Aeolian refers to processes or features related to the action of the wind, such as the transportation and deposition of sediments in deserts and coastal areas. These wind-driven mechanisms shape landscapes over time, forming dunes, loess deposits, and eroded rock formations. Discover how Aeolian forces impact your environment by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
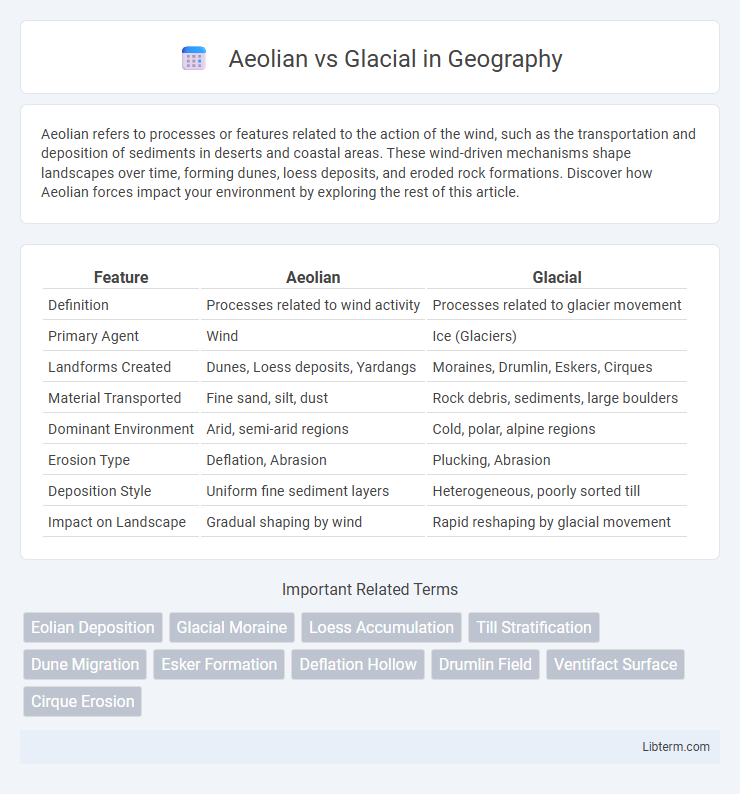
| Feature | Aeolian | Glacial |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes related to wind activity | Processes related to glacier movement |
| Primary Agent | Wind | Ice (Glaciers) |
| Landforms Created | Dunes, Loess deposits, Yardangs | Moraines, Drumlin, Eskers, Cirques |
| Material Transported | Fine sand, silt, dust | Rock debris, sediments, large boulders |
| Dominant Environment | Arid, semi-arid regions | Cold, polar, alpine regions |
| Erosion Type | Deflation, Abrasion | Plucking, Abrasion |
| Deposition Style | Uniform fine sediment layers | Heterogeneous, poorly sorted till |
| Impact on Landscape | Gradual shaping by wind | Rapid reshaping by glacial movement |
Introduction to Aeolian and Glacial Processes
Aeolian processes involve the transportation and deposition of sediment by wind, shaping landscapes through erosion, deflation, and dune formation. Glacial processes are driven by the movement and melting of ice masses, leading to erosion, sediment transport, and deposition, creating features like moraines and glacial valleys. These distinct dynamic systems play crucial roles in shaping Earth's surface environments across various climatic contexts.
Defining Aeolian and Glacial Erosion
Aeolian erosion is defined as the process by which wind removes surface materials, primarily affecting arid and semi-arid environments where loose sediments are transported over large distances. In contrast, glacial erosion occurs through the movement of glaciers, which scrape and carve the landscape by plucking and abrasion, shaping valleys and fjords. These distinct mechanisms highlight the significant role of atmospheric and cryospheric forces in shaping Earth's surface over geological time.
Key Differences Between Aeolian and Glacial Landforms
Aeolian landforms are shaped primarily by wind erosion and deposition, creating features such as dunes, loess plains, and yardangs characterized by fine, well-sorted sediments. Glacial landforms result from ice movement and melting, producing moraines, drumlins, and fjords composed largely of unsorted till and striated bedrock. Aeolian processes dominate in arid and semi-arid environments, while glacial processes occur in cold climates with active ice sheets or glaciers.
Mechanisms of Aeolian Transport
Aeolian transport involves the movement of sediment by wind through processes such as suspension, saltation, and creep, primarily affecting fine particles like sand and dust. Wind velocity must exceed a threshold velocity to initiate sediment movement, which is influenced by particle size, shape, and surface moisture. Unlike glacial transport that relies on ice movement to carry sediments, aeolian mechanisms depend on aerodynamic forces to lift and shift particles across landscapes.
Glacial Movement and Deposition Explained
Glacial movement occurs as ice masses flow slowly due to gravity, causing processes like plucking and abrasion that shape the landscape. Deposition from glaciers results in distinct landforms such as moraines, drumlins, and eskers, formed from sediment transported and deposited by ice and meltwater. These glacial deposits are characterized by unsorted, angular materials known as till, contrasting with the well-sorted sediments typical of aeolian environments.
Notable Aeolian Landforms Around the World
Notable aeolian landforms around the world include the towering sand dunes of the Sahara Desert, the crescent-shaped barchan dunes in the Gobi Desert, and the extensive loess deposits found in the Mississippi Valley. These features result from wind-driven processes like deflation and saltation, contrasting with glacial landforms formed by ice erosion and deposition. Aeolian landscapes showcase unique patterns of sediment transport and deposition, reflecting arid environments shaped predominantly by wind rather than ice.
Iconic Glacial Landscapes and Features
Iconic glacial landscapes are characterized by features such as U-shaped valleys, fjords, and moraines formed by the movement and melting of glaciers over millennia. These landscapes contrast with aeolian formations, which are shaped by wind erosion and deposition, resulting in dunes and loess deposits. Glacial features often include cirques, drumlins, and glacial lakes, emphasizing the powerful role of ice in sculpting the earth's surface.
Climatic Influences on Aeolian and Glacial Activity
Aeolian and glacial activities are primarily driven by distinct climatic conditions, where aeolian processes dominate in arid and semi-arid regions characterized by strong winds and limited vegetation, facilitating the transport and deposition of fine sediments. Glacial activity occurs in cold climates with sustained low temperatures supporting the formation and movement of glaciers, resulting in erosion, deposition, and landscape sculpting through ice flow dynamics. Variability in temperature, precipitation, and wind intensity directly influences the intensity and extent of both aeolian and glacial processes, shaping terrestrial surfaces in contrasting environmental settings.
Environmental Impact of Aeolian vs Glacial Processes
Aeolian processes transport and deposit fine sediments like silt and sand, contributing to soil formation and shaping ecosystems but can also cause dust storms that degrade air quality and harm human health. Glacial processes reshape landscapes by eroding bedrock and carrying large sediment loads, creating fertile soils in post-glacial regions that support diverse habitats, though glacial melt contributes to rising sea levels influencing global climate patterns. Both processes play critical roles in sediment redistribution, influencing environmental dynamics differently through their scale, sediment size, and long-term ecological effects.
Summary: Aeolian vs Glacial—Comparative Analysis
Aeolian processes involve the transportation and deposition of sediments by wind, typically producing well-sorted, fine-grained materials like sand dunes and loess deposits. In contrast, glacial processes are characterized by the movement of ice that transports a wide range of sediment sizes, resulting in unsorted till, moraines, and U-shaped valleys. The key difference lies in sediment sorting and landscape features: aeolian environments create stratified layers with uniform grain size, while glacial environments produce heterogeneous deposits with mixed grain sizes and distinctive erosional landforms.
Aeolian Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com