Estuarine deltas form where river sediments meet tidal waters, creating rich, dynamic environments essential for biodiversity and coastal protection. These deltas support fisheries, filter pollutants, and act as buffers against storm surges, playing a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Explore the rest of the article to understand how your local estuarine delta impacts both nature and human activity.
Table of Comparison
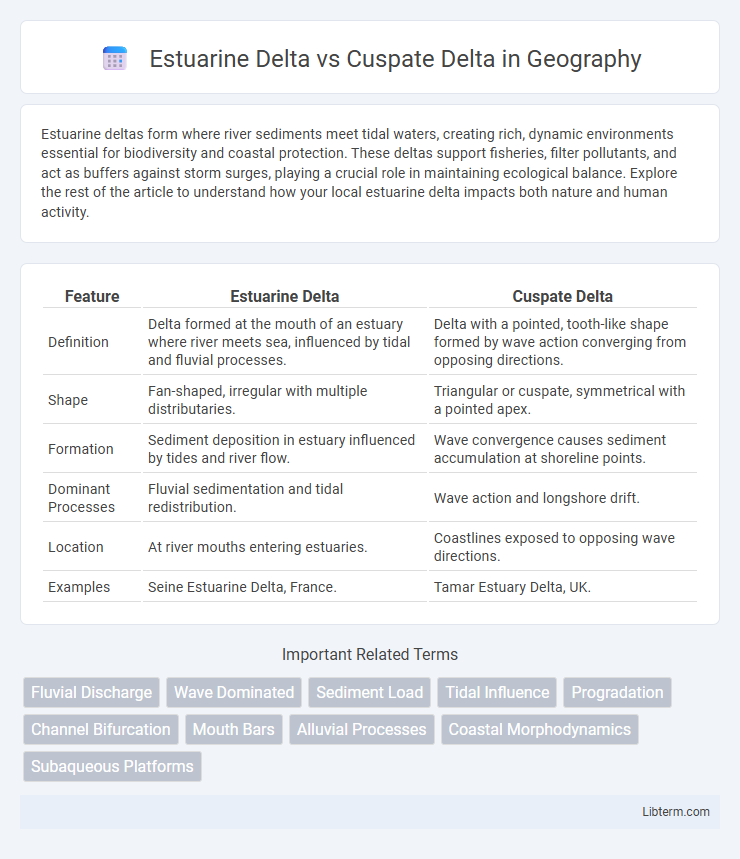
| Feature | Estuarine Delta | Cuspate Delta |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delta formed at the mouth of an estuary where river meets sea, influenced by tidal and fluvial processes. | Delta with a pointed, tooth-like shape formed by wave action converging from opposing directions. |
| Shape | Fan-shaped, irregular with multiple distributaries. | Triangular or cuspate, symmetrical with a pointed apex. |
| Formation | Sediment deposition in estuary influenced by tides and river flow. | Wave convergence causes sediment accumulation at shoreline points. |
| Dominant Processes | Fluvial sedimentation and tidal redistribution. | Wave action and longshore drift. |
| Location | At river mouths entering estuaries. | Coastlines exposed to opposing wave directions. |
| Examples | Seine Estuarine Delta, France. | Tamar Estuary Delta, UK. |
Introduction to Delta Types
Estuarine deltas form where river sediments accumulate at the mouth of an estuary, characterized by complex tidal influences and mixing of freshwater and saltwater, resulting in irregular, lobed sediment deposition. Cuspate deltas develop from the interaction of river discharge with wave-driven sediment transport, creating a symmetrical, pointed protrusion shaped by lateral sediment spread along the shoreline. Understanding these contrasting delta types highlights the interplay between fluvial processes, tidal dynamics, and wave action in coastal geomorphology.
Defining Estuarine Deltas
Estuarine deltas form at river mouths where freshwater meets tidal estuaries, characterized by complex sediment deposition influenced by both fluvial and tidal processes. These deltas display extensive mixing zones and sediment sorting that support diverse ecosystems and dynamic hydrological patterns. Unlike cuspate deltas, which are shaped primarily by wave action forming symmetrical triangles, estuarine deltas evolve from the interplay of tides, river flow, and sedimentation within sheltered environments.
Characteristics of Cuspate Deltas
Cuspate deltas are characterized by a pointed, tooth-like shape formed by the action of waves and currents converging from different directions, creating a symmetrical, triangular landform. These deltas typically develop in areas with strong, consistent wave action and a relatively low sediment supply, leading to the smooth, fan-shaped shoreline with minimal distributary channels. Unlike estuarine deltas, cuspate deltas lack a defined estuary and are dominated by wave-dominated sediment redistribution rather than river-dominated deposition.
Formation Processes of Estuarine Deltas
Estuarine deltas form through the deposition of sediment where a river meets an estuary, characterized by the mixing of fresh and saltwater that slows water flow and encourages sediment accumulation. Tidal action and varying salinity levels influence sediment sorting and delta morphology, resulting in complex channel networks within estuarine deltas. Unlike cuspate deltas, which develop from wave action shaping sediment into triangular points, estuarine deltas primarily rely on riverine sediment supply and tidal dynamics for their formation.
Morphological Features of Cuspate Deltas
Cuspate deltas are characterized by a pointed, triangular shape formed by the converging action of wave and current processes, creating a balanced sediment deposition on both sides. Unlike estuarine deltas, which develop in funnel-shaped estuaries with significant fluvial and tidal influences, cuspate deltas extend seaward with symmetrical lobes due to consistent sediment supply from multiple directions. Their morphological features include sharp apexes, a broad open seaward fringe, and minimal sheltering bays or inlets, reflecting dominant wave action shaping the delta front.
Sediment Dynamics in Estuarine vs Cuspate Deltas
Sediment dynamics in estuarine deltas are characterized by bidirectional flow patterns causing sediment deposition and re-suspension influenced by tidal currents, river discharge, and salinity gradients. In contrast, cuspate deltas experience sediment accumulation primarily through longshore drift and wave action, promoting a triangular shape formed by balanced sediment deposition from opposing littoral currents. Estuarine deltas often show complex sediment sorting with fine-grained materials trapped in sheltered areas, while cuspate deltas feature coarser sediments distributed along protruding lobes shaped by persistent wave energy.
Ecological Significance of Each Delta Type
Estuarine deltas support diverse ecosystems by blending freshwater and seawater, creating nutrient-rich habitats essential for fish spawning and migratory bird populations. Cuspate deltas enhance ecological productivity through their triangular, protruding shape that promotes sediment deposition and complex shoreline habitats, benefiting various aquatic species. Both delta types serve as critical buffers against coastal erosion and provide crucial breeding and feeding grounds for wildlife, maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Human Impacts on Estuarine and Cuspate Deltas
Human activities such as urbanization, industrial development, and dam construction significantly alter sediment supply and water flow in estuarine deltas, leading to habitat degradation and increased vulnerability to sea-level rise. In cuspate deltas, coastal engineering projects like groins and breakwaters disrupt natural sediment transport, causing erosion and changes in delta morphology. Both delta types face challenges from pollution and land reclamation, which threaten biodiversity and reduce the resilience of ecosystems to climate change.
Notable Examples Worldwide
The Amazon River delta exemplifies a vast estuarine delta characterized by a broad, funnel-shaped estuary with significant freshwater input blending with seawater, supporting rich biodiversity and extensive sediment deposits. The Nile Delta represents a classic cuspate delta, featuring a pointed, triangular shape formed by longshore drift and wave action, creating fertile lands critical for agriculture. Other notable examples include the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta as a large estuarine system with complex tidal influences, while the Tiber River Delta in Italy illustrates a smaller, cuspate delta influenced by Mediterranean wave dynamics.
Comparative Analysis: Estuarine Delta vs Cuspate Delta
Estuarine deltas form where river sediments accumulate within estuaries, characterized by a complex mix of freshwater and tidal influences, promoting nutrient-rich habitats and diverse ecosystems. Cuspate deltas develop through wave-driven sediment deposition along coastlines, resulting in a pointed, symmetrical shape with less freshwater influence and more wave energy impact. Comparative analysis highlights estuarine deltas' strong tidal modulation and organic sedimentation versus cuspate deltas' dominance by wave action and symmetrical geomorphology.
Estuarine Delta Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com