A functional region is an area defined by a central point and the surrounding locations affected by it, such as a metropolitan area served by a major city. This region is organized around a focal hub and linked through transportation, communication, or economic activity. Discover how understanding functional regions can enhance your perspective on spatial relationships throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
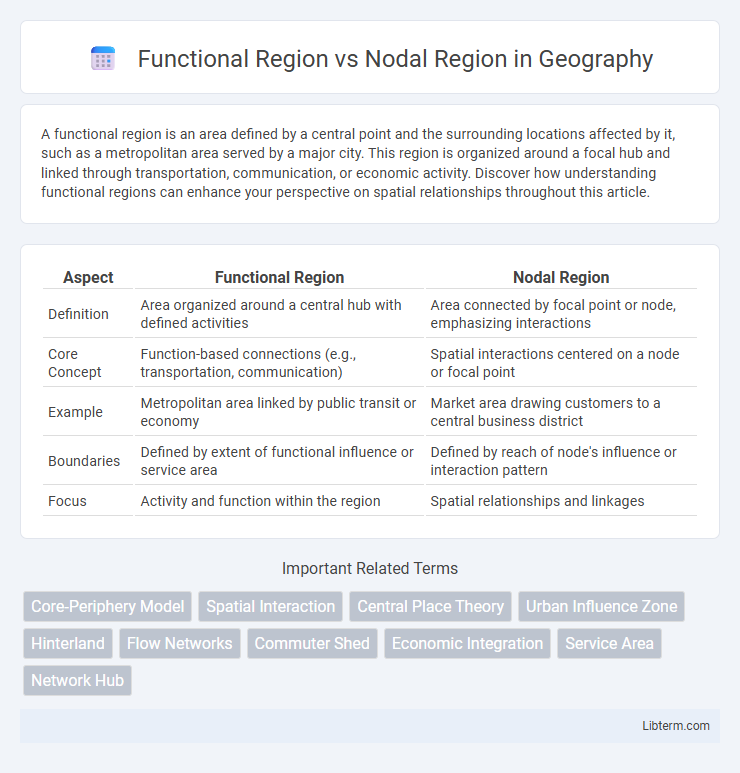
| Aspect | Functional Region | Nodal Region |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Area organized around a central hub with defined activities | Area connected by focal point or node, emphasizing interactions |
| Core Concept | Function-based connections (e.g., transportation, communication) | Spatial interactions centered on a node or focal point |
| Example | Metropolitan area linked by public transit or economy | Market area drawing customers to a central business district |
| Boundaries | Defined by extent of functional influence or service area | Defined by reach of node's influence or interaction pattern |
| Focus | Activity and function within the region | Spatial relationships and linkages |
Introduction to Functional and Nodal Regions
Functional regions are defined by a central node and the surrounding areas that are connected through various interactions such as communication, transportation, or economic activities. Nodal regions specifically emphasize the role of a focal point where functions are coordinated and services are concentrated, influencing the spatial organization around it. Both concepts highlight spatial relationships but differ in that functional regions focus on overall area connected by specific functions, while nodal regions center on the influence of a central node.
Defining Functional Regions
Functional regions are defined by specific activities or interactions that occur within a certain area, such as economic connections, transportation networks, or service provision. These regions are often centered around a key node, like a city or hub, which facilitates communication and movement, influencing the entire region's functionality. The boundaries of functional regions are dynamic, shaped by the flow of goods, services, and information rather than fixed political or physical features.
Characteristics of Functional Regions
Functional regions are defined by specific activities or purposes such as trade, communication, or transportation networks, which create a unified area organized around a central node. These regions exhibit strong spatial interactions within, where flows of goods, services, or information converge and circulate efficiently. Boundaries of functional regions are often fluid and depend on the extent of the activity or influence exerted by the central hub.
Defining Nodal Regions
Nodal regions are defined by the central focal point, or node, from which surrounding areas are organized based on functional connections such as economic activities, transportation, or communication networks. This central node drives interactions within the region, facilitating the flow of goods, services, or information to and from peripheral zones. Unlike functional regions that emphasize overall spatial activities, nodal regions specifically highlight the importance of a core hub that anchors regional relationships.
Characteristics of Nodal Regions
Nodal regions, also known as functional regions, are defined by a central focal point or node from which activities or interactions radiate, such as a metropolitan area centered around a city. These regions are characterized by the flow of goods, services, or information that connect the surrounding areas to the node, highlighting economic and social integration. Boundaries of nodal regions are often fluid and depend on the intensity of the interaction with the central node, reflecting dynamic spatial relationships.
Key Differences Between Functional and Nodal Regions
Functional regions are defined by a specific activity or function that occurs within them, often centered around a focal point such as a city or a service hub, exemplified by metropolitan areas with commuting patterns. Nodal regions, on the other hand, are characterized by the influence of a central node or focal point, with areas connected through social, economic, or communication ties, like the broadcast area of a radio station. The key difference lies in functional regions emphasizing collective activities and interactions, whereas nodal regions focus on spatial connections radiating from a core node.
Real-World Examples of Functional Regions
Functional regions are defined by specific interactions or connections, such as a metropolitan area with a central city and its surrounding suburbs connected through commuting or economic activities. The New York City metropolitan area exemplifies a functional region, where its transportation networks, media markets, and economic linkages unify diverse localities around a central urban hub. In contrast, nodal regions center around a focal point, often a single node like a TV station's broadcast reach or a trade area dominated by a shopping mall.
Real-World Examples of Nodal Regions
Nodal regions are defined around a central point or node where the surrounding areas are connected through various functions, such as communication or transportation networks. A classic example is the metropolitan area centered around New York City, where economic activities, media outlets, and transportation hubs like airports and subways radiate from the city core. Another example includes the broadcast region of a television station, where the signal coverage area revolves around a central transmitter, highlighting the functional ties between the node and its periphery.
Importance in Geography and Urban Planning
Functional regions, defined by economic activities or social interactions centered around a core node, are essential in urban planning for efficient infrastructure development and service delivery. Nodal regions, identified by the dominance of a specific central place or node, help geographers analyze spatial organization and human behavior patterns. Understanding these regions supports strategic urban growth, transportation networks, and resource management, optimizing regional connectivity and functional integration.
Conclusion: Functional Region vs Nodal Region
Functional regions are defined by specific activities or functions that occur within them, establishing a coherent area centered around a focal point or node. Nodal regions emphasize the importance of a central node, such as a city or transport hub, where spatial interactions and connections radiate outward. Distinguishing between functional and nodal regions aids in understanding spatial organization by highlighting either activity-based boundaries or node-centric influence.
Functional Region Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com