Plain language enhances clarity, making your message easy to understand and accessible to a broader audience. It reduces misunderstandings and improves engagement by using straightforward vocabulary and simple sentence structures. Discover how adopting plain language can transform your communication by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
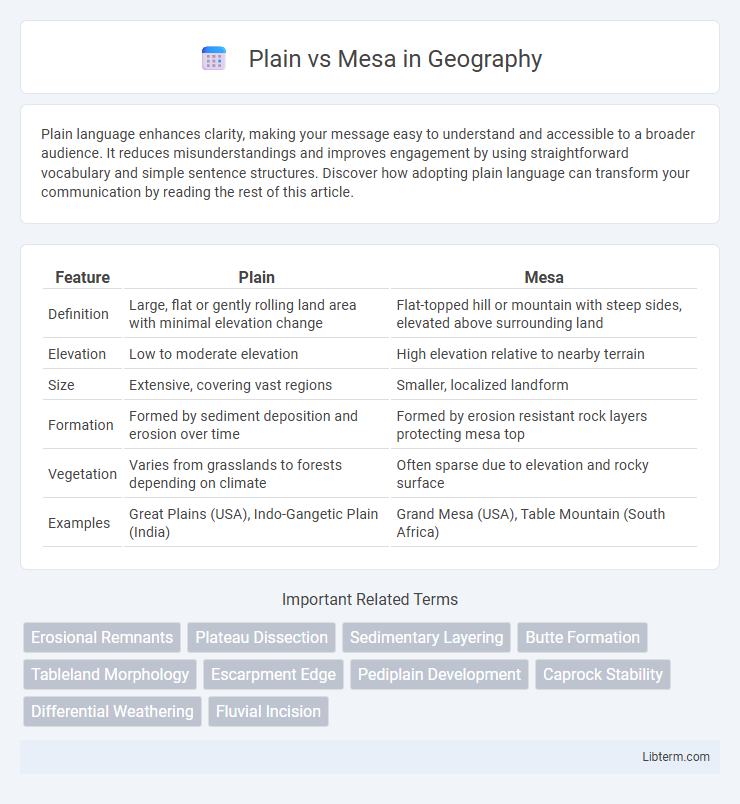
| Feature | Plain | Mesa |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, flat or gently rolling land area with minimal elevation change | Flat-topped hill or mountain with steep sides, elevated above surrounding land |
| Elevation | Low to moderate elevation | High elevation relative to nearby terrain |
| Size | Extensive, covering vast regions | Smaller, localized landform |
| Formation | Formed by sediment deposition and erosion over time | Formed by erosion resistant rock layers protecting mesa top |
| Vegetation | Varies from grasslands to forests depending on climate | Often sparse due to elevation and rocky surface |
| Examples | Great Plains (USA), Indo-Gangetic Plain (India) | Grand Mesa (USA), Table Mountain (South Africa) |
Introduction to Plains and Mesas
Plains are expansive, flat, or gently rolling areas of land with low elevation, often formed by sediment deposition over long periods, making them ideal for agriculture and settlements. Mesas are elevated landforms with steep, often vertical sides and a flat top, created by erosion resistant rock layers protecting softer layers beneath. These contrasting features highlight the geological processes shaping Earth's surface and influence regional ecosystems and human activities.
Defining Plains: Key Characteristics
Plains are expansive, flat or gently undulating landforms characterized by minimal elevation changes and fertile soil, often supporting diverse vegetation and agriculture. They typically exhibit consistent topography with few natural obstacles, making them ideal for farming, settlement, and transportation. Key characteristics include low relief, broad open spaces, and significant deposits of sedimentary materials from rivers or glacial activity.
What is a Mesa? Mesa Features Explained
A mesa is a flat-topped landform with steep, often vertical sides, formed through erosion processes that isolate a plateau-like structure in arid or semi-arid environments. These geological features are characterized by their distinct horizontal layers of rock, resistant caprock that protects softer underlying layers, and a broad, flat summit. Mesas serve as key indicators of regional erosion patterns and contribute to diverse habitats due to their unique elevation and isolation.
Formation Processes: Plains vs Mesas
Plains form through extensive sediment deposition, often from rivers and wind, creating broad, flat land surfaces with minimal elevation changes. Mesas develop from erosional processes, where harder rock layers resist weathering while surrounding softer materials erode away, resulting in isolated, flat-topped hills with steep sides. The key difference lies in plains being accumulative landforms, whereas mesas are primarily erosional remnants.
Geographic Distribution and Major Examples
Plains are extensive flatlands primarily found in regions like the Great Plains of North America, the Indo-Gangetic Plain in South Asia, and the Pampas of South America, characterized by fertile soil and gradual elevation changes. Mesas, on the other hand, are isolated, flat-topped hills with steep sides, common in arid areas such as the Colorado Plateau in the southwestern United States and parts of northern Africa. Key examples include the Llano Estacado plain in Texas and New Mexico versus famous mesas like Utah's Monument Valley.
Ecological Differences Between Plains and Mesas
Plains exhibit extensive, flat grasslands supporting diverse herbaceous plants and large grazing mammals, benefiting from rich soil and abundant water availability. Mesas, characterized by their elevated, flat-topped formations with steep sides, host xerophytic vegetation adapted to arid conditions and limited soil depth. The ecological divergence arises from variations in altitude, soil composition, and moisture retention, influencing species diversity and habitat structures uniquely in each landform.
Human Settlements: Life on Plains vs Mesas
Human settlements on plains benefit from expansive flat terrain, facilitating agriculture, infrastructure development, and transportation networks. In contrast, mesas offer natural defensive advantages and often support smaller, isolated communities due to limited space and access challenges. Plains settlements typically experience easier resource distribution, while mesa inhabitants adapt to steeper landscapes, influencing architectural styles and social organization.
Economic Importance of Plains and Mesas
Plains are vital for agriculture due to their fertile soil and flat terrain, supporting extensive crop cultivation and livestock farming, which drive regional economies. Mesas, while less suitable for farming, contribute economically through mineral extraction, tourism, and grazing activities on their plateau surfaces. These distinct landforms shape economic activities, with plains predominantly enhancing food production and mesas providing resources and recreational opportunities.
Unique Flora and Fauna: Comparing Ecosystems
Plains ecosystems feature vast grasslands that support herbivores like bison and predators such as coyotes, alongside unique plants like buffalo grass and wildflowers adapted to open, windy environments. Mesa environments, characterized by elevated flat-topped hills with steep cliffs, harbor specialized desert flora such as sagebrush and cacti, and fauna including rock squirrels, raptors, and reptiles adapted to arid, rocky conditions. The contrasting vegetation and animal life in plains versus mesas demonstrate distinct adaptations to differing soil, climate, and elevation factors, influencing biodiversity and ecological interactions.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Plain and Mesa Terrains
When choosing between plain and mesa terrains, consider the intended use and environmental factors; plains offer extensive arable land and ease of construction due to flat surfaces, while mesas provide natural defense advantages and unique ecological habitats with elevated landforms. Agricultural productivity thrives on plains due to fertile soil and water accessibility, whereas mesas are more suitable for conservation and tourism activities owing to their scenic cliffs and biodiversity. Evaluate factors like soil quality, climate, and infrastructure needs to make an informed decision tailored to specific project goals.
Plain Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com