Granite is a durable, natural stone commonly used for countertops, flooring, and architectural features due to its resistance to heat, scratches, and stains. Its unique mineral composition and wide range of colors make it a popular choice for enhancing home aesthetics and adding long-lasting value. Discover more about granite's benefits, maintenance tips, and design ideas in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
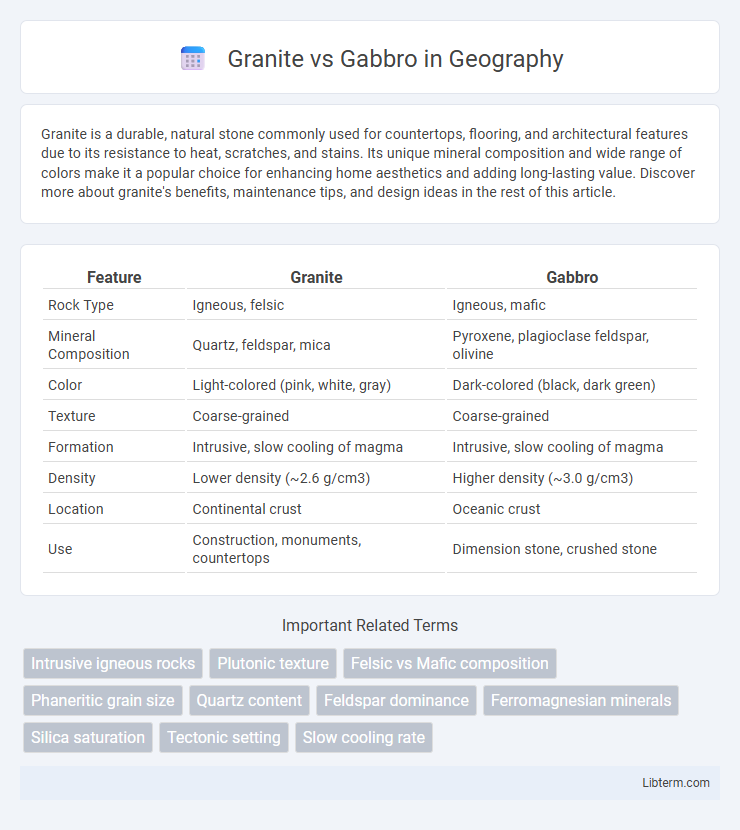
| Feature | Granite | Gabbro |
|---|---|---|
| Rock Type | Igneous, felsic | Igneous, mafic |
| Mineral Composition | Quartz, feldspar, mica | Pyroxene, plagioclase feldspar, olivine |
| Color | Light-colored (pink, white, gray) | Dark-colored (black, dark green) |
| Texture | Coarse-grained | Coarse-grained |
| Formation | Intrusive, slow cooling of magma | Intrusive, slow cooling of magma |
| Density | Lower density (~2.6 g/cm3) | Higher density (~3.0 g/cm3) |
| Location | Continental crust | Oceanic crust |
| Use | Construction, monuments, countertops | Dimension stone, crushed stone |
Introduction to Granite and Gabbro
Granite is a light-colored, coarse-grained igneous rock composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica, known for its durability and widespread use in construction and monuments. Gabbro is a dark, coarse-grained igneous rock composed primarily of calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar and pyroxene, often used as a crushed stone in road construction and as an aggregate. Both rocks form from the slow cooling of magma beneath the Earth's surface, but granite typically originates from felsic magma, while gabbro forms from mafic magma.
Geological Formation Differences
Granite forms from the slow crystallization of silica-rich magma deep within the Earth's continental crust, resulting in a coarse-grained texture with visible quartz and feldspar crystals. Gabbro originates from the slow cooling of magma that is rich in iron and magnesium beneath the oceanic crust, producing a dense, dark-colored rock predominantly composed of pyroxene and plagioclase. These differences in mineral composition and formation environment reflect their distinct geological processes and tectonic settings.
Mineral Composition Comparison
Granite primarily consists of quartz, feldspar (both orthoclase and plagioclase), and mica, giving it a lighter appearance with visible crystals of varied mineral types. Gabbro is composed predominantly of pyroxene and calcium-rich plagioclase feldspar, resulting in a darker, denser rock with fewer quartz grains. The distinct differences in mineral composition between granite and gabbro influence their color, texture, and geological use cases.
Color and Texture Variations
Granite exhibits a wide range of colors including pink, white, gray, and black due to its mineral composition, mainly quartz, feldspar, and mica, while gabbro typically appears in darker shades like black, dark green, and dark gray, reflecting its high content of pyroxene and plagioclase feldspar. Granite's texture is coarse-grained with visible interlocking crystals, giving it a speckled appearance, whereas gabbro has a coarse to medium-grained texture with larger, more uniform crystals that create a denser, more solid look. These color and texture variations make granite popular for decorative and construction uses, while gabbro is often chosen for industrial purposes and as a dimensional stone.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Granite exhibits a coarse-grained texture with high quartz content, resulting in greater hardness and resistance to abrasion, typically scoring around 6-7 on the Mohs scale. Gabbro has a denser, fine to medium-grained texture, dominated by pyroxene and plagioclase, which imparts higher compressive strength but lower resistance to chemical weathering than granite. The mechanical properties of granite make it ideal for architectural applications requiring durability, while gabbro's strength favors its use in heavy construction and road base materials.
Common Uses in Construction
Granite is widely used in construction for countertops, flooring, and exterior cladding due to its durability and attractive grain patterns. Gabbro, though less common, is favored for heavy-duty applications such as road base and railway ballast because of its dense, coarse-grained texture and high compressive strength. Both stones offer excellent resistance to weathering, making them suitable for structural and decorative elements in buildings and infrastructure projects.
Durability and Weather Resistance
Granite exhibits superior durability and weather resistance due to its high quartz and feldspar content, making it highly resistant to abrasion, heat, and acid rain. Gabbro, composed mainly of pyroxene and plagioclase, tends to be denser but less resistant to chemical weathering and freeze-thaw cycles compared to granite. The interlocking crystal structure of granite enhances its ability to withstand environmental stress, making it a preferred choice for exterior applications requiring long-lasting performance.
Popular Locations and Sources
Granite is predominantly sourced from regions such as the United States, Brazil, India, and China, with famous quarries found in Vermont, Georgia, and South Dakota. Gabbro is commonly extracted from locations including Norway, Canada, and Italy, with significant deposits in the Lofoten Islands and the Adirondack Mountains. Both rocks are widely used in construction and decorative applications, with granite favored for its durability and aesthetic variety, while gabbro is valued for its strength and dark appearance.
Maintenance and Care Guidelines
Granite requires regular sealing to prevent staining and maintain its polished surface, making it a low-maintenance choice with proper care. Gabbro, being denser and less porous than granite, resists moisture and stains better but still benefits from periodic sealing and gentle cleaning with pH-neutral detergents. Both stones should avoid acidic or abrasive cleaners to preserve their durability and aesthetic appeal over time.
Choosing Between Granite and Gabbro
Choosing between granite and gabbro depends on factors like appearance, durability, and cost. Granite is a lighter, more popular option with a granular texture and wide color range, ideal for kitchen countertops and decorative surfaces. Gabbro, a darker, coarse-grained igneous rock, offers superior strength and resistance to weathering, making it suitable for exterior applications and heavy-duty construction.
Granite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com