Urban geography examines the spatial aspects of cities and how human activities shape urban environments. It explores patterns of population distribution, infrastructure development, economic zones, and social interactions within metropolitan areas. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how your city's layout influences daily life and future growth.
Table of Comparison
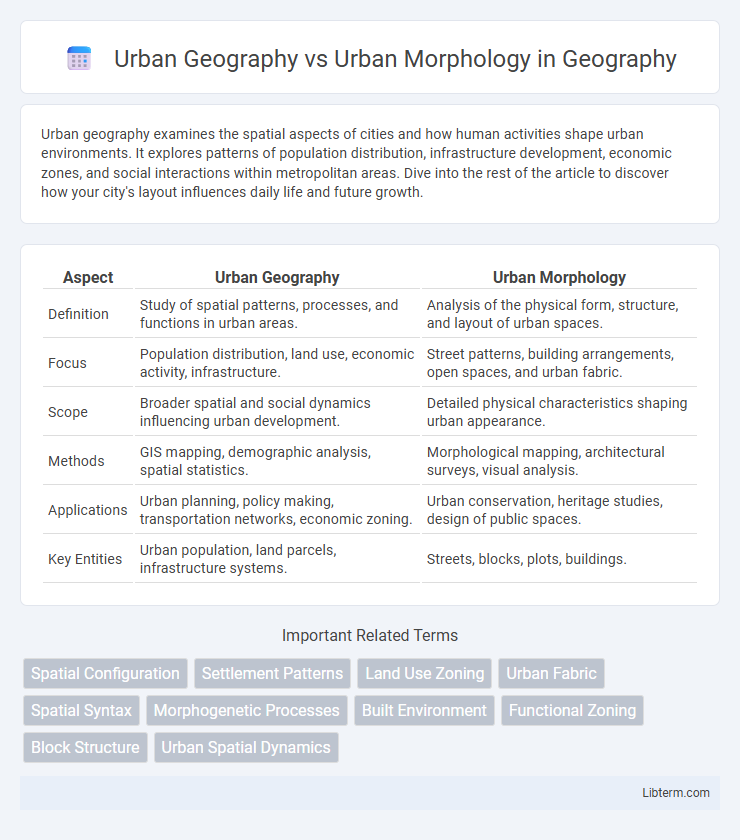
| Aspect | Urban Geography | Urban Morphology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of spatial patterns, processes, and functions in urban areas. | Analysis of the physical form, structure, and layout of urban spaces. |
| Focus | Population distribution, land use, economic activity, infrastructure. | Street patterns, building arrangements, open spaces, and urban fabric. |
| Scope | Broader spatial and social dynamics influencing urban development. | Detailed physical characteristics shaping urban appearance. |
| Methods | GIS mapping, demographic analysis, spatial statistics. | Morphological mapping, architectural surveys, visual analysis. |
| Applications | Urban planning, policy making, transportation networks, economic zoning. | Urban conservation, heritage studies, design of public spaces. |
| Key Entities | Urban population, land parcels, infrastructure systems. | Streets, blocks, plots, buildings. |
Introduction to Urban Geography and Urban Morphology
Urban Geography examines spatial patterns and human activities within cities, focusing on the distribution of populations, land use, and economic functions in urban environments. Urban Morphology studies the physical structure and layout of urban spaces, analyzing the formation, evolution, and design of streets, buildings, and open spaces. Both fields provide critical insights into urban development by integrating social dynamics with tangible spatial configurations.
Defining Urban Geography
Urban geography examines spatial patterns, processes, and interactions within urban areas, analyzing population distribution, land use, and economic activities to understand city dynamics. It focuses on how urban environments develop and transform in response to social, economic, and environmental factors. Urban morphology concentrates on the physical form and structure of cities, studying the layout, design, and organization of urban spaces and built environments.
Defining Urban Morphology
Urban morphology focuses on the study of the physical form and structure of urban spaces, analyzing patterns of streets, buildings, and land use to understand how cities develop and evolve over time. It investigates the spatial configuration and design of urban areas, emphasizing the historical and social processes shaping urban landscapes. Whereas urban geography examines broader social, economic, and environmental interactions within urban settings, urban morphology provides a detailed examination of the tangible, built environment.
Key Differences Between Urban Geography and Urban Morphology
Urban Geography examines the spatial patterns, social dynamics, and economic activities within urban areas, emphasizing human interactions and the distribution of urban functions. Urban Morphology analyzes the physical form, layout, and structure of urban spaces, focusing on the design, arrangement of buildings, street patterns, and land use. The key difference lies in Urban Geography's focus on socio-economic processes and spatial relationships, while Urban Morphology centers on the physical components and the evolution of urban form.
Historical Development of Both Fields
Urban geography emerged in the early 20th century as a branch of human geography focusing on spatial patterns and processes within cities, influenced by economic, social, and political factors. Urban morphology developed as a sub-discipline concentrating on the physical structure and form of urban areas, tracing historical transformations in street layouts, building types, and land use over time. Key figures such as M.R.G. Conzen and Paolo Soleri contributed to understanding urban form evolution, integrating historical cartographic analysis with spatial theory.
Core Concepts in Urban Geography
Urban geography examines spatial patterns and human-environment interactions within cities, emphasizing location, population distribution, and economic activities. Core concepts include urban structure models, land use patterns, and the study of urban systems' growth and connectivity. Urban morphology, in contrast, analyzes the physical form, layout, and historical development of urban spaces, focusing on street networks, building types, and plot configurations.
Fundamental Elements of Urban Morphology
Urban morphology examines the fundamental elements of urban form, including streets, plots, and buildings, to analyze the physical layout and design of cities, while urban geography focuses on the spatial distribution and interaction of urban phenomena at various scales. Streets serve as the primary framework for urban movement and connectivity, plots represent the smallest land units defining property boundaries, and buildings constitute the vertical structures shaping the cityscape. Understanding these elements allows urban morphologists to decode the historical development patterns and social functions embedded in urban environments.
Analytical Tools and Techniques Used in Each Discipline
Urban geography employs spatial analysis, GIS mapping, and statistical models to understand population distribution, land use patterns, and urban growth dynamics. Urban morphology focuses on the physical form of cities using techniques like morphological mapping, pattern analysis, and typological classification to study street layouts, building types, and open spaces. Both disciplines utilize remote sensing and archival data, but urban geography emphasizes socio-economic data integration, while urban morphology prioritizes the analysis of built environment structures.
Interactions and Overlaps Between Urban Geography and Urban Morphology
Urban geography examines spatial patterns, human activities, and social processes within urban areas, while urban morphology focuses on the physical form, structure, and layout of cities. Both disciplines intersect in analyzing how urban form influences social behavior and economic activities, with urban morphology providing tangible context for geographic phenomena. Understanding their overlap enhances urban planning by integrating spatial dynamics with built environment characteristics, fostering sustainable and efficient city development.
Implications for Urban Planning and Policy
Urban geography analyzes spatial patterns and human activities in cities, providing data on population distribution and economic functions critical for resource allocation and infrastructure development. Urban morphology studies the physical form and structure of urban spaces, offering insights into land use, street networks, and building patterns essential for zoning and heritage conservation policies. Integrating both disciplines enables urban planners to design comprehensive policies that address social dynamics while preserving functional and aesthetic urban environments.
Urban Geography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com