An oxbow lake forms when a river creates a meander that becomes cut off from the main channel, resulting in a crescent-shaped body of water. This ecological feature provides unique habitats for diverse wildlife and plays a crucial role in flood management and water purification. Discover more about how oxbow lakes develop and their environmental significance in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
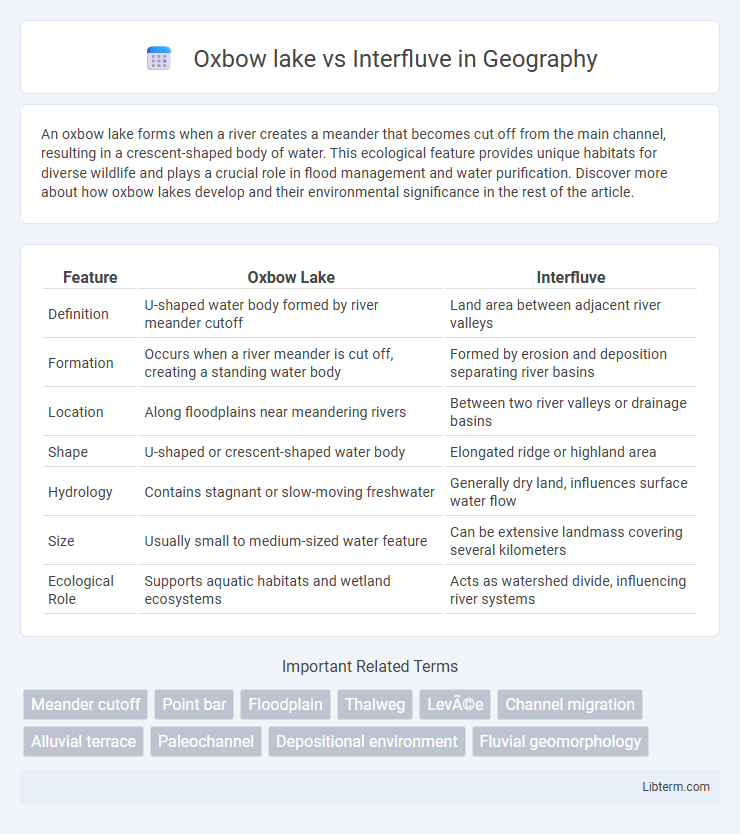
| Feature | Oxbow Lake | Interfluve |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | U-shaped water body formed by river meander cutoff | Land area between adjacent river valleys |
| Formation | Occurs when a river meander is cut off, creating a standing water body | Formed by erosion and deposition separating river basins |
| Location | Along floodplains near meandering rivers | Between two river valleys or drainage basins |
| Shape | U-shaped or crescent-shaped water body | Elongated ridge or highland area |
| Hydrology | Contains stagnant or slow-moving freshwater | Generally dry land, influences surface water flow |
| Size | Usually small to medium-sized water feature | Can be extensive landmass covering several kilometers |
| Ecological Role | Supports aquatic habitats and wetland ecosystems | Acts as watershed divide, influencing river systems |
Introduction to Oxbow Lakes and Interfluves
Oxbow lakes form through the natural process of river meander cutoff, creating crescent-shaped water bodies isolated from the main channel, commonly found in floodplains with dynamic fluvial activity. Interfluves are elevated land areas between adjacent river valleys, shaped primarily by erosion and sediment deposition, influencing watershed boundaries and drainage patterns. Both features characterize fluvial landscapes but represent different geomorphological processes and habitat types within river systems.
Formation Processes: Oxbow Lakes vs Interfluves
Oxbow lakes form through fluvial processes where meandering rivers create cutoffs, isolating a crescent-shaped water body from the main channel due to erosion and deposition of sediment. Interfluves develop as elevated landforms between adjacent river valleys, shaped primarily by long-term tectonic uplift, differential erosion, and sediment deposition, rather than direct fluvial activity. The key distinction lies in oxbow lakes being remnants of active river dynamics, while interfluves represent stable, erosion-resistant ridges delineating separate drainage basins.
Geographical Locations and Distribution
Oxbow lakes commonly form in meandering river valleys across floodplains in regions such as the Mississippi River Basin in the United States and the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta in South Asia. Interfluves, elevated landforms situated between adjacent river valleys, are prominently found in areas with dissected plateaus like the Brazilian Highlands and the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States. The distinct geographical distribution of oxbow lakes and interfluves reflects fluvial dynamics and topographic variations influencing landscape evolution globally.
Key Physical Characteristics
An oxbow lake is a crescent-shaped body of water formed when a river meander is cut off from the main channel, characterized by stagnant water and sediment deposition along its curved banks. An interfluve is a higher land area or ridge situated between adjacent river valleys, typically featuring well-drained soils and distinct topographical elevation relative to surrounding floodplains. Oxbow lakes represent former active fluvial environments, while interfluves function as geomorphological divides influencing watershed boundaries and drainage patterns.
Role in River Dynamics and Landforms
Oxbow lakes form as meandering rivers change course, creating crescent-shaped water bodies that indicate past river paths and contribute to sediment deposition and habitat diversity. Interfluves are elevated landforms between adjacent river valleys that influence drainage patterns, water flow distribution, and soil erosion dynamics in a watershed. Together, oxbow lakes and interfluves shape fluvial landscapes by regulating hydrological processes and promoting geomorphological evolution.
Ecological Importance and Biodiversity
Oxbow lakes provide unique aquatic habitats rich in biodiversity due to their still waters, supporting diverse fish, amphibians, and plant species adapted to calm environments. Interfluves, elevated lands between rivers, foster distinct terrestrial ecosystems with varied flora and fauna, often serving as refuges for species during floods. Both features contribute to regional ecological balance by maintaining habitat heterogeneity and promoting species diversity within riverine landscapes.
Human Impact and Land Use
Oxbow lakes often form in river floodplains where human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and dam construction alter natural water flow and sediment deposition, impacting aquatic ecosystems and local biodiversity. Interfluves, being elevated landforms between river valleys, are more frequently utilized for agriculture, settlements, and infrastructure due to their relative stability and reduced flood risk, though intensive land use can lead to soil degradation and habitat fragmentation. Human interventions in both oxbow lake and interfluve areas significantly influence hydrology, land use patterns, and ecological balance, requiring sustainable management practices to mitigate environmental impacts.
Comparison of Hydrological Functions
Oxbow lakes serve as natural water retention basins, capturing floodwaters and supporting groundwater recharge, whereas interfluves primarily function as elevated landforms directing surface runoff between river valleys. The hydrological role of oxbow lakes includes sediment trapping and habitat provision for aquatic species, contrasting with interfluves that influence drainage patterns and soil moisture distribution. Oxbow lakes contribute to flood mitigation through temporary water storage, while interfluves affect watershed connectivity by shaping the flow pathways of precipitation and subsurface water.
Environmental Challenges and Conservation
Oxbow lakes face environmental challenges such as sedimentation, nutrient loading, and habitat loss due to agricultural runoff and urban development. Interfluves encounter erosion and deforestation pressures that disrupt local hydrology and biodiversity, complicating conservation efforts. Effective management strategies for both landforms require integrated watershed protection, sustainable land use practices, and restoration projects to maintain ecological balance.
Summary: Distinguishing Oxbow Lakes from Interfluves
Oxbow lakes form as curved water bodies created when a river meander is cut off from the main channel, typically found in floodplains, while interfluves are elevated landforms situated between adjacent river valleys. Oxbow lakes represent residual aquatic features with distinct lentic ecosystems, whereas interfluves serve as drainage divides influencing watershed patterns. These differences highlight contrasting geomorphological processes: fluvial cutoff for oxbow lakes versus erosional remnants for interfluves.
Oxbow lake Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com