Mountains shape the Earth's landscape with their towering peaks and diverse ecosystems, offering breathtaking views and unique wildlife habitats. These natural formations play a crucial role in climate regulation and water cycles, impacting both local and global environments. Explore the rest of the article to discover the fascinating geology, flora, and outdoor adventures that mountains provide for you.
Table of Comparison
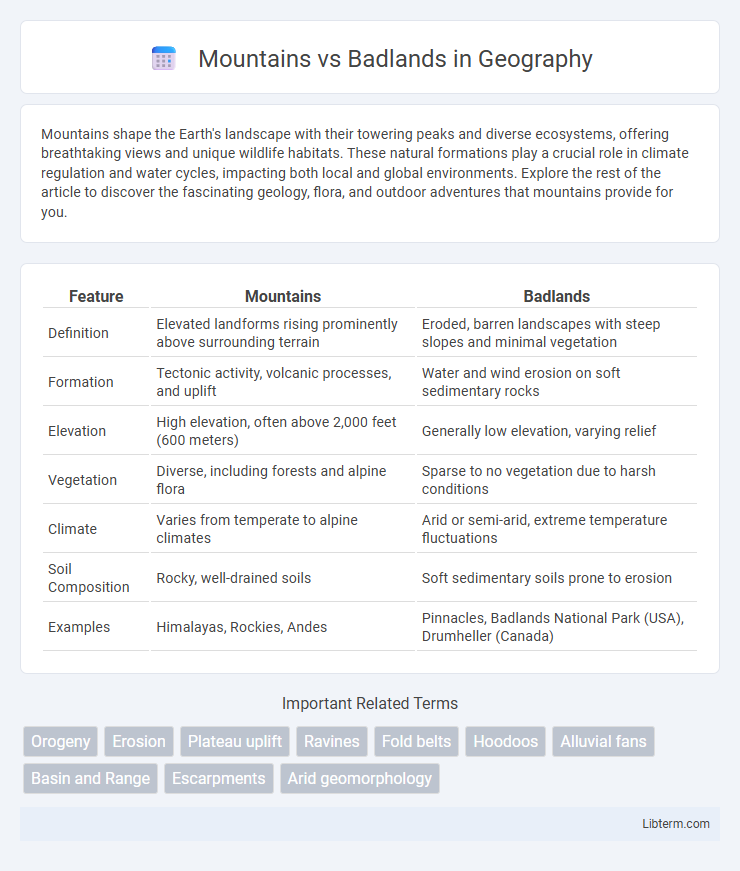
| Feature | Mountains | Badlands |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated landforms rising prominently above surrounding terrain | Eroded, barren landscapes with steep slopes and minimal vegetation |
| Formation | Tectonic activity, volcanic processes, and uplift | Water and wind erosion on soft sedimentary rocks |
| Elevation | High elevation, often above 2,000 feet (600 meters) | Generally low elevation, varying relief |
| Vegetation | Diverse, including forests and alpine flora | Sparse to no vegetation due to harsh conditions |
| Climate | Varies from temperate to alpine climates | Arid or semi-arid, extreme temperature fluctuations |
| Soil Composition | Rocky, well-drained soils | Soft sedimentary soils prone to erosion |
| Examples | Himalayas, Rockies, Andes | Pinnacles, Badlands National Park (USA), Drumheller (Canada) |
Introduction: Contrasting Mountains and Badlands
Mountains feature towering elevations with rugged terrain formed by tectonic forces, characterized by rich biodiversity and cooler climates. Badlands are eroded landscapes with steep slopes, sparse vegetation, and distinctive sedimentary layers, shaped primarily by water and wind erosion. These contrasting landforms illustrate diverse geological processes and ecosystems shaped by climate and topography.
Geological Formation and Origins
Mountains form through tectonic plate movements, including processes like folding, faulting, and volcanic activity, which create elevated landforms over millions of years. Badlands result from intense erosion of soft sedimentary rocks such as clay and shale, often in arid regions, leading to rugged terrain with steep slopes and minimal vegetation. While mountains primarily originate from internal geodynamic forces, badlands evolve through external weathering and erosional processes acting on deposited sediments.
Landscape Features: Peaks vs. Erosional Wonders
Mountains showcase towering peaks and rugged ridges formed by tectonic activity and volcanic processes, characterized by steep slopes and high elevations. In contrast, Badlands reveal intricate erosional wonders with deeply incised ravines, sharp spires, and layered sedimentary rock formations sculpted by water and wind over millennia. These landscapes provide starkly different visual textures: mountains inspire awe with their majestic heights, while badlands captivate through complex patterns of erosion and exposed geological strata.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Mountains experience cooler temperatures and higher precipitation due to elevation, often leading to snowfall in winter and frequent rainstorms during warmer months. Badlands, characterized by arid and semi-arid climates, have low annual rainfall and extreme temperature fluctuations between day and night. These contrasting climate conditions result in distinct erosion patterns, with mountains supporting diverse vegetation while badlands remain largely barren.
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Mountains support diverse ecosystems characterized by distinct altitudinal zones hosting endemic flora and fauna, benefiting from varied microclimates and rich soil profiles. Badlands exhibit harsh, arid conditions with sparse vegetation primarily consisting of drought-resistant shrubs and grasses, resulting in lower biodiversity but specialized species adapted to extreme erosion and nutrient-poor soils. The contrasting ecosystems highlight mountains as biodiversity hotspots with complex ecological niches, whereas badlands serve as unique habitats supporting resilient organisms in challenging environments.
Outdoor Activities and Adventure Opportunities
Mountains provide diverse outdoor activities like hiking, rock climbing, skiing, and mountain biking, catering to various skill levels and adventure seekers. Badlands offer unique experiences such as fossil hunting, off-road driving, and exploring rugged terrain with dramatic geological formations. Both landscapes attract nature enthusiasts and photographers seeking immersive adventure and spectacular views.
Cultural and Historical Significance
Mountains have long held profound cultural and historical significance as sacred sites, places of spiritual pilgrimage, and natural fortresses that shaped civilizations and mythologies worldwide. Badlands, characterized by their eroded, rugged landscapes, often preserve rich fossil records and ancient artifacts, serving as vital windows into prehistoric life and indigenous histories. Both terrains offer unique insights into human adaptation and cultural evolution through the ages.
Tourism Appeal and Accessibility
Mountains offer diverse tourism appeal with activities like hiking, skiing, and scenic viewpoints attracting adventure seekers and nature lovers. Badlands provide unique geological formations and fossil hunting experiences that draw tourists interested in paleontology and striking landscapes. Accessibility varies as mountainous regions often have developed infrastructure and mountain resorts, while badlands may require off-road vehicles and guided tours due to rugged terrain and limited facilities.
Conservation Challenges and Environmental Impact
Mountains face conservation challenges such as habitat fragmentation and climate change-induced species migration, which threaten biodiversity and water resources. Badlands experience severe soil erosion and limited vegetation cover, exacerbating land degradation and habitat loss. Both ecosystems require targeted land management strategies to mitigate environmental impacts and preserve unique geological and biological features.
Choosing Your Destination: Mountains or Badlands?
When choosing your destination between mountains and badlands, consider the terrain and activities you prefer: mountains offer hiking, skiing, and breathtaking alpine views, whereas badlands provide unique geological formations, fossil hunting, and stark, rugged landscapes. Weather conditions differ significantly, with mountains often experiencing cooler temperatures and more precipitation compared to the arid, sun-baked environment of badlands. Your choice depends on whether you seek outdoor adventure with elevation challenges or exploration of dramatic, eroded terrain rich in natural history.
Mountains Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com