Mediterranean climate features hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, creating ideal conditions for diverse vegetation and agriculture such as olives and grapes. This climate type is commonly found in regions bordering the Mediterranean Sea, as well as in parts of California, Chile, South Africa, and Australia. Discover how Mediterranean climate influences ecosystems and human lifestyles by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
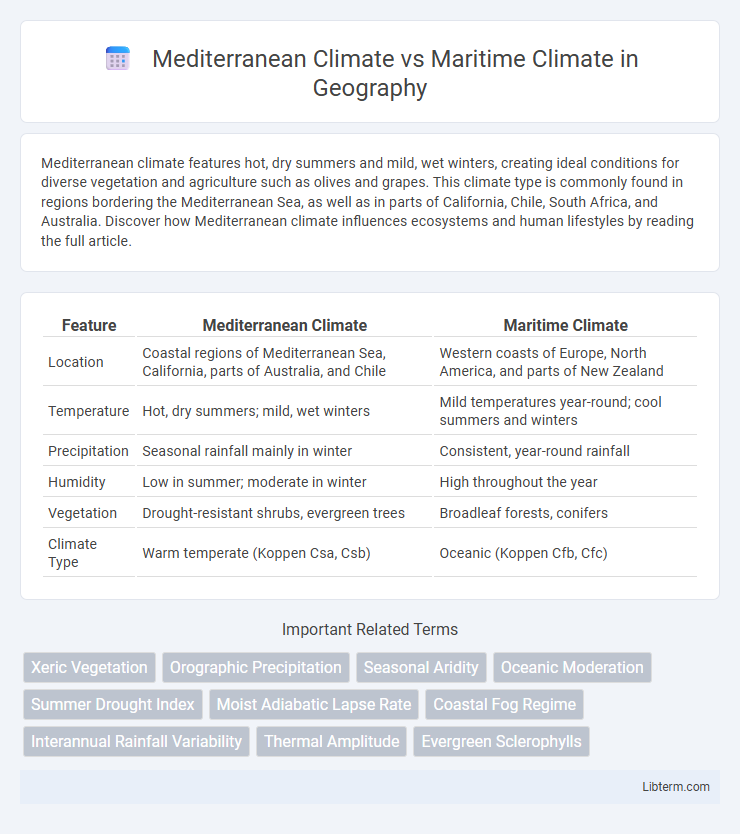
| Feature | Mediterranean Climate | Maritime Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Coastal regions of Mediterranean Sea, California, parts of Australia, and Chile | Western coasts of Europe, North America, and parts of New Zealand |
| Temperature | Hot, dry summers; mild, wet winters | Mild temperatures year-round; cool summers and winters |
| Precipitation | Seasonal rainfall mainly in winter | Consistent, year-round rainfall |
| Humidity | Low in summer; moderate in winter | High throughout the year |
| Vegetation | Drought-resistant shrubs, evergreen trees | Broadleaf forests, conifers |
| Climate Type | Warm temperate (Koppen Csa, Csb) | Oceanic (Koppen Cfb, Cfc) |
Defining Mediterranean and Maritime Climates
Mediterranean climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, typically found in regions bordering the Mediterranean Sea, parts of California, and South Australia. Maritime climate features moderate temperatures with high humidity and frequent precipitation throughout the year, common in coastal areas influenced by oceanic air masses like Western Europe and the Pacific Northwest. The defining difference lies in seasonal precipitation patterns, where Mediterranean climates experience a distinct dry summer season, unlike the consistently moist maritime climates.
Geographical Distribution and Examples
Mediterranean climate is predominantly found along the western coasts of continents between 30deg and 45deg latitude, characterized by wet winters and dry summers, with examples including coastal California, the Mediterranean Basin, and parts of southwestern Australia. Maritime climate occurs mainly on the western coasts of continents in mid-latitudes, with mild, wet winters and cool summers influenced by proximity to large oceans, as seen in regions like the Pacific Northwest of the United States, western Europe, and New Zealand. The key geographical distinction is that Mediterranean climates experience a pronounced dry season, while maritime climates maintain more consistent precipitation year-round.
Key Temperature Differences
Mediterranean climates experience hot, dry summers with average temperatures ranging from 25degC to 30degC, and mild, wet winters with temperatures rarely dropping below 10degC. Maritime climates feature mild summers and cool winters, with temperature ranges typically between 10degC and 20degC year-round due to the moderating influence of nearby oceans. The key temperature difference lies in the pronounced summer heat of Mediterranean climates versus the consistently moderate temperatures of maritime climates.
Seasonal Rainfall Patterns
Mediterranean climate features wet winters and dry summers due to the shift of the polar front and subtropical highs, resulting in most rainfall occurring between October and April. Maritime climate exhibits more evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year, influenced by proximity to large oceans that moderate temperatures and atmospheric moisture levels. Seasonal rainfall patterns in Mediterranean regions show a pronounced dry season contrasted with the consistent precipitation found in maritime climates.
Influence of Ocean Currents
Mediterranean climates are primarily influenced by warm ocean currents such as the Atlantic's Canary Current, which moderates temperatures and contributes to dry summers and mild, wet winters. Maritime climates are shaped by cooler, persistent ocean currents like the North Atlantic Drift, promoting consistent rainfall and moderate temperature fluctuations year-round. Ocean currents directly influence humidity levels and seasonal weather patterns, defining the unique characteristics of both Mediterranean and maritime climates.
Typical Vegetation and Biodiversity
Mediterranean climate regions support drought-resistant vegetation such as evergreen shrubs, olive trees, and aromatic herbs, with biodiversity adapted to hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Maritime climates foster lush, temperate rainforests and broadleaf deciduous forests, with abundant moisture promoting diverse plant species like ferns, mosses, and conifers. The contrast in precipitation patterns influences the distinct ecosystems, where Mediterranean biodiversity includes fire-adapted species, while maritime zones sustain high biodiversity with year-round moisture availability.
Impact on Agriculture and Crops
Mediterranean climates, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, support the cultivation of drought-resistant crops such as olives, grapes, and citrus fruits, making these regions ideal for viticulture and orchard farming. Maritime climates, with their mild temperatures and consistent precipitation throughout the year, favor the growth of cool-weather crops like potatoes, barley, and leafy vegetables, enhancing soil moisture retention and reducing irrigation needs. Differences in seasonal rainfall distribution and temperature stability between these climates directly influence crop selection, yield quality, and agricultural practices.
Weather Extremes and Climate Variability
Mediterranean climate zones experience hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters with rare but intense weather extremes such as droughts and heatwaves, often influenced by shifting high-pressure systems. Maritime climates, characterized by mild temperatures year-round and consistent precipitation, face fewer temperature extremes but show higher variability in storm frequency and precipitation intensity due to the proximity to large water bodies. Climate variability in Mediterranean regions is marked by seasonal drought severity, while maritime climates display more stable thermal ranges but fluctuating storm-driven rainfall patterns.
Effects on Local Lifestyle and Culture
Mediterranean climate, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, influences local lifestyle through outdoor activities, agriculture focused on olives, grapes, and citrus fruits, and cultural traditions centered around seasonal harvest festivals. Maritime climate, with its mild temperatures year-round and frequent rainfall, supports a lifestyle adapted to variable weather, promoting industries like fishing and forestry, and fostering cultural practices that emphasize indoor communal gatherings and resilient architectural designs. These climatic differences shape regional diets, social behaviors, and economic activities, creating distinct cultural identities linked to their environmental conditions.
Climate Change: Future Outlook for Both Climates
Mediterranean climates, characterized by hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, face increasing risks from prolonged droughts, heatwaves, and reduced precipitation due to climate change. Maritime climates, with mild temperatures and consistent rainfall, are projected to experience more intense storms and rising sea levels, threatening coastal ecosystems and infrastructure. Both climates demand adaptive strategies centered on water resource management and habitat resilience to mitigate the impacts of shifting weather patterns and extreme events.
Mediterranean Climate Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com