The plate interior of a vehicle refers to the area inside the license plate frame or holder where the plate is mounted securely. Understanding the design and materials of the plate interior helps ensure proper fit and durability, protecting your license plate from damage and weather elements. Discover more about maintaining and customizing your plate interior in the full article.
Table of Comparison
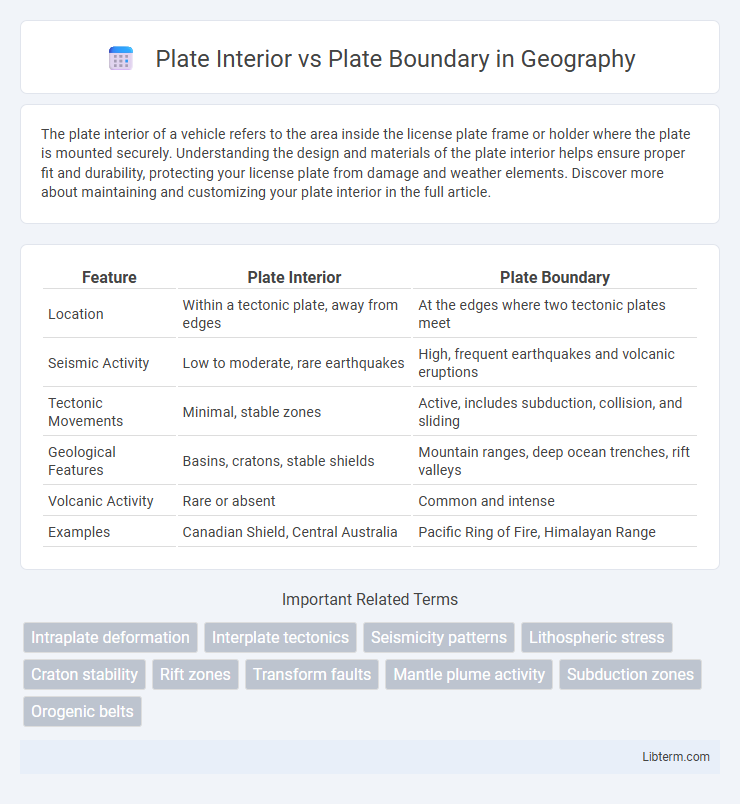
| Feature | Plate Interior | Plate Boundary |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Within a tectonic plate, away from edges | At the edges where two tectonic plates meet |
| Seismic Activity | Low to moderate, rare earthquakes | High, frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions |
| Tectonic Movements | Minimal, stable zones | Active, includes subduction, collision, and sliding |
| Geological Features | Basins, cratons, stable shields | Mountain ranges, deep ocean trenches, rift valleys |
| Volcanic Activity | Rare or absent | Common and intense |
| Examples | Canadian Shield, Central Australia | Pacific Ring of Fire, Himalayan Range |
Introduction to Plate Tectonics
Plate interiors are regions located away from tectonic plate boundaries, characterized by relatively stable geologic conditions and infrequent seismic activity. Plate boundaries, on the other hand, are zones where tectonic plates interact, leading to frequent earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain-building processes. Understanding the differences between plate interiors and boundaries is essential in the study of plate tectonics, which explains the movement and interaction of Earth's lithospheric plates.
Defining Plate Interiors
Plate interiors are regions situated away from tectonic plate boundaries, characterized by relatively stable geological conditions and limited seismic activity. These areas exhibit features such as ancient cratons, stable continental cores, and intraplate earthquakes caused by stresses transmitted from plate boundaries. Understanding the processes within plate interiors is essential for comprehending continental stability and intraplate tectonics distinct from the dynamic interactions at plate boundaries.
Understanding Plate Boundaries
Plate boundaries are the zones where tectonic plates meet, characterized by significant geological activity such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building. Unlike the stable interiors of plates, these boundaries are classified into three main types: divergent, convergent, and transform, each exhibiting distinct movements and interactions. Understanding plate boundaries is crucial for studying Earth's dynamic processes and predicting natural hazards connected to tectonic activity.
Geological Processes in Plate Interiors
Plate interiors experience geological processes such as intraplate volcanism, seismic activity, and crustal deformation, often driven by mantle plumes or far-field tectonic stresses. Unlike plate boundaries where interactions between plates dominate, these processes occur away from margins and contribute to features like basaltic flood lava provinces, rift zones, and intracratonic basins. Understanding intraplate dynamics is crucial for assessing seismic hazards and the formation of unique geological structures within continental interiors.
Tectonic Activity at Plate Boundaries
Tectonic activity is most intense at plate boundaries, where interactions between tectonic plates cause earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building. Divergent boundaries generate new crust through seafloor spreading, while convergent boundaries lead to subduction zones with deep seismic activity and volcanic arcs. Transform boundaries primarily produce strike-slip earthquakes due to lateral sliding of plates past each other.
Earthquake Patterns: Interior vs Boundary
Earthquake patterns differ significantly between plate interiors and plate boundaries, with the majority of seismic activity occurring along plate boundaries due to tectonic stress accumulation and release. Plate boundary earthquakes are characterized by frequent, high-magnitude events along convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries, whereas plate interior earthquakes are less common, typically lower in magnitude, but can cause significant damage due to their unexpected locations. Understanding the distinction in seismicity helps improve earthquake hazard assessment and preparedness in both boundary zones and stable continental interiors.
Volcanism: Plate Boundaries vs Interiors
Volcanism at plate boundaries occurs primarily due to tectonic plate interactions, with divergent boundaries forming mid-ocean ridges and convergent boundaries generating subduction-related volcanic arcs. In contrast, plate interior volcanism is typically linked to mantle plumes or hotspots, producing volcanic features such as the Hawaiian Islands far from plate edges. The chemical composition and eruption styles differ notably, with boundary volcanism often more explosive due to subduction zone processes, while interior hotspot volcanism tends to result in effusive basaltic flows.
Crustal Deformation Differences
Crustal deformation at plate interiors typically manifests as broad, distributed strain with low seismic activity due to the relative stability away from plate margins. In contrast, plate boundaries experience intense, localized deformation characterized by faults, folds, and frequent earthquakes resulting from direct tectonic interactions such as subduction, collision, or transform motion. The difference in deformation style influences regional topography, seismic hazard distribution, and geological structures, with plate boundaries being zones of high stress accumulation and rapid crustal modification.
Major Examples of Each Zone
The Pacific Plate's interior features the Hawaiian Islands, formed by volcanic hotspots far from plate boundaries, exemplifying intraplate tectonic activity. The San Andreas Fault along the boundary between the Pacific and North American Plates represents a major transform plate boundary characterized by lateral sliding and frequent earthquakes. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a divergent boundary between the Eurasian and North American Plates, showcases seafloor spreading and volcanic activity creating new oceanic crust.
Plate Interior and Boundary Significance in Earth Science
Plate boundaries are zones of intense geological activity, including earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, playing a crucial role in shaping Earth's surface. In contrast, plate interiors experience less tectonic activity but are significant for their stability, hosting ancient cratons and influencing long-term continental evolution. Understanding both plate boundaries and interiors is essential for comprehending Earth's dynamic processes and geological history.
Plate Interior Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com