Channels serve as essential pathways for delivering content, distributing products, or facilitating communication between businesses and their audiences. Understanding the right channels for your specific needs can significantly boost engagement, reach, and overall success. Explore the rest of the article to discover which channels best align with your goals and how to leverage them effectively.
Table of Comparison
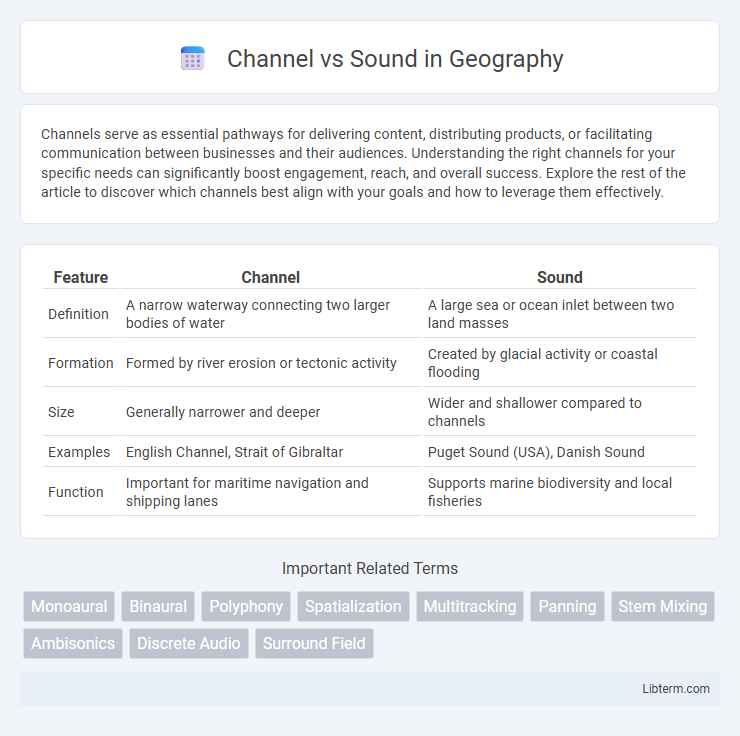
| Feature | Channel | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A narrow waterway connecting two larger bodies of water | A large sea or ocean inlet between two land masses |
| Formation | Formed by river erosion or tectonic activity | Created by glacial activity or coastal flooding |
| Size | Generally narrower and deeper | Wider and shallower compared to channels |
| Examples | English Channel, Strait of Gibraltar | Puget Sound (USA), Danish Sound |
| Function | Important for maritime navigation and shipping lanes | Supports marine biodiversity and local fisheries |
Understanding Channels in Audio Systems
Channels in audio systems refer to the individual paths through which audio signals are transmitted and played back, such as left, right, or surround sound channels in stereo and multi-channel setups. Understanding channels helps in distinguishing between mono (single channel), stereo (two channels), and surround sound formats (five or more channels), each impacting the spatial distribution and immersion of the audio experience. Proper channel configuration is essential for achieving accurate sound localization and a balanced listening environment in professional audio production and consumer playback systems.
Defining Sound: Qualities and Characteristics
Sound is a complex auditory phenomenon characterized by properties such as frequency, amplitude, timbre, and duration, which collectively define its quality and perceptual attributes. It consists of vibrations transmitted through a medium like air, producing waves that vary in pitch and loudness, crucial for distinguishing different sounds. These inherent characteristics differentiate sound from channels, where a channel refers to the medium or pathway through which sound signals are transmitted or recorded.
Stereo vs Mono: Differences in Channels
Stereo audio consists of two separate channels, left and right, allowing for spatial sound distribution and a more immersive listening experience. In contrast, mono audio uses a single channel, delivering the same sound uniformly to all speakers. Stereo is ideal for music production and media where directionality enhances perception, while mono is preferred for clarity in speech-centric applications.
How Channels Affect Sound Reproduction
Channels significantly influence sound reproduction by determining the spatial distribution and clarity of audio signals. Multi-channel setups, such as stereo or surround sound systems, create immersive listening experiences by delivering distinct audio streams to different speakers, enhancing depth and directionality. The number and arrangement of channels directly affect how accurately sound sources are localized and how natural the audio feels to the listener.
The Role of Surround Sound and Multiple Channels
Surround sound enhances audio immersion by utilizing multiple channels, typically ranging from 5.1 to 7.1 configurations, to create a three-dimensional listening experience. Each channel corresponds to a specific speaker placement, delivering distinct audio elements such as front, rear, center, and subwoofer frequencies, which collectively enrich spatial accuracy and depth. This multi-channel approach surpasses traditional stereo sound by allowing precise sound localization and realistic environmental effects in home theaters and gaming systems.
Sound Quality: Impact of Channel Configuration
Sound quality is significantly influenced by the channel configuration, as the number of audio channels determines spatial accuracy and depth perception. Stereo systems with two channels offer basic left-right separation, while multi-channel formats like 5.1 or 7.1 surround sound enhance immersion by delivering discrete audio signals to multiple speakers. This channel arrangement improves clarity, directionality, and overall auditory experience, crucial for high-fidelity sound reproduction in home theaters and professional audio setups.
Audio Formats: Channel and Sound Considerations
Audio formats differ significantly in their handling of channels and sound complexity, influencing playback quality and compatibility. Multichannel formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X support immersive surround sound by encoding multiple audio channels, enhancing spatial audio perception compared to stereo or mono formats. Considerations for selecting an audio format include the number of audio channels, sound resolution, compression type, and intended playback environment to ensure optimal sound clarity and immersive experience.
Practical Applications: Choosing the Right Channel Setup
Selecting the right channel setup significantly enhances audio quality based on the intended use, with stereo (2-channel) ideal for music playback providing clear left-right sound localization, while multi-channel formats like 5.1 or 7.1 are crucial in home theater systems for immersive surround sound experience. For podcast production or voice recordings, mono (1-channel) is practical due to its simplicity and consistent sound delivery across all playback systems. Gaming often benefits from 3D audio configurations involving multiple channels to accurately simulate spatial audio cues and improve player immersion.
Common Channel and Sound Misconceptions
Common misconceptions confuse the terms channel and sound, often treating them as interchangeable despite their distinct meanings in audio technology. A channel refers to a discrete audio path or signal, such as left or right in stereo systems, while sound is the actual audio wave perceived by listeners. Clarifying this distinction helps avoid errors in audio mixing, recording, and playback, ensuring accurate sound reproduction and proper equipment configuration.
Future Trends in Channel and Sound Technology
Emerging trends in channel technology emphasize immersive multi-channel audio systems leveraging object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos and MPEG-H, enabling personalized sound experiences tailored to specific listener environments. Sound technology advancements prioritize spatial audio integration and AI-driven sound enhancement, improving clarity and realism in virtual and augmented reality applications. The convergence of 5G networks and edge computing supports real-time adaptive channel configurations that optimize audio streaming quality and latency for interactive media platforms.
Channel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com