Raster images are composed of pixels arranged in a grid, making them ideal for detailed and complex visuals like photographs. Their quality depends on resolution, so scaling up can lead to pixelation and loss of clarity. Explore the rest of the article to learn how raster images differ from vector graphics and when to use each type for your projects.
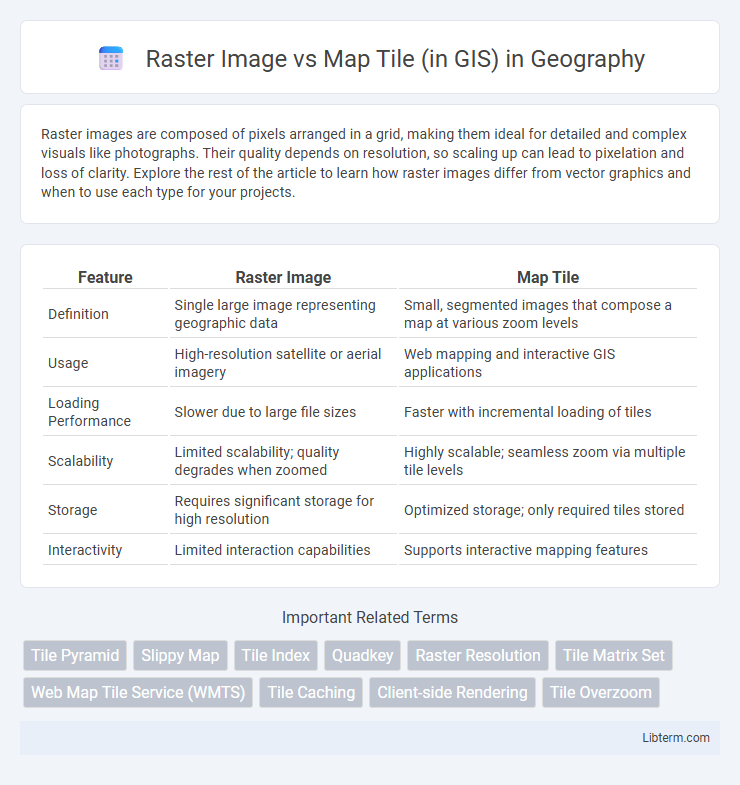
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Raster Image | Map Tile |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single large image representing geographic data | Small, segmented images that compose a map at various zoom levels |
| Usage | High-resolution satellite or aerial imagery | Web mapping and interactive GIS applications |
| Loading Performance | Slower due to large file sizes | Faster with incremental loading of tiles |
| Scalability | Limited scalability; quality degrades when zoomed | Highly scalable; seamless zoom via multiple tile levels |
| Storage | Requires significant storage for high resolution | Optimized storage; only required tiles stored |
| Interactivity | Limited interaction capabilities | Supports interactive mapping features |
Introduction to Raster Images and Map Tiles in GIS
Raster images in GIS are digital grids composed of pixels, each storing spatial information such as elevation or land cover, enabling detailed visual representation of geographic areas. Map tiles divide large raster datasets into smaller, standardized square segments, facilitating efficient loading, rendering, and interaction in web mapping applications. This tiling approach optimizes performance by allowing users to access only the necessary portions of extensive geospatial data without sacrificing resolution or spatial accuracy.
Understanding Raster Images: Definition and Characteristics
Raster images in GIS are digital pictures composed of a grid of pixels, each representing spatial data values such as temperature, elevation, or land cover. These images have fixed resolutions and display detailed continuous data, making them ideal for terrain models, satellite imagery, and aerial photographs. Unlike map tiles, which are pre-rendered segments used for efficient map navigation, raster images provide raw, high-resolution data crucial for spatial analysis and visualization.
What Are Map Tiles? Structure and Functionality
Map tiles are small, square images that collectively form a continuous map when displayed in GIS applications, enabling efficient loading and rendering of spatial data. Each tile represents a specific geographic area at a particular zoom level, structured in a grid system using coordinates or a quadtree hierarchy for easy indexing and retrieval. This modular approach optimizes performance by loading only visible tiles, supporting seamless zooming and panning across large-scale maps without overwhelming system resources.
Key Differences Between Raster Images and Map Tiles
Raster images in GIS are static, high-resolution files representing geographic data as pixel-based grids, typically used for detailed analysis and display. Map tiles are smaller, dynamically loaded segments of maps designed to improve performance and seamless navigation at multiple zoom levels, often sourced from tile servers. Unlike raster images, map tiles optimize web mapping by enabling scalable, responsive interaction with geographic information systems.
Storage and Data Management Comparison
Raster images in GIS are typically stored as large, continuous grid files, often requiring substantial storage space due to high resolution and uncompressed data formats. Map tiles segment raster data into smaller, fixed-size square images, enabling efficient storage, faster data retrieval, and improved scalability through tiled caching and on-demand loading. Data management for map tiles benefits from hierarchical indexing systems and support for various zoom levels, significantly optimizing performance compared to managing entire raster images as single files.
Performance and Scalability in GIS Applications
Raster images in GIS consist of pixel-based data that can become large and slow to process when zooming or panning, impacting performance negatively. Map tiles divide spatial data into smaller, pre-rendered segments, enabling faster loading times and smoother interaction by only fetching required tiles dynamically. This segmentation dramatically improves scalability by reducing server load and bandwidth usage in high-demand GIS applications.
Rendering and Visualization Techniques
Raster images in GIS are pixel-based representations that display continuous data, relying on techniques like resampling and color relief rendering to enhance visual clarity at various scales. Map tiles segment spatial data into manageable, pre-rendered square images that improve performance and enable efficient loading through dynamic tiling and caching methods. Rendering map tiles uses multi-resolution pyramids and vector tile layering to provide scalable, fast, and seamless visualization across different zoom levels.
Advantages and Limitations of Raster Images
Raster images in GIS provide high-resolution visual representations, capturing detailed continuous data such as elevation or aerial photography with pixel-based precision. They allow sophisticated spatial analysis like overlay and classification but require substantial storage and processing power due to large file sizes. Limitations include loss of quality when zooming and challenges in handling discrete spatial features compared to vector-based map tiles.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Map Tiles
Map tiles in GIS enhance user experience by enabling faster loading times and smooth navigation through tiled pre-rendered images, making large-scale maps highly responsive. They reduce server load by caching individual tiles but may suffer from limited flexibility when customizing styles or updating data, requiring regeneration of tiles for changes. Although map tiles optimize performance and scalability, they can increase storage demands due to the large number of generated tile images across multiple zoom levels.
Choosing Between Raster Images and Map Tiles for Your GIS Project
When choosing between raster images and map tiles for your GIS project, consider that raster images provide high-resolution, continuous data ideal for detailed analysis and visualization of satellite imagery or aerial photography. Map tiles, on the other hand, enable efficient, scalable web mapping by dividing geographic data into manageable, pre-rendered or dynamically generated sections, improving performance and user experience in interactive maps. Evaluate data size, application requirements, and responsiveness to determine whether static raster layers or tiled maps best suit your GIS workflow.
Raster Image Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com