Mumbai. Primate cities centralize national services and infrastructure, leading to urban primacy and regional disparities, whereas megacities may be one of several large urban centers in a country, emphasizing population density and extensive metropolitan sprawl. The key difference lies in primate cities' disproportionate dominance within a national context compared to megacities' sheer scale of population and urban complexity.
Historical Examples of Primate Cities
Primate cities are urban centers that dominate the economic, political, and cultural life of a country, often overshadowing all other cities combined, with historical examples including London in the UK during the 19th century and Paris in France throughout the 18th and 19th centuries. These primate cities typically emerge in countries with centralized governance and colonial histories. In contrast, megacities are defined by their large population size, such as Tokyo or Mumbai, without necessarily dominating their nation's economy or politics.
Notable Megacities Around the World
Notable megacities like Tokyo, Delhi, and Shanghai each house populations exceeding 10 million, serving as major economic, cultural, and political hubs on a global scale. Unlike primate cities, which dominate their national urban hierarchy alone--such as Bangkok in Thailand or Mexico City in Mexico--megacities often coexist with multiple other large cities within the same country. This distinction highlights the urban diversity and complexity found in countries with megacities compared to those dominated by a single primate city.
Economic Impacts of Primate Cities vs. Megacities
Primate cities often concentrate a disproportionate share of national economic activity, driving GDP growth and attracting investments due to centralized administrative and commercial functions. Megacities, while also significant economic hubs, tend to generate diverse economies with multiple industry sectors, fostering innovation and large labor markets but sometimes facing challenges like congestion and infrastructure strain. The economic impact of primate cities includes enhancing national competitiveness but risks regional disparities, whereas megacities contribute to broader urban agglomeration economies and global connectivity.
Social and Urban Challenges
Primate cities often face acute social challenges such as unequal wealth distribution, overcrowding, and strain on infrastructure due to their dominance in national urban hierarchy, resulting in heightened poverty and inadequate public services. Megacities struggle with complex urban issues including traffic congestion, air pollution, housing shortages, and social fragmentation caused by rapid population growth exceeding 10 million inhabitants. Both urban forms experience governance difficulties in managing resources effectively, but primate cities concentrate pressures unevenly, while megacities confront multifaceted problems across sprawling metropolitan regions.
Urban Planning and Development Strategies
Primate cities dominate their country's urban hierarchy by concentrating population, economic activity, and infrastructure in one major center, necessitating urban planning strategies that address congestion, resource allocation, and service delivery within a single metropolitan area. Megacities, characterized by populations exceeding 10 million, require complex, multi-scalar development strategies focusing on sustainable transportation networks, decentralized economic zones, and inclusive housing policies to manage rapid urban growth and reduce spatial inequalities. Urban planners must tailor interventions that accommodate the unique demands of primate cities' centralized dominance versus megacities' polycentric expansion, emphasizing balanced regional development and resilience.
Future Trends in Urbanization: Primate vs. Megacity
Primate cities, characterized by their dominance in population and economic activities within a country, are expected to face increasing challenges due to concentrated urban pressure and infrastructure demands, while megacities, defined by populations exceeding 10 million, are projected to grow rapidly driven by global migration and economic globalization. Future urbanization trends indicate megacities will require innovative solutions in sustainable development, smart infrastructure, and climate resilience to manage sprawling growth and resource allocation efficiently. Emerging policies emphasize balanced regional development to mitigate the excessive primacy of single cities and promote multi-centric urban networks for better economic diversification and social equity.
Primate city Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com