Satellite imagery analysis enables precise monitoring of environmental changes, urban development, and disaster management through detailed data captured from space. Advanced algorithms interpret these images to provide actionable insights for agriculture, forestry, and security applications. Explore the rest of the article to discover how satellite imagery can enhance your data-driven decisions.
Table of Comparison
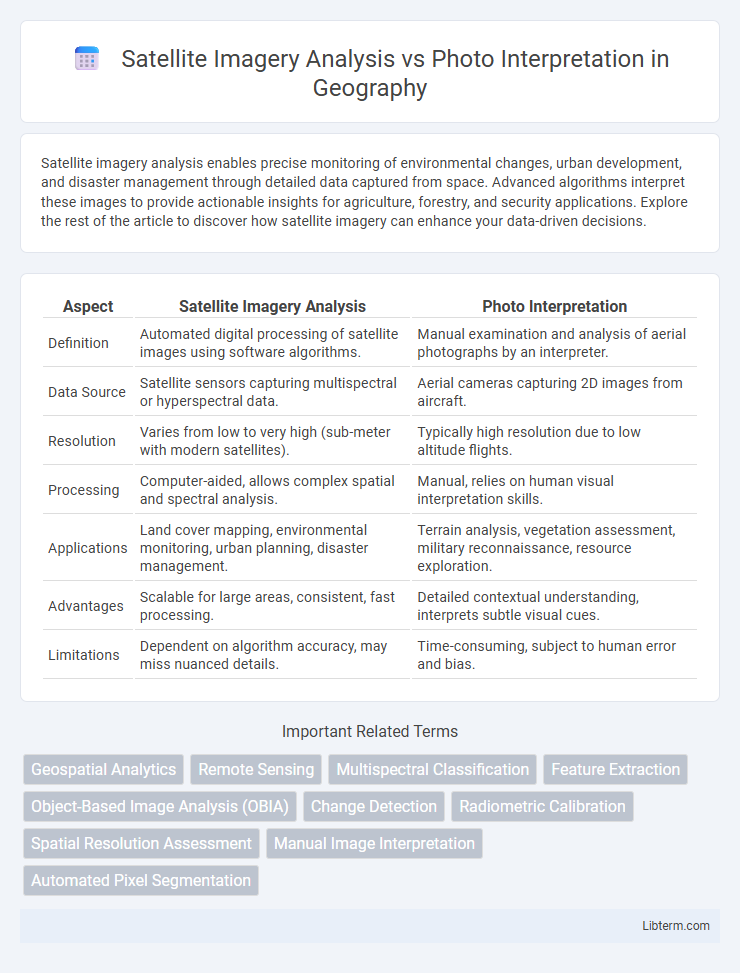
| Aspect | Satellite Imagery Analysis | Photo Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated digital processing of satellite images using software algorithms. | Manual examination and analysis of aerial photographs by an interpreter. |
| Data Source | Satellite sensors capturing multispectral or hyperspectral data. | Aerial cameras capturing 2D images from aircraft. |
| Resolution | Varies from low to very high (sub-meter with modern satellites). | Typically high resolution due to low altitude flights. |
| Processing | Computer-aided, allows complex spatial and spectral analysis. | Manual, relies on human visual interpretation skills. |
| Applications | Land cover mapping, environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster management. | Terrain analysis, vegetation assessment, military reconnaissance, resource exploration. |
| Advantages | Scalable for large areas, consistent, fast processing. | Detailed contextual understanding, interprets subtle visual cues. |
| Limitations | Dependent on algorithm accuracy, may miss nuanced details. | Time-consuming, subject to human error and bias. |
Introduction to Satellite Imagery Analysis and Photo Interpretation
Satellite imagery analysis involves processing and analyzing data collected by satellites to extract meaningful information about Earth's surface, such as land use, vegetation health, and urban development patterns. Photo interpretation is the traditional method of visually examining aerial photographs or satellite images to identify features and assess environmental conditions based on shape, texture, tone, and shadow. Advanced satellite imagery analysis incorporates digital techniques like image classification and change detection, enhancing accuracy beyond manual photo interpretation.
Defining Satellite Imagery Analysis
Satellite imagery analysis involves extracting meaningful information from geospatial data captured by satellites using advanced algorithms, machine learning, and automated processing techniques. This analysis focuses on interpreting multispectral, hyperspectral, and radar data to monitor environmental changes, urban development, and natural disasters with high precision. Unlike traditional photo interpretation, satellite imagery analysis leverages computational tools to enhance accuracy, scalability, and quantitative assessment of spatial phenomena.
Understanding Photo Interpretation
Photo interpretation involves the systematic examination of aerial photographs or satellite images to identify objects, patterns, and relationships on the Earth's surface. Understanding photo interpretation requires knowledge of image characteristics such as tone, texture, shape, size, and shadow, which help analysts differentiate features like vegetation, water bodies, and urban areas. Mastery in interpreting these visual cues is essential for applications in environmental monitoring, land use planning, and disaster management.
Key Differences Between Satellite Analysis and Photo Interpretation
Satellite imagery analysis leverages multispectral and hyperspectral data to extract detailed environmental and geographical information, enabling automated change detection and large-scale monitoring. Photo interpretation primarily relies on visual analysis of aerial photographs, focusing on identifying surface features through shape, tone, texture, and pattern recognition by human experts. The key difference lies in satellite analysis's capacity for multi-layered data integration and algorithmic processing, whereas photo interpretation depends on manual examination and limited spectral information.
Technological Tools Involved in Both Methods
Satellite imagery analysis employs advanced technologies such as multispectral and hyperspectral sensors, machine learning algorithms, and geospatial information systems (GIS) to extract detailed data from satellite images. Photo interpretation relies on traditional optical devices like magnifying glasses, stereoscopes, and manual digitizing methods, often combined with basic digital image processing tools for enhancing clarity. Both methods benefit from Geographic Information System (GIS) integration for spatial analysis, but satellite imagery analysis leverages automated data extraction and real-time remote sensing capabilities for superior accuracy and efficiency.
Applications in Environmental Monitoring
Satellite imagery analysis provides detailed, multispectral data enabling precise tracking of deforestation, urban sprawl, and climate change impacts, while photo interpretation relies on visual assessment of aerial photographs for land use and vegetation health. Advanced algorithms in satellite imagery facilitate automated detection of pollution events and natural disasters, improving response times and accuracy in environmental monitoring. Both methods complement each other, with satellite imagery offering scalable, frequent updates and photo interpretation providing nuanced contextual insights.
Accuracy and Limitations Compared
Satellite imagery analysis offers higher accuracy through advanced algorithms and machine learning, enabling precise detection of land use changes and environmental monitoring. Photo interpretation, relying on human expertise, allows contextual understanding but is subject to subjective bias and slower processing time. Limitations of satellite imagery include resolution constraints and atmospheric interference, while photo interpretation is limited by human error and fatigue.
Role of Human Expertise vs Automation
Satellite imagery analysis leverages advanced algorithms and machine learning for rapid data processing, but human expertise remains essential for contextual understanding, anomaly detection, and decision-making based on nuanced patterns. Photo interpretation traditionally depends on skilled analysts to manually examine images, identifying features and changes through experience and intuition. The integration of automation enhances efficiency, yet the synergy between artificial intelligence and human judgment maximizes accuracy and reliability in geospatial intelligence.
Future Trends in Remote Sensing Analysis
Future trends in remote sensing analysis emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance satellite imagery analysis, enabling faster and more accurate extraction of geospatial information. Advances in hyperspectral imaging and real-time data processing are expected to revolutionize photo interpretation by providing deeper insights into environmental changes and urban development. Collaborative platforms leveraging cloud computing will facilitate seamless access and analysis of vast datasets, driving innovation in predictive analytics and decision-making across industries.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
Satellite imagery analysis offers automated, large-scale data processing ideal for monitoring environmental changes and urban development, while photo interpretation provides detailed, manual evaluation suited for specialized tasks like military reconnaissance or archaeological surveys. Selecting the right method depends on factors such as project scale, required accuracy, and available resources; satellite imagery excels in broad, repeatable analysis, whereas photo interpretation delivers nuanced insights through expert human judgment. Integrating both methods can optimize outcomes when comprehensive spatial understanding and precision are necessary.
Satellite Imagery Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com