Rift zones are areas where the Earth's tectonic plates are moving apart, causing the crust to thin and create deep valleys or rifts. These geological features often lead to volcanic activity as magma rises to fill the gaps between diverging plates. Discover how rift zones shape our planet's landscape and impact your understanding of Earth's dynamic processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
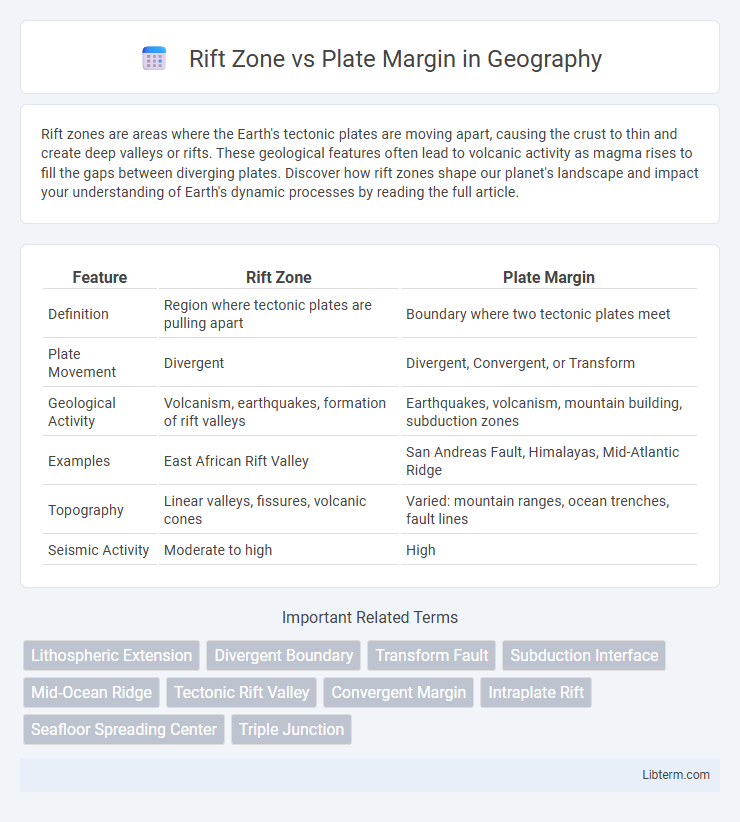
| Feature | Rift Zone | Plate Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Region where tectonic plates are pulling apart | Boundary where two tectonic plates meet |
| Plate Movement | Divergent | Divergent, Convergent, or Transform |
| Geological Activity | Volcanism, earthquakes, formation of rift valleys | Earthquakes, volcanism, mountain building, subduction zones |
| Examples | East African Rift Valley | San Andreas Fault, Himalayas, Mid-Atlantic Ridge |
| Topography | Linear valleys, fissures, volcanic cones | Varied: mountain ranges, ocean trenches, fault lines |
| Seismic Activity | Moderate to high | High |
Rift Zone vs Plate Margin: Key Differences
Rift zones and plate margins are distinct geological features characterized by different tectonic activities. Rift zones form within tectonic plates where the lithosphere is being pulled apart, leading to the creation of new crust through volcanic activity, while plate margins are boundaries between tectonic plates involving processes like subduction, collision, or sliding past one another. The key differences lie in their location, the type of stress they experience, and the resulting geological phenomena such as rift valley formation in rift zones versus earthquakes and mountain building at plate margins.
Geological Definitions: Rift Zones and Plate Margins
Rift zones are geological regions where tectonic plates are diverging, leading to the formation of new crust as magma rises from the mantle, commonly observed in areas like the East African Rift. Plate margins, also known as plate boundaries, are the edges where two tectonic plates meet, classified into divergent, convergent, and transform types, each associated with distinct geological activities such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building. Understanding the distinctions between rift zones and plate margins is crucial for comprehending tectonic processes that shape Earth's surface.
Plate Tectonics Overview
Plate margins are boundaries where tectonic plates converge, diverge, or slide past each other, creating significant geological activity such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building. Rift zones occur within divergent plate margins, where the lithosphere stretches and thins, leading to the formation of new oceanic crust and rift valleys. Understanding these dynamic interactions reveals the fundamental processes driving plate tectonics and shaping Earth's surface.
Types of Plate Margins
Plate margins are classified into three main types: divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries, each with distinct geological activity. Rift zones occur at divergent plate margins where tectonic plates move apart, causing the Earth's crust to thin and form rift valleys and volcanic activity. Convergent margins involve plates colliding, creating mountain ranges or subduction zones, while transform margins slide past each other, resulting in seismic activity along faults.
Rift Zone Formation Processes
Rift zones form through extensional tectonics where the Earth's lithosphere is pulled apart, causing thinning and fracturing. Magma rises to fill the created voids, leading to volcanic activity and the development of rift valleys. This process contrasts with plate margins, where interactions between plates can be convergent, divergent, or transform, but rift zones specifically represent areas of active lithospheric extension.
Plate Margin Dynamics and Interactions
Plate margins are boundaries where tectonic plates interact through convergent, divergent, or transform movements, driving seismic activity, mountain building, and volcanic eruptions. Rift zones occur at divergent plate margins where lithospheric plates pull apart, forming new crust and creating valleys or ocean basins. Plate margin dynamics control the energy release and geological structures, with interactions varying from subduction and collision at convergent margins to extensional forces at rift zones.
Geological Features of Rift Zones
Rift zones are characterized by extensive crustal extension, leading to the formation of deep valleys, fault-block mountains, and volcanic activity due to magma rising as tectonic plates diverge. Unlike plate margins with compressional forces, rift zones display prominent normal faulting patterns and the creation of new oceanic crust in some cases, such as the East African Rift or the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The geological features include linear basins filled with sediments, fissure eruptions, and significant geothermal activity linked to mantle upwelling and lithospheric thinning.
Volcanic and Seismic Activities Comparison
Rift zones, located at divergent plate boundaries, exhibit intense volcanic activity characterized by the formation of new crust through magma upwelling and basaltic lava flows, while seismic events are typically moderate and shallow. Plate margins, especially convergent boundaries, experience more powerful and frequent earthquakes due to subduction processes, accompanied by explosive volcanism from volatile-rich magma. Intraplate rifts show ongoing crustal extension and fissure eruptions, whereas plate margins combine both volcanic arc systems and megathrust earthquakes, resulting in heightened geohazard potential.
Real-World Examples: Rift Zones & Plate Margins
The East African Rift Zone exemplifies a continental rift where tectonic plates are diverging, causing the formation of valleys and volcanic activity. In contrast, the Pacific Plate's boundary with the North American Plate along the San Andreas Fault is a transform plate margin characterized by horizontal sliding and frequent earthquakes. These real-world examples highlight Rift Zones as areas of crustal extension, while Plate Margins exhibit diverse tectonic interactions including divergence, convergence, and transform movements.
Significance in Earth’s Geology
Rift zones and plate margins are crucial in understanding Earth's tectonic activity and geological evolution. Rift zones, where the lithosphere stretches and thins, often lead to the formation of new ocean basins and volcanic activity, exemplified by the East African Rift. Plate margins, including divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries, drive mountain building, earthquakes, and subduction processes essential for recycling Earth's crust and shaping continental structures.
Rift Zone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com