An isohyet is a line on a map that connects points of equal rainfall, providing crucial data for understanding precipitation patterns in a region. This information helps in agricultural planning, water resource management, and climate studies by illustrating rainfall distribution over specific areas. Explore the rest of the article to discover how isohyets influence environmental strategies and your local weather predictions.
Table of Comparison
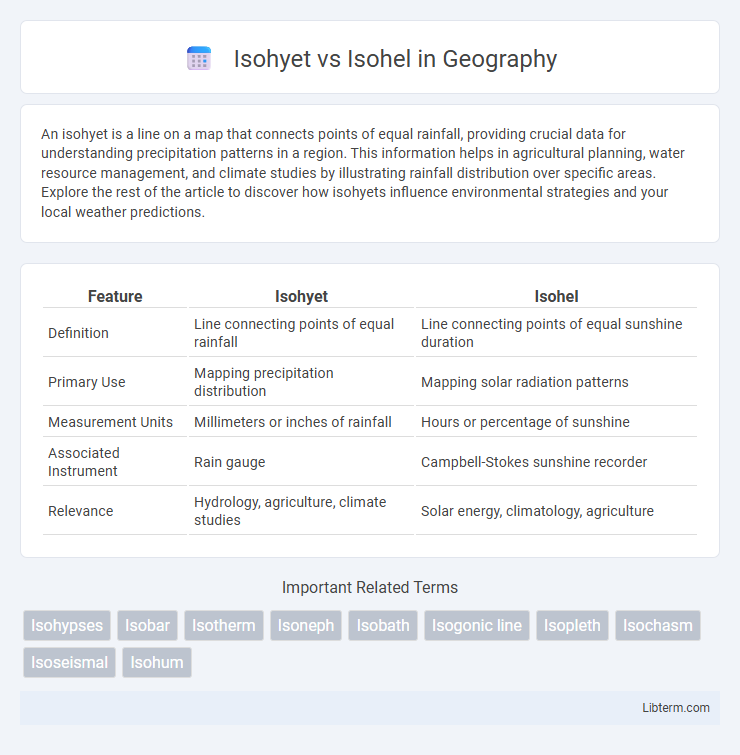
| Feature | Isohyet | Isohel |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Line connecting points of equal rainfall | Line connecting points of equal sunshine duration |
| Primary Use | Mapping precipitation distribution | Mapping solar radiation patterns |
| Measurement Units | Millimeters or inches of rainfall | Hours or percentage of sunshine |
| Associated Instrument | Rain gauge | Campbell-Stokes sunshine recorder |
| Relevance | Hydrology, agriculture, climate studies | Solar energy, climatology, agriculture |
Introduction to Contour Lines in Meteorology
Isohyets represent contour lines connecting points of equal precipitation, essential for analyzing rainfall distribution in meteorology, while Isohels link locations with identical sunlight durations, aiding solar radiation studies. Both contour lines facilitate spatial visualization of meteorological variables on weather maps, enabling accurate assessment of climatic patterns. Understanding Isohyets and Isohels enhances forecasting and environmental planning by illustrating moisture and sunlight variability across regions.
Understanding Isohyets: Definition and Purpose
Isohyets are lines on a map that connect points of equal precipitation, providing a clear visual representation of rainfall distribution across a region. These contours are crucial in hydrology and meteorology for analyzing precipitation patterns, aiding in water resource management, and forecasting agricultural productivity. Isohels, by contrast, connect points of equal sunlight duration, serving a different purpose in climate studies and solar energy assessment.
Exploring Isohels: Definition and Importance
Isohels are contour lines on maps that connect points of equal sunlight duration, making them crucial for climatology and solar energy studies. These lines help in identifying regions with similar solar exposure, which influences agriculture, urban planning, and renewable energy deployment. Understanding isophels provides insights into sunlight distribution patterns, enabling better environmental and economic decision-making.
Key Differences Between Isohyets and Isohels
Isohyets represent lines connecting points of equal rainfall, essential for hydrological and climatological studies, while Isohels link locations with identical sunshine duration, critical for solar energy and climate analysis. Isohyets primarily indicate precipitation distribution, influencing water resource management, whereas Isohels provide insights into solar exposure, guiding agriculture and energy planning. Both spatial data tools differ fundamentally in the meteorological variable they map: precipitation for Isohyets and sunshine hours for Isohels.
Methods of Drawing Isohyet and Isohel Maps
Isohyet maps are drawn by interpolating rainfall data from various meteorological stations using methods like the Thiessen polygon technique or the isohyetal method, which involves plotting points of equal precipitation and connecting them to form smooth curves. Isohel maps, on the other hand, are created by measuring solar radiation hours or sunshine duration and connecting points of equal sunlight intensity using data from pyranometers or sunshine recorders. Both map types rely on spatial data interpolation but differ in their data sources and measurement instruments to represent precipitation and solar radiation patterns respectively.
Applications of Isohyet Maps in Hydrology
Isohyet maps, delineating lines of equal rainfall, are essential in hydrology for analyzing precipitation distribution, calculating watershed runoff, and designing effective flood control systems. These maps help hydrologists determine rainfall intensity and patterns across a region, which aids in water resource management and irrigation planning. In contrast, isohel maps, which indicate equal sunshine duration, have limited direct application in hydrological studies compared to isohyets.
Uses of Isohel Maps in Climatology
Isohel maps, which depict the distribution of sunshine duration across regions, are crucial in climatology for assessing solar radiation patterns and their effects on local climates. These maps help in identifying areas with high or low sunlight exposure, aiding in agricultural planning, solar energy potential evaluation, and ecological studies. Isohel data supports climate modeling and forecasting by illustrating sunshine variability, which influences temperature and weather patterns.
Significance of Accurate Weather Data Collection
Isohyets illustrate precipitation distribution, while isohels map sunshine duration, both crucial for precise climate analysis. Accurate weather data collection ensures reliable isohyets and isohels, informing water resource management and solar energy planning. High-resolution meteorological data enhances the calibration of these maps, improving decision-making in agriculture and urban development.
Challenges in Interpreting Isohyet and Isohel Maps
Interpreting Isohyet maps is challenging due to variability in rainfall distribution and temporal changes, requiring accurate data collection and interpolation techniques to represent precipitation patterns reliably. Isohel maps, which depict solar radiation intensity, face difficulties from factors like cloud cover variability and terrain shading that complicate the estimation of sunlight exposure. Both map types demand careful consideration of geographic and climatic factors to avoid misrepresentation of environmental conditions in meteorological and climatological studies.
Conclusion: Isohyet and Isohel in Weather Analysis
Isohyets are contour lines connecting points of equal rainfall, essential for understanding precipitation distribution and hydrological studies. Isohels map regions of equal sunshine duration, providing critical data for solar radiation analysis and climate research. Combining isohyets and isohels enhances comprehensive weather analysis, supporting improved agricultural planning and renewable energy assessment.
Isohyet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com