A plateau is an elevated flatland that rises sharply above the surrounding area, often formed by geological processes such as volcanic activity or erosion. These landforms can significantly impact local climate, vegetation, and human activities by providing unique habitats and agricultural opportunities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how plateaus influence ecosystems and settlements.
Table of Comparison
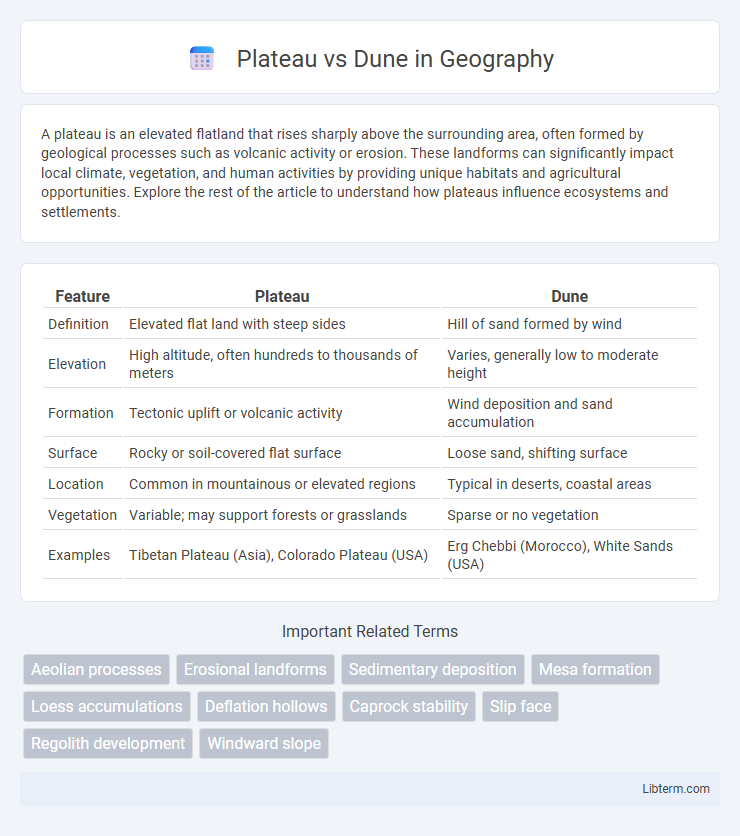
| Feature | Plateau | Dune |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated flat land with steep sides | Hill of sand formed by wind |
| Elevation | High altitude, often hundreds to thousands of meters | Varies, generally low to moderate height |
| Formation | Tectonic uplift or volcanic activity | Wind deposition and sand accumulation |
| Surface | Rocky or soil-covered flat surface | Loose sand, shifting surface |
| Location | Common in mountainous or elevated regions | Typical in deserts, coastal areas |
| Vegetation | Variable; may support forests or grasslands | Sparse or no vegetation |
| Examples | Tibetan Plateau (Asia), Colorado Plateau (USA) | Erg Chebbi (Morocco), White Sands (USA) |
Plateau vs Dune: Definition and Key Differences
A plateau is an elevated flatland rising sharply above surrounding areas, characterized by relatively level terrain and significant height, often formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity. In contrast, a dune is a mound or ridge of loose sand shaped by wind, typically found in deserts or coastal regions, and is constantly shifting due to wind erosion and deposition. The key differences between a plateau and a dune lie in their composition, formation processes, and stability, with plateaus composed of solid rock and exhibiting long-term stability, while dunes consist of loose sand particles and are highly dynamic.
Geological Formation of Plateaus and Dunes
Plateaus form through processes such as volcanic activity, tectonic uplift, and erosion that elevate large, flat regions above surrounding areas, often composed of sedimentary or igneous rock layers. Dunes develop from wind-driven accumulation and movement of sand particles, typically in arid or coastal environments, shaped by factors like wind direction, sediment supply, and vegetation. Geological formations of plateaus reveal stable lithospheric blocks, while dunes exhibit dynamic sedimentary structures influenced by prevailing climatic conditions.
Types of Plateaus and Dunes
Plateaus are elevated flat-topped landforms classified into various types including dissected plateaus, which are heavily eroded, volcanic plateaus formed by lava flows, and tectonic plateaus created by crustal uplift. Dunes, composed of sand accumulated by wind action, are categorized into types such as crescent-shaped barchan dunes, linear seif dunes, star-shaped dunes with multiple arms, and parabolic dunes stabilized by vegetation. Understanding these distinct types highlights the geological and environmental processes shaping diverse landscapes on Earth.
Physical Characteristics: Plateau vs Dune
A plateau is an elevated flat-topped landform that rises sharply above the surrounding area, often characterized by steep cliffs and extensive horizontal layers of rock. In contrast, a dune is a mound or ridge of loose sand shaped by wind, typically found in deserts or coastal regions, and lacks the solid rock foundation seen in plateaus. While plateaus have significant elevation changes with stable geological formations, dunes are dynamic and constantly reshaped by wind patterns.
Climate Influence on Plateaus and Dunes
Plateaus typically form in regions with stable, dry climates where limited rainfall minimizes erosion, allowing elevated landforms to persist over time. Dunes, on the other hand, develop in arid or semi-arid environments with strong winds that transport and accumulate sand, shaping dynamic, constantly changing landscapes. Climate factors such as wind velocity, precipitation levels, and temperature fluctuations critically influence the formation, stability, and morphology of both plateaus and dunes.
Ecological Importance of Plateaus and Dunes
Plateaus support unique ecosystems with diverse flora and fauna adapted to elevated, stable environments, contributing to biodiversity and soil conservation. Dunes act as natural barriers against coastal erosion, providing critical habitats for specialized plants and animals while stabilizing sandy terrains. Both landforms play vital roles in maintaining ecological balance by influencing microclimates and water retention in their respective regions.
Global Distribution: Where Plateaus and Dunes Occur
Plateaus predominantly occur in regions with tectonic uplift and volcanic activity, such as the Colorado Plateau in North America and the Deccan Plateau in India, often found on every continent. Dunes are mainly distributed in arid and semi-arid environments, including the Sahara Desert in Africa, the Arabian Desert in the Middle East, and coastal areas like the Namib Desert in Namibia, formed by wind-driven sand accumulation. Both landscapes reflect distinct geomorphological processes that influence their global distribution patterns.
Human Interaction and Uses
Plateaus offer flat, elevated land that supports agriculture, settlement, and infrastructure development due to their stable terrain and access to water sources. Dunes, composed of shifting sand, present challenges for permanent human settlement but are exploited for recreational activities and serve as natural barriers against coastal erosion. Human interaction with plateaus often involves cultivation and urbanization, while dunes are valued for their ecological role and tourism potential.
Plateaus and Dunes in Culture and History
Plateaus often hold cultural significance as ancient sites of civilization, such as the Deccan Plateau in India, which nurtured diverse cultures and rich historical heritage. Dunes, symbolizing the desert's ever-changing landscape, feature prominently in nomadic traditions and folklore across regions like the Sahara, embodying survival and adaptation. Both formations shape human settlement patterns and spiritual beliefs, reflecting the interplay between geography and cultural identity.
Comparing Erosion and Sustainability: Plateau vs Dune
Plateaus exhibit slower erosion rates due to their hard rock composition, supporting more stable ecosystems and long-term sustainability, whereas dunes experience rapid erosion caused by wind and water shifting loose sand, resulting in fluctuating habitats. The vegetation on plateaus helps anchor soil and minimize erosion, while dunes rely on sparse plant life and moisture levels, making them more vulnerable to environmental changes. Understanding these differences highlights the importance of protecting plateau environments for sustainable land management, while implementing dune stabilization techniques to preserve their fragile ecosystems.
Plateau Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com