Isohel refers to a bright halo or sun dog often seen on either side of the sun, caused by the refraction of sunlight through ice crystals in the atmosphere. These atmospheric optical phenomena appear as luminous spots and can provide valuable insights into weather conditions and the presence of thin cirrus clouds. Discover how understanding isohels can enhance your knowledge of meteorological patterns in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
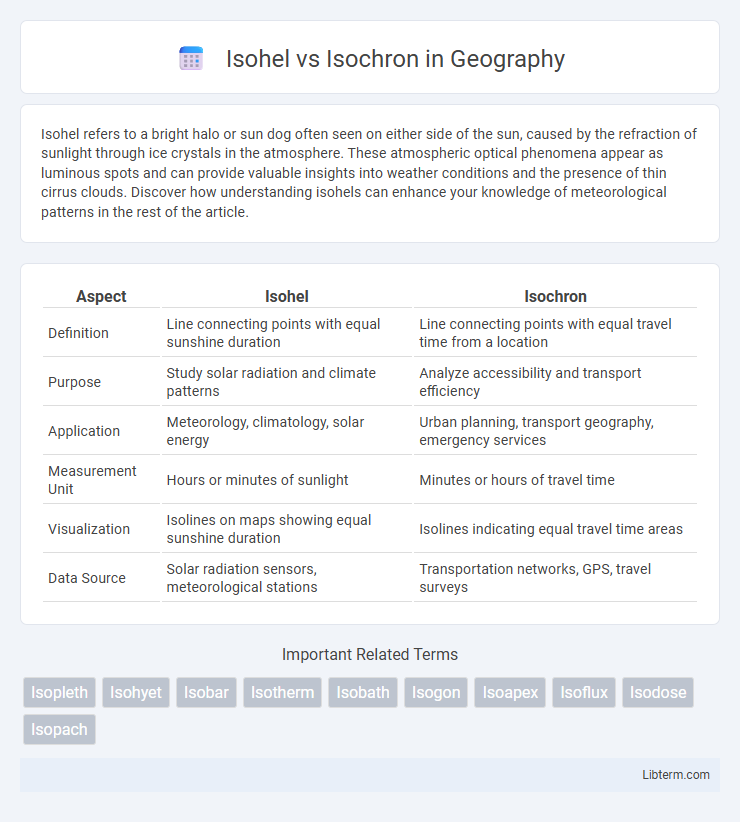
| Aspect | Isohel | Isochron |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Line connecting points with equal sunshine duration | Line connecting points with equal travel time from a location |
| Purpose | Study solar radiation and climate patterns | Analyze accessibility and transport efficiency |
| Application | Meteorology, climatology, solar energy | Urban planning, transport geography, emergency services |
| Measurement Unit | Hours or minutes of sunlight | Minutes or hours of travel time |
| Visualization | Isolines on maps showing equal sunshine duration | Isolines indicating equal travel time areas |
| Data Source | Solar radiation sensors, meteorological stations | Transportation networks, GPS, travel surveys |
Introduction to Isohels and Isochrons
Isohels represent lines connecting points of equal sunshine duration, providing valuable data for analyzing sunlight exposure and solar energy potential in geographic areas. Isochrons are lines that link points experiencing the same travel time from a specific location, crucial for transportation planning and time-based geographic studies. Understanding these concepts aids in optimizing urban design, environmental assessment, and efficient route mapping.
Understanding Isohels: Definition and Applications
Isohels are lines on a map connecting points that receive equal hours of sunlight, critical in studies of solar radiation and climate analysis. They help urban planners and agricultural experts optimize building orientation and crop selection by mapping sunlight exposure accurately. Understanding isohes enables efficient solar energy deployment and enhances environmental monitoring by illustrating spatial solar distribution.
Defining Isochrons: Meaning and Uses
Isochrons are lines on a map connecting points that experience the same travel time from a specific location, crucial in fields like seismology and transportation planning. They help visualize areas reachable within equal time frames, aiding in emergency response and urban development. Understanding isochrons improves decision-making by highlighting time-based accessibility rather than just distance.
Key Differences Between Isohel and Isochron
Isohels represent lines of equal sunlight exposure on a map, primarily used in climatology to analyze solar radiation patterns, whereas isochrons depict lines connecting points of equal travel time, often employed in transportation and geochronology studies. The key difference lies in their measurement focus: isohels measure solar irradiance durations, while isochrons represent equal temporal intervals or arrival times. Understanding these distinctions aids in selecting appropriate mapping techniques for solar energy assessments or synchronization of event timings.
Mapping Techniques Using Isohels
Isohels represent lines of equal sunshine duration, providing vital data for solar radiation mapping and climate analysis, while isochrons connect points experiencing the same time-based events, such as seismic wave arrivals. Mapping techniques using isohels involve satellite data and ground-based solar radiation measurements to chart sunlight exposure patterns, crucial for renewable energy planning and agricultural optimization. Geographic Information System (GIS) platforms enhance the precision of isohel mapping by integrating meteorological data, enabling detailed spatial analysis of solar irradiance variations.
Geological and Meteorological Relevance of Isochrons
Isochrons in geology represent lines connecting points of equal age, critical for understanding the temporal distribution of rock formations and tectonic events, whereas isohels map equal sunlight exposure and are key in meteorological studies of solar radiation patterns. Isochrons enable geologists to date geological events precisely, aiding in reconstructing Earth's history and evaluating sediment deposition rates. Meteorologists utilize isohels to analyze solar irradiance, influencing climate models and weather forecasting accuracy.
Visual Representation: Isohels vs Isochrons
Isohels visually represent points of equal solar radiation or sunshine duration on a map, often displayed with curved lines that highlight patterns of sunlight exposure across different geographic areas. Isochrons, in contrast, depict equal travel or arrival times, typically illustrated as concentric or radiating lines from a point, emphasizing time-based accessibility rather than climatic features. The distinct visual emphasis of Isohels on sunlight intensity contrasts with Isochrons' focus on temporal distances, aiding in solar energy planning and transportation analysis, respectively.
Practical Examples of Isohel and Isochron Usage
Isohel maps illustrate solar radiation distribution by showing areas receiving equal sunshine duration, commonly used in agriculture to optimize crop planting schedules based on sunlight exposure. Isochron maps depict equal travel times from a specific point, essential in urban planning and transportation logistics for designing efficient public transit routes and emergency response plans. Both tools enhance decision-making by visualizing temporal and spatial data critical for environmental management and infrastructure development.
Importance in Scientific Research and Analysis
Isohel maps illustrate lines of equal sunlight exposure, essential for studying solar radiation patterns and their impact on ecosystems and climate change models. Isochron maps show areas reachable within equal travel times, crucial for urban planning, emergency response optimization, and transport network efficiency analysis. Both tools provide spatial insights that enhance environmental research and infrastructure development by representing temporal or exposure-related data accurately.
Summary: Choosing Between Isohels and Isochrons
Isohels depict lines of equal sunlight duration, essential for solar energy planning and climatic studies, while isochrons represent lines of equal travel time, crucial for transportation logistics and hazard evacuation modeling. Selecting between isohels and isochrons depends on application goals: isohels optimize solar exposure analysis, whereas isochrons prioritize time-based accessibility mapping. Understanding their distinct purposes enhances decision-making in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and emergency response strategies.
Isohel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com