Topography studies the surface features of the Earth or other planets, focusing on the shapes and arrangements of natural and artificial elements. Accurate topographic maps are essential for urban planning, environmental management, and outdoor activities like hiking. Explore the rest of the article to understand how topography impacts your daily life and various industries.
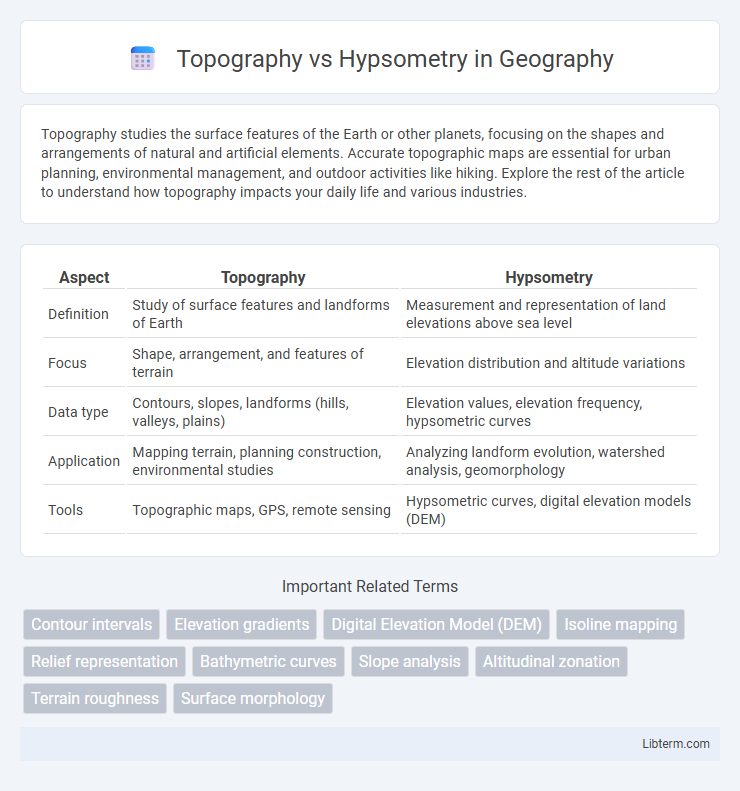
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Topography | Hypsometry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of surface features and landforms of Earth | Measurement and representation of land elevations above sea level |
| Focus | Shape, arrangement, and features of terrain | Elevation distribution and altitude variations |
| Data type | Contours, slopes, landforms (hills, valleys, plains) | Elevation values, elevation frequency, hypsometric curves |
| Application | Mapping terrain, planning construction, environmental studies | Analyzing landform evolution, watershed analysis, geomorphology |
| Tools | Topographic maps, GPS, remote sensing | Hypsometric curves, digital elevation models (DEM) |
Introduction to Topography and Hypsometry
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and description of the physical features of an area, including its terrain, elevations, and landforms, crucial for geographic and environmental studies. Hypsometry specifically measures the elevation of land surfaces relative to sea level, providing essential data for analyzing terrain height and landscape morphology. Understanding both topography and hypsometry enables accurate representation and interpretation of Earth's surface characteristics, supporting applications in geology, urban planning, and environmental management.
Defining Topography: Concepts and Applications
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and description of the physical features of the Earth's surface, including natural and artificial elevations, shapes, and contours. It encompasses the study of terrain features such as hills, valleys, slopes, and plateaus and is essential for applications in geology, civil engineering, and environmental planning. Topographic data is commonly represented through maps, digital elevation models (DEMs), and contour lines, enabling precise analysis for land development, resource management, and infrastructure design.
What is Hypsometry? Overview and Methods
Hypsometry refers to the measurement and analysis of land elevation relative to sea level, providing crucial data for understanding Earth's surface features and variations in terrain height. Methods for hypsometric analysis include the creation of hypsometric curves, which graph the distribution of elevation within a given area, and digital elevation models (DEMs) that facilitate precise altitude profiling using remote sensing and GIS technologies. These techniques enable detailed assessment of geological formations, watershed characterization, and environmental planning by quantifying the vertical dimension of landscapes.
Key Differences Between Topography and Hypsometry
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and description of the physical features of an area, including contours, elevations, and landforms, whereas hypsometry specifically measures and represents the elevation relative to sea level. Topographic maps highlight the shape and features of the terrain, such as hills, valleys, and slopes, while hypsometric maps emphasize the distribution of elevation across a region using color gradients or shading. The key difference lies in topography's broader focus on all land features, while hypsometry concentrates exclusively on elevation and height variations.
Tools and Techniques in Topographic Mapping
Topographic mapping employs tools such as theodolites, total stations, GPS devices, and LiDAR technology to accurately measure and represent terrain features, elevations, and contours. Techniques include photogrammetry, satellite remote sensing, and digital elevation models (DEMs) to create detailed maps illustrating the Earth's surface morphology. Unlike hypsometry, which primarily analyzes elevation data and height variations, topography integrates spatial measurements to depict both natural and artificial landscape elements comprehensively.
Methods of Hypsometric Analysis
Hypsometric analysis methods involve studying the elevation distribution within a specific area to understand landscape development and geomorphic processes. Techniques such as hypsometric curve plotting, hypsometric integral calculation, and digital elevation model (DEM) analysis are commonly used to quantify terrain characteristics and assess erosion levels. These methods provide critical insights into the geomorphological stage of a watershed or landform by comparing relative land surface elevations.
Importance of Topography in Environmental Studies
Topography, which refers to the detailed mapping and description of the physical features of a terrain, is crucial in environmental studies for understanding landform shapes and elevations that influence water flow, soil erosion, and habitat distribution. Hypsometry, the measurement of land elevation relative to sea level, complements topography but focuses more on elevation data rather than spatial configuration. Accurate topographic data supports environmental modeling, risk assessment for natural disasters like floods and landslides, and effective land-use planning that promotes sustainable ecosystem management.
Role of Hypsometry in Geographical Research
Hypsometry plays a crucial role in geographical research by quantifying the elevation distribution of landforms, which aids in understanding terrain characteristics and landscape evolution. It provides critical data for watershed analysis, erosion studies, and climate modeling, enabling researchers to assess how elevation impacts environmental processes. Unlike general topography, which describes surface features, hypsometry delivers precise elevation metrics essential for spatial analysis and geospatial planning.
Comparative Applications in Earth Sciences
Topography and hypsometry both analyze Earth's surface features, with topography mapping landforms and terrain elevations, while hypsometry focuses on the distribution of elevation across a region or the entire planet. Topographic data is crucial for understanding landform morphology, watershed management, and hazard assessment, whereas hypsometric analysis aids in studying erosion rates, landscape evolution, and global elevation patterns. Comparative application of these methods enhances environmental modeling, geomorphological research, and geospatial planning in Earth sciences.
Summary: Choosing Between Topography and Hypsometry
Topography provides detailed information about the Earth's surface features, including elevation and terrain shapes, essential for physical landscape analysis and engineering projects. Hypsometry focuses specifically on measuring land elevation relative to sea level, useful for creating elevation profiles and understanding watershed characteristics. Choosing between topography and hypsometry depends on whether comprehensive terrain mapping or precise elevation data is needed for environmental assessment, urban planning, or geospatial studies.
Topography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com