A plateau is a flat, elevated landform that rises sharply above the surrounding terrain, often formed by tectonic activity or volcanic processes. These landforms can significantly affect local climate, agriculture, and human settlement due to their unique topographical and ecological characteristics. Explore the rest of the article to understand how plateaus influence ecosystems and human life.
Table of Comparison
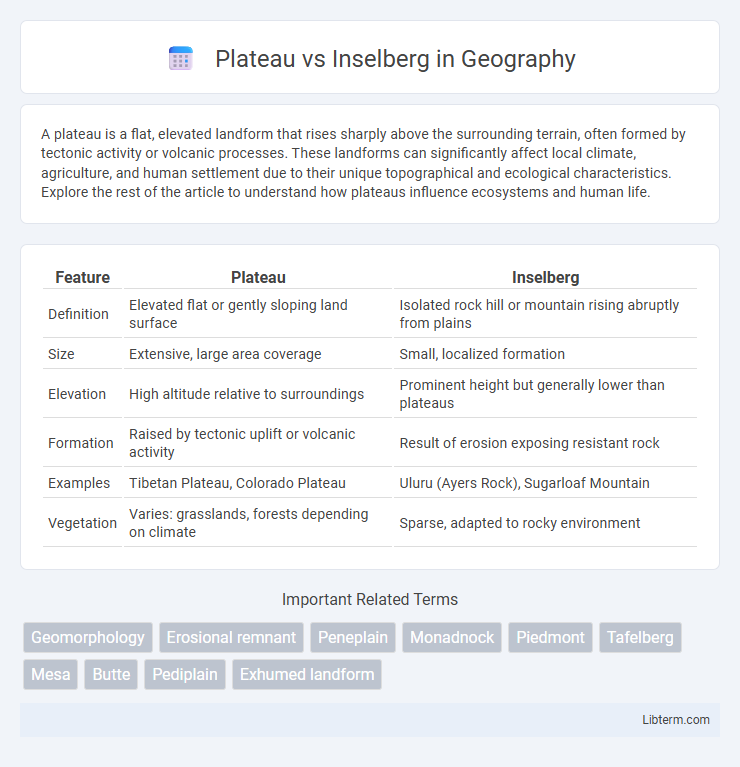
| Feature | Plateau | Inselberg |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated flat or gently sloping land surface | Isolated rock hill or mountain rising abruptly from plains |
| Size | Extensive, large area coverage | Small, localized formation |
| Elevation | High altitude relative to surroundings | Prominent height but generally lower than plateaus |
| Formation | Raised by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity | Result of erosion exposing resistant rock |
| Examples | Tibetan Plateau, Colorado Plateau | Uluru (Ayers Rock), Sugarloaf Mountain |
| Vegetation | Varies: grasslands, forests depending on climate | Sparse, adapted to rocky environment |
Definition of Plateau
A plateau is an elevated flatland that rises sharply above surrounding areas, often formed by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity. Unlike an inselberg, which is an isolated hill or mountain rising abruptly from a plain, a plateau covers a broad region with relatively level terrain. Plateaus are characterized by their extensive flat surfaces and significant elevation compared to adjacent landforms.
Definition of Inselberg
An inselberg is a prominent isolated hill or mountain that rises abruptly from a gently sloping or virtually level surrounding plain, typically composed of hard, erosion-resistant rock. Unlike plateaus, which are extensive flat-topped highlands with broad, elevated surfaces, inselbergs are singular landforms formed through long-term weathering and erosion processes. Inselbergs often indicate ancient landscapes where softer surrounding rocks have eroded away, leaving the harder rock standing prominently above the terrain.
Geological Formation of Plateaus
Plateaus are extensive, elevated flatlands formed through processes such as tectonic uplift, volcanic activity, or erosion-resistant rock layers that withstand weathering. Inselbergs, by contrast, are isolated hills or mountains rising abruptly from plains, typically shaped by long-term erosion surrounding harder rock masses. Understanding plateau formation involves studying geological factors like crustal movements, sediment deposition, and volcanic layering that create vast elevated surfaces.
Geological Formation of Inselbergs
Inselbergs are isolated rock hills or mountains that rise abruptly from relatively flat surrounding plains, formed primarily through long-term weathering and erosion processes that leave resistant rock masses exposed. These geological formations often consist of hard igneous or metamorphic rocks that withstand surface erosion better than the surrounding softer materials, resulting in prominent features. Unlike plateaus, which are extensive elevated flatlands shaped by tectonic uplift or volcanic activity, inselbergs represent remnants of ancient landscapes sculpted by differential erosion.
Key Differences Between Plateau and Inselberg
A plateau is an extensive flat-topped elevated landform that covers a large area, characterized by relatively level surfaces rising sharply above the surrounding terrain. In contrast, an inselberg is an isolated hill or mountain rising abruptly from a plain, typically formed from resistant rock that withstands erosion. Key differences include size, with plateaus spanning vast regions and inselbergs being solitary features, and formation processes, where plateaus result from uplift or volcanic activity and inselbergs emerge due to differential weathering and erosion.
Examples of Famous Plateaus
The Deccan Plateau in India, the Colorado Plateau in the United States, and the Tibetan Plateau in Asia are prominent examples of famous plateaus known for their extensive elevated flat terrains. Unlike inselbergs, which are isolated rock hills or mountains rising abruptly from a plain, plateaus cover large areas and are characterized by broad, elevated surfaces. The plateaus often serve as critical ecological zones and influence regional climate patterns.
Examples of Famous Inselbergs
Famous inselbergs include Uluru in Australia, known for its massive sandstone monolith rising abruptly from the surrounding plain, and Sugarloaf Mountain in Brazil, a granite peak standing prominently by the Rio de Janeiro coastline. Other notable inselbergs are Matobo Hills in Zimbabwe, featuring distinctive granite formations, and Ayers Rock, also in Australia, a culturally significant and geologically unique inselberg. These isolated hills contrast sharply with plateaus, which are extensive, elevated flatlands rather than solitary rock formations.
Ecological Significance
Plateaus provide extensive habitats supporting diverse ecosystems due to their large, flat surfaces and varying elevations, which influence microclimates and vegetation patterns. Inselbergs, isolated rock formations rising abruptly from plains, create unique ecological niches harboring specialized flora and fauna adapted to harsh, rocky environments. Both landforms contribute to biodiversity conservation by offering refuge and promoting species endemism in otherwise uniform landscapes.
Human Activities and Uses
Plateaus, with their extensive flat surfaces, support agriculture, urban development, and mining activities due to fertile soils and accessible land. Inselbergs, isolated rock formations, limit agricultural use but often serve as landmarks, provide mineral resources, and attract tourism or cultural significance for indigenous communities. Both landforms influence settlement patterns and resource management based on their unique topographies and ecosystems.
Conclusion: Plateau vs Inselberg
Plateaus are extensive, elevated flatlands formed by geological uplift or lava accumulation, while inselbergs are isolated rock hills rising abruptly from flat plains, shaped primarily by erosion. The key difference lies in scale and formation: plateaus cover vast areas and maintain broad flat surfaces, whereas inselbergs are singular, prominent features with steep sides. Understanding these distinctions aids in geological mapping and landscape interpretation for environmental and land-use planning.
Plateau Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com