Accretion is a fundamental process in astrophysics where particles gradually accumulate to form larger bodies, such as planets or stars. This natural growth mechanism plays a crucial role in shaping the structure of galaxies and planetary systems. Discover how understanding accretion can reveal more about the origins of celestial bodies in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
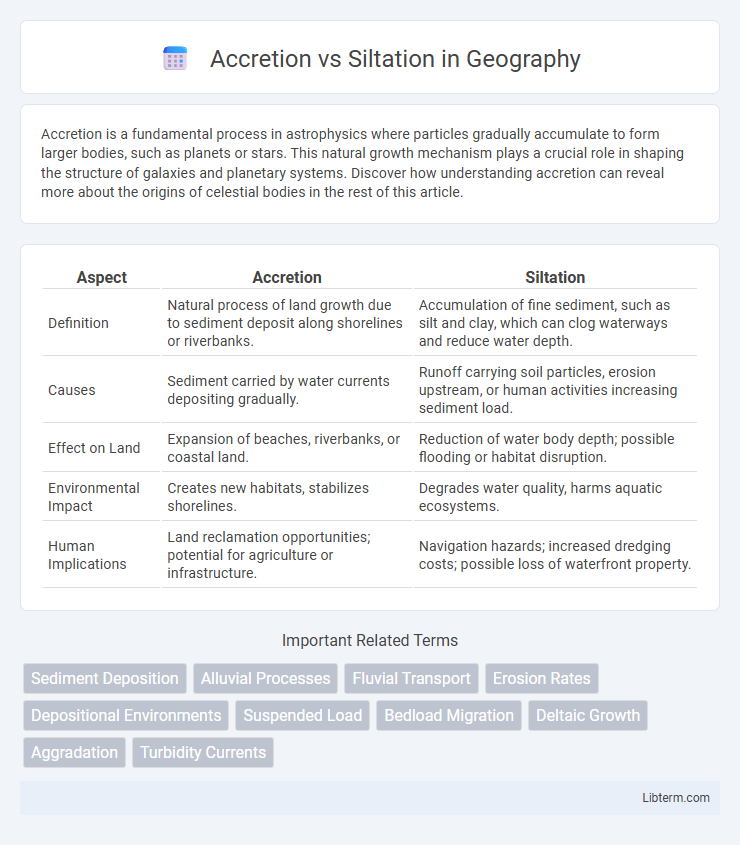
| Aspect | Accretion | Siltation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Natural process of land growth due to sediment deposit along shorelines or riverbanks. | Accumulation of fine sediment, such as silt and clay, which can clog waterways and reduce water depth. |
| Causes | Sediment carried by water currents depositing gradually. | Runoff carrying soil particles, erosion upstream, or human activities increasing sediment load. |
| Effect on Land | Expansion of beaches, riverbanks, or coastal land. | Reduction of water body depth; possible flooding or habitat disruption. |
| Environmental Impact | Creates new habitats, stabilizes shorelines. | Degrades water quality, harms aquatic ecosystems. |
| Human Implications | Land reclamation opportunities; potential for agriculture or infrastructure. | Navigation hazards; increased dredging costs; possible loss of waterfront property. |
Understanding Accretion and Siltation
Accretion is the gradual accumulation of sediment or soil along shorelines or riverbanks, resulting in land expansion, while siltation refers to the process where fine particles like silt and clay settle and accumulate, often causing sediment buildup in water bodies. Understanding accretion involves recognizing natural or human-induced sediment deposition that increases land area, whereas siltation typically leads to the reduction of water depth and can impact aquatic ecosystems. Both processes are crucial in coastal and riverine environments, affecting navigation, habitat formation, and land use planning.
Key Differences Between Accretion and Siltation
Accretion refers to the gradual accumulation of sediment or land deposits along a shoreline, often caused by natural processes such as wave action and tidal flow, resulting in land expansion. Siltation, however, involves the buildup of fine sediment particles like silt and clay in water bodies, leading to reduced water depth and potential ecological disruption. The key difference lies in accretion contributing to land growth, while siltation primarily causes sedimentation that may hinder aquatic environments.
Geological Processes Behind Accretion
Accretion is a geological process that involves the gradual accumulation of sediment, sand, and other materials along coastlines or riverbanks, leading to the expansion of landmass. This process takes place through natural actions such as wave deposition, tidal flows, and sediment transport by rivers, which deposit materials that solidify over time. In contrast, siltation refers to the excessive buildup of fine sediments in water bodies, often causing reduced water depth and navigation issues, without necessarily contributing to land formation.
Causes and Effects of Siltation
Siltation occurs due to the accumulation of fine sediment particles like silt and clay in water bodies, primarily caused by soil erosion from deforestation, agriculture, and construction activities. This leads to reduced water depth, impaired aquatic habitats, and decreased capacity of reservoirs and dams. The environmental impacts include disrupted fish breeding grounds, diminished water quality, and increased flood risk due to sediment buildup.
Accretion in Coastal and River Environments
Accretion in coastal and river environments refers to the gradual buildup of sediment, such as sand, gravel, or silt, deposited by water currents, which expands land areas and shorelines. This natural process enhances habitat formation, supports coastal ecosystems, and can counteract erosion impacts by strengthening shore stability. Sediment supply, wave energy, tidal patterns, and vegetation play critical roles in controlling accretion rates and patterns in these dynamic environments.
Environmental Impacts of Siltation
Siltation significantly degrades aquatic ecosystems by smothering fish habitats and reducing water quality, which disrupts feeding and breeding patterns. It accelerates eutrophication by increasing nutrient loads, leading to harmful algal blooms and oxygen depletion in water bodies. The accumulation of fine sediments also impairs aquatic vegetation growth, undermining the overall biodiversity and stability of freshwater and marine environments.
Benefits of Accretion to Ecosystems
Accretion enriches coastal and riverine ecosystems by gradually building up land masses, which provides critical habitats for diverse plant and animal species. This natural process enhances soil fertility, promoting vegetation growth and stabilizing shorelines against erosion. As a result, accretion supports biodiversity, improves water quality, and strengthens ecosystem resilience in the face of environmental changes.
Siltation Challenges in Waterways and Reservoirs
Siltation in waterways and reservoirs reduces water storage capacity and disrupts aquatic ecosystems by depositing fine sediment that alters natural flow patterns. This sediment build-up can lead to increased flood risks, hinder navigation, and impact water quality by elevating turbidity and nutrient loads. Effective management strategies, such as sediment dredging and watershed erosion control, are critical to mitigating the long-term challenges posed by siltation in these aquatic environments.
Human Activities Influencing Accretion and Siltation
Human activities significantly influence accretion and siltation by altering sediment supply and water flow patterns. Deforestation, urban construction, and agriculture increase soil erosion, thereby accelerating siltation in rivers and coastal areas. Conversely, dam construction and river channelization disrupt sediment transport, often reducing natural accretion processes critical for maintaining wetlands and shorelines.
Strategies for Managing Accretion and Siltation
Effective strategies for managing accretion and siltation include dredging to remove excess sediments and restore navigable waterways, alongside the implementation of sediment traps and retention basins to control sediment flow. Vegetative stabilization using native plants helps reduce soil erosion and promotes natural sediment deposition processes, enhancing shoreline stability. Regular monitoring through sediment surveys and hydrodynamic modeling supports adaptive management, ensuring timely interventions to minimize environmental and infrastructural impacts.
Accretion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com