Hill landscapes offer a unique blend of natural beauty and recreational opportunities, making them ideal for hiking, photography, and wildlife observation. Their elevation provides panoramic views that enhance outdoor experiences and promote physical well-being. Discover how hills can transform your next adventure by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
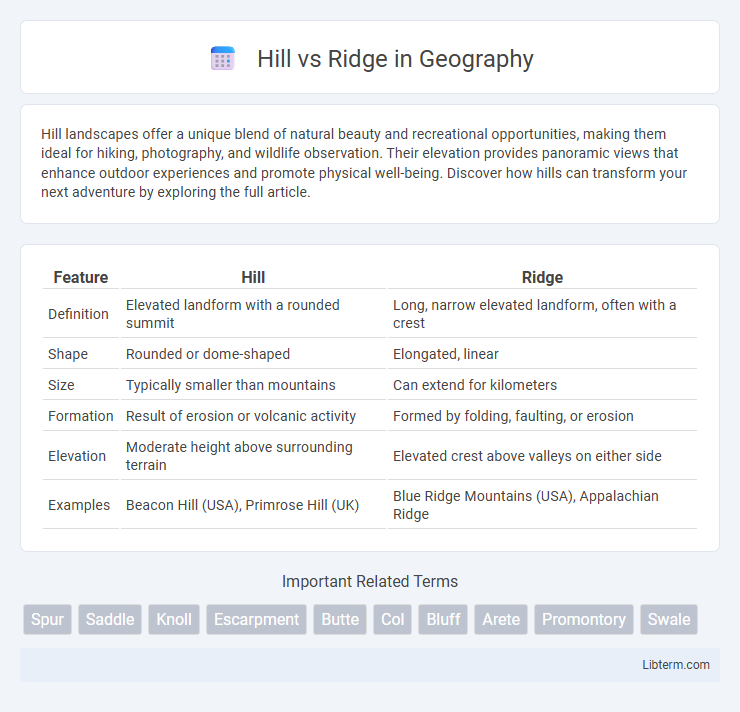
| Feature | Hill | Ridge |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated landform with a rounded summit | Long, narrow elevated landform, often with a crest |
| Shape | Rounded or dome-shaped | Elongated, linear |
| Size | Typically smaller than mountains | Can extend for kilometers |
| Formation | Result of erosion or volcanic activity | Formed by folding, faulting, or erosion |
| Elevation | Moderate height above surrounding terrain | Elevated crest above valleys on either side |
| Examples | Beacon Hill (USA), Primrose Hill (UK) | Blue Ridge Mountains (USA), Appalachian Ridge |
Introduction: Understanding Hills and Ridges
Hills and ridges are prominent landforms characterized by elevated terrain, but they differ in shape and formation. A hill is a rounded elevation of the earth's surface, typically smaller and less steep than mountains, while a ridge is a long, narrow elevated crest often formed by tectonic activity or erosion processes. Understanding the distinctions between hills and ridges is essential for geological mapping, land use planning, and environmental studies.
Definition of a Hill
A hill is a natural elevation of the earth's surface, typically smaller and less steep than a mountain, characterized by a rounded top and distinct rise above the surrounding terrain. Hills often reach heights ranging from a few hundred to several hundred meters, affecting local climate and vegetation patterns due to their elevation. Unlike ridges, which are elongated landforms with a continuous crest, hills usually present a solitary or gently rolling shape.
Definition of a Ridge
A ridge is a long, narrow elevation of land that forms a continuous crest along the top of hills or mountains, often characterized by steep sides and a sharp peak. It separates two adjacent valleys or drainage areas and represents a prominent topographic feature in landscape morphology. The definition of a ridge emphasizes its linear structure and typically higher elevation compared to surrounding terrain.
Key Differences: Hill vs Ridge
A hill is a natural elevation of the earth's surface with a rounded summit, typically lower and less steep than a mountain, while a ridge is a long, narrow elevated landform often formed by tectonic activity or erosion. Hills are isolated or scattered landforms with gentle slopes, whereas ridges extend over considerable distances with sharp crests. The key difference lies in their shape and formation: hills are broad and rounded elevations, ridges are elongated and narrow elevations.
Geographical Formation of Hills
Hills are elevated landforms that rise gently above the surrounding terrain with rounded summits, formed primarily through processes such as erosion, sediment deposition, and tectonic activity. Unlike ridges, which are elongated and sharply defined geological features often created by folding or faulting, hills develop from the gradual accumulation or wearing down of earth materials. Their moderate slope and isolated or clustered arrangement distinguish hills as prominent yet less steep topographical features in the landscape.
Geological Formation of Ridges
Ridges form as long, narrow elevations of land created by geological processes such as tectonic plate movements, folding, faulting, and erosion-resistant rock layers. Unlike hills, which are often isolated or rounded elevations, ridges typically represent the crest of folded strata or linear features resulting from differential erosion of sedimentary rock sequences. The presence of harder rock types like sandstone or limestone along fold axes or fault lines promotes ridge formation, distinguishing them from softer surrounding materials.
Landscape Features: Shape and Size Comparison
Hill landscapes typically exhibit rounded or conical shapes with moderate elevation, often covering smaller areas compared to ridges. Ridges present elongated, narrow landforms with steep slopes, extending over greater distances and displaying linear contours. The size disparity highlights hills as isolated or clustered elevations, whereas ridges form continuous elevated crests influencing drainage and ecosystem patterns.
Ecological Significance of Hills and Ridges
Hills and ridges play essential ecological roles by providing diverse habitats and promoting biodiversity through varied microclimates and soil conditions. Hills often support unique vegetation zones due to altitude-related temperature and moisture gradients, while ridges can act as natural corridors facilitating wildlife movement and genetic exchange. Both landforms contribute to watershed stability by reducing soil erosion and regulating water flow, crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Human Activities and Uses
Hill landscapes often serve as locations for agriculture, grazing, and residential development due to their moderate slopes and accessibility. Ridge areas, characterized by their narrow, elevated formations, are frequently utilized for wind energy installations, telecommunications towers, and recreational activities like hiking. Both features influence human settlement patterns and resource exploitation, shaping regional land use practices.
Summary: Hill vs Ridge
Hill vs Ridge presents a detailed comparison between two prominent geographical landforms based on elevation, slope, and formation characteristics. Hills typically exhibit lower elevation and rounded summits with gentle slopes, whereas ridges feature elongated crests with steeper inclines and more pronounced linear structures. This distinction influences land use, erosion patterns, and ecological habitats, making the understanding of these features crucial in geomorphology and environmental planning.
Hill Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com