The Gulf region is known for its strategic economic importance, rich cultural heritage, and rapidly evolving urban landscapes. Boasting vast oil reserves and booming trade hubs, it plays a crucial role in global energy markets and commerce. Explore the full article to discover how the Gulf's dynamic growth impacts your future opportunities.
Table of Comparison
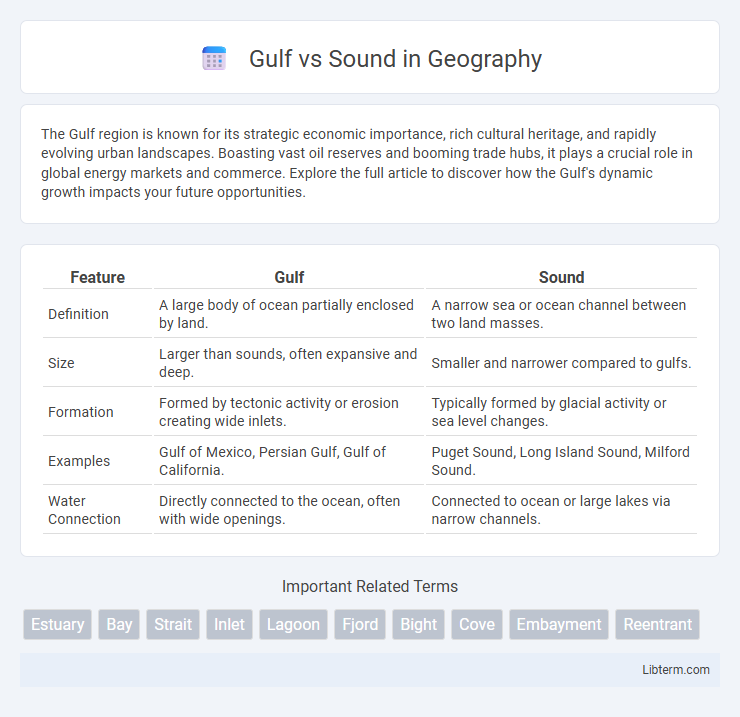
| Feature | Gulf | Sound |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A large body of ocean partially enclosed by land. | A narrow sea or ocean channel between two land masses. |
| Size | Larger than sounds, often expansive and deep. | Smaller and narrower compared to gulfs. |
| Formation | Formed by tectonic activity or erosion creating wide inlets. | Typically formed by glacial activity or sea level changes. |
| Examples | Gulf of Mexico, Persian Gulf, Gulf of California. | Puget Sound, Long Island Sound, Milford Sound. |
| Water Connection | Directly connected to the ocean, often with wide openings. | Connected to ocean or large lakes via narrow channels. |
Understanding the Definitions: Gulf vs Sound
A gulf is a large coastal indentation of the sea or ocean that is typically wider and deeper, partially enclosed by land, creating a significant body of water connected to a larger body. A sound, by contrast, is a narrower coastal waterway or inlet, often serving as a channel between the mainland and an island or between two landmasses. Understanding these definitions clarifies that gulfs are generally vast and open, while sounds function more as confined passages or bays.
Geographical Formation: How Gulfs and Sounds Are Created
Gulfs form as large coastal indentations where tectonic activity or sea level rise floods river valleys, creating deep, semi-enclosed bodies of water connected to oceans. Sounds develop primarily through glacial activity or the flooding of narrow inlets, often appearing as wider passages between mainland and islands. Both landforms result from complex interactions between geological processes and sea-level changes, shaping diverse coastal ecosystems.
Key Differences Between a Gulf and a Sound
A gulf is a large coastal indentation with a narrower opening to the sea, often deeper and more enclosed than a sound. A sound is typically a wide inlet or a passage between the mainland and an island, generally shallower and more open. Key differences include size, depth, and degree of enclosure, with gulfs being larger and more enclosed than sounds.
Examples of Famous Gulfs Around the World
The Gulf of Mexico is one of the most renowned gulfs, bordered by the United States, Mexico, and Cuba, playing a critical role in marine biodiversity and oil production. The Persian Gulf, situated between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula, is a vital region for global energy supplies due to its vast oil reserves. Another famous example is the Gulf of Aden, located between Yemen and Somalia, serving as a strategic maritime route connecting the Red Sea to the Arabian Sea.
Notable Sounds and Their Locations
Notable sounds such as the Puget Sound in Washington State and the Long Island Sound bordering Connecticut and New York represent significant, elongated coastal inlets with complex ecosystems. These sounds typically feature brackish water and support diverse marine life, distinguishing them from larger, open gulfs like the Gulf of Mexico or the Persian Gulf. The Puget Sound's intricate network of channels and inlets highlights how sounds serve as important natural harbors and ecological zones along continental coastlines.
Ecological Significance: Gulf vs Sound
A gulf typically features deeper waters and stronger tidal currents, supporting diverse marine habitats and serving as crucial spawning grounds for many fish species. Sounds are often shallower with calmer waters, creating ideal environments for estuarine ecosystems, including salt marshes and seagrass beds that provide essential nursery habitats for various aquatic organisms. Both gulfs and sounds contribute significantly to coastal biodiversity and play vital roles in nutrient cycling and carbon sequestration.
Economic and Cultural Importance
Gulfs, such as the Gulf of Mexico, serve as vital economic hubs due to their rich oil reserves, busy shipping lanes, and abundant fisheries, driving significant international trade and energy production. Sounds like Puget Sound function as crucial cultural centers that support diverse marine ecosystems and vibrant communities, fostering fishing industries and tourism. Both gulfs and sounds contribute uniquely to regional economies by combining natural resource exploitation with cultural heritage preservation.
Marine Life and Biodiversity Comparison
Gulfs and sounds both serve as vital marine habitats but differ significantly in biodiversity due to their unique geographic and hydrological features. Gulfs, often larger and more enclosed, support diverse ecosystems with abundant fish species, coral reefs, and marine mammals due to nutrient-rich waters and stable salinity. Sounds, typically narrower and more estuarine, provide critical breeding grounds for shellfish, seabirds, and juvenile fish, fostering rich biodiversity influenced by freshwater inflow and tidal mixing.
Navigation and Human Activities in Gulfs and Sounds
Gulfs often provide deeper and more sheltered waters than sounds, making them ideal for large-scale maritime navigation, commercial shipping, and ports. Sounds, characterized by their narrower and sometimes shallower waterways, support local fishing, recreational boating, and smaller vessel transit. Human activities in gulfs typically involve extensive industrial and urban development due to their strategic access to open oceans, while sounds usually foster ecological tourism and community-based resource management.
Choosing the Right Term: Gulf or Sound
Choosing the right term between "gulf" and "sound" depends on their specific geographic characteristics. A gulf is typically a large, deep inlet of the sea partially enclosed by land, often with a narrow mouth, such as the Gulf of Mexico. In contrast, a sound is usually a narrower, shallow body of water between the mainland and an island or a series of islands, like the Puget Sound, making the distinction crucial for accurate geographic description.
Gulf Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com