State Farm offers comprehensive insurance solutions designed to protect your home, auto, and life with personalized coverage options. Their reliable customer service and extensive agent network ensure you receive tailored support when it matters most. Discover how State Farm can safeguard your future by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
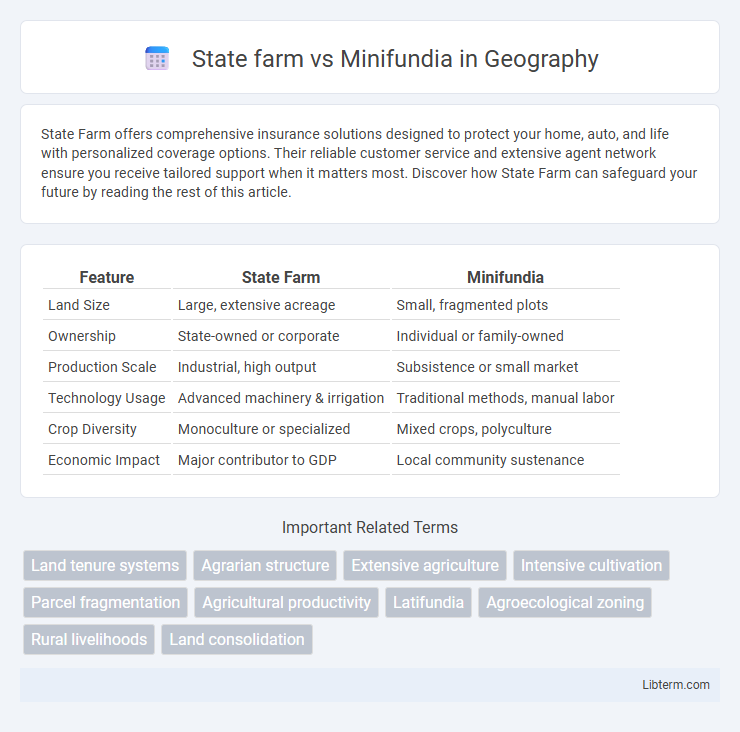
| Feature | State Farm | Minifundia |
|---|---|---|
| Land Size | Large, extensive acreage | Small, fragmented plots |
| Ownership | State-owned or corporate | Individual or family-owned |
| Production Scale | Industrial, high output | Subsistence or small market |
| Technology Usage | Advanced machinery & irrigation | Traditional methods, manual labor |
| Crop Diversity | Monoculture or specialized | Mixed crops, polyculture |
| Economic Impact | Major contributor to GDP | Local community sustenance |
Overview of State Farms and Minifundia
State Farm, the largest auto insurer in the United States, offers comprehensive coverage with a strong emphasis on customer service and extensive agent networks. Minifundia specializes in micro-investments, allowing small-scale investors to diversify portfolios by purchasing fractional real estate or agricultural assets online. While State Farm focuses on insurance solutions, Minifundia provides innovative crowdfunding options for asset diversification.
Historical Background and Development
State Farm, founded in 1922 by George J. Mecherle, initially aimed to provide affordable auto insurance tailored for farmers. Minifundia, emerging in the 21st century, is a fintech platform designed to democratize investment by allowing small-scale investors to participate in real estate crowdfunding. The development of State Farm reflects a century-long evolution into a leading insurance provider, while Minifundia represents the modern shift towards digital financial services and inclusive investment opportunities.
Key Differences in Land Ownership
State Farm land ownership typically involves large-scale, corporate-held agricultural properties with centralized management and standardized operational practices. Minifundia refers to small, family-owned parcels of land, often fragmentary and managed through traditional methods that emphasize subsistence farming and local community ties. The key difference lies in the scale and ownership structure, where State Farm represents extensive agribusiness operations, while Minifundia embodies smallholder farming characterized by limited land resources and individualized stewardship.
Economic Impact Comparison
State Farm, as a major insurance provider, significantly influences the economy through extensive employment, premium revenues exceeding $80 billion annually, and investments in infrastructure and community development. Minifundia, operating on a smaller scale, primarily impacts local economies by supporting smallholder farmers, promoting sustainable agricultural practices, and enhancing rural employment opportunities. The economic footprint of State Farm shapes broader market dynamics and financial security, while Minifundia's localized focus drives grassroots economic growth and food security in underserved regions.
Agricultural Productivity
State Farm's investment in agricultural technology and infrastructure significantly enhances productivity through advanced crop management systems and sustainable practices. In contrast, Minifundia prioritizes small-scale, community-based farming models that improve yields by leveraging local knowledge and diversified crop cultivation. These differing approaches highlight how large-scale corporate strategies and grassroots initiatives uniquely contribute to agricultural productivity improvements.
Social and Cultural Implications
The State Farm vs Minifundia debate highlights significant social and cultural implications, as State Farm represents large-scale, institutional agriculture often linked to corporate influence and monoculture practices, while Minifundia embodies small-scale, traditional farming deeply rooted in local customs and community identity. This contrast underscores tensions between modernization and preservation of cultural heritage, affecting rural livelihoods and social structures. The shift towards industrial farming seen in State Farm models risks marginalizing indigenous knowledge and disrupting social cohesion within farming communities reliant on Minifundia systems.
Environmental Sustainability
State Farm emphasizes environmental sustainability by integrating eco-friendly practices into its insurance operations, including investing in renewable energy projects and promoting green building standards. Minifundia prioritizes sustainable agriculture by supporting small-scale farmers who implement organic farming and soil conservation techniques to reduce environmental impact. Both organizations contribute to environmental sustainability through distinct approaches: State Farm through corporate responsibility initiatives and Minifundia by fostering sustainable land use and biodiversity.
Government Policies and Support
State Farm's operations benefit significantly from robust government policies, including stringent insurance regulations and comprehensive consumer protection laws that foster trust and stability in the market. Conversely, Minifundia leverages targeted government support programs aimed at promoting microinsurance and financial inclusion, enhancing access to coverage for underserved populations. Both entities capitalize on distinct regulatory frameworks and policy initiatives that shape their strategic approaches and market penetration in the insurance sector.
Challenges Facing State Farms and Minifundia
State Farms face challenges such as regulatory compliance, market competition, and the need for technological upgrades to improve efficiency and customer service. Minifundia struggles with limited resources, fragmented land ownership, and vulnerability to climate change, which hinder productivity and economic growth. Both entities must adapt to evolving environmental and economic pressures to sustain their operations effectively.
Future Trends and Prospects
State Farm, leading in insurance with robust technological integration, is poised to expand AI-driven risk assessment and personalized policy offerings. Minifundia leverages blockchain for real estate investments, anticipating growth through increased adoption of tokenized assets and decentralized finance solutions. Both entities are likely to benefit from digital transformation trends, with State Farm focusing on data analytics and Minifundia on enhancing transparency and liquidity in asset management.
State farm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com