Topographic contour lines represent the elevation and shape of the land, allowing you to visualize terrain on a flat map. These lines connect points of equal elevation, helping hikers, engineers, and planners understand slopes, hilltops, and valleys with precision. Explore the rest of this article to learn how to read and effectively use topographic contour maps for your projects.
Table of Comparison
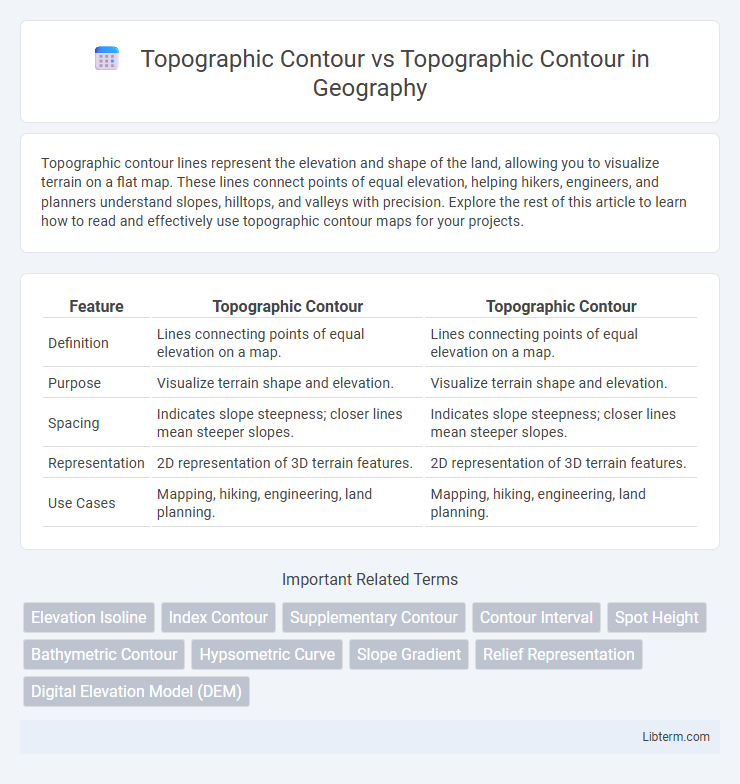
| Feature | Topographic Contour | Topographic Contour |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lines connecting points of equal elevation on a map. | Lines connecting points of equal elevation on a map. |
| Purpose | Visualize terrain shape and elevation. | Visualize terrain shape and elevation. |
| Spacing | Indicates slope steepness; closer lines mean steeper slopes. | Indicates slope steepness; closer lines mean steeper slopes. |
| Representation | 2D representation of 3D terrain features. | 2D representation of 3D terrain features. |
| Use Cases | Mapping, hiking, engineering, land planning. | Mapping, hiking, engineering, land planning. |
Understanding Topographic Contour Basics
Topographic contour lines represent elevations on a map, connecting points of equal height to depict terrain shape and slope. Understanding topographic contour basics involves recognizing contour intervals, which specify the vertical distance between lines, vital for interpreting landscape steepness or flatness. Accurate reading of these contours enhances navigation, land surveying, and geographic analysis by visualizing elevation changes effectively.
Definition of Topographic Contour Lines
Topographic contour lines represent elevation on a map by connecting points of equal height above sea level, illustrating the shape and slope of the terrain accurately. These lines enable the visualization of landforms such as hills, valleys, and slopes without depicting every detail, providing a simplified yet precise representation of the topography. Understanding contour intervals, the vertical distance between consecutive contour lines, is essential for interpreting the elevation changes and gradient steepness on topographic maps.
Key Features of Topographic Contours
Topographic contours represent lines of equal elevation on a map, depicting the three-dimensional shape of the terrain on a two-dimensional surface. Key features include contour interval, which defines the vertical spacing between lines, and contour lines that never intersect, ensuring accurate representation of landforms. Closely spaced contours indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced contours suggest gentle terrain, making them essential for understanding elevation changes and landscape features.
Types of Topographic Contours Explained
Topographic contours can be categorized into three primary types: index contours, intermediate contours, and supplementary contours. Index contours are bold lines marked with elevation values, aiding in easy terrain interpretation. Intermediate contours fill the spaces between index contours with finer, unmarked lines, while supplementary contours represent subtle terrain changes and are often dashed or dotted.
Importance of Topographic Contours in Mapping
Topographic contours are essential in mapping for accurately representing the elevation and shape of the terrain, enabling detailed visualization of landforms such as hills, valleys, and slopes. These contours facilitate precise planning in engineering, construction, and environmental management by providing critical information about gradients and elevation differences. Accurate topographic contours improve navigation, land use planning, and resource management by offering reliable spatial data for geographic and topographic analysis.
Comparative Analysis: Topographic Contour vs Topographic Contour
Topographic contour lines represent elevations and landforms on maps, with differences emerging in contour interval and detail scale; larger intervals result in less detailed relief representation, while smaller intervals offer finer terrain granularity. Comparing topographic contours on large-scale maps reveals minute changes in elevation, useful for engineering and precise land use planning, whereas small-scale maps emphasize broader landform trends for regional analysis. Variations in contour line spacing between maps enable the assessment of slope steepness and terrain ruggedness, critical for navigation, environmental studies, and construction projects.
Interpretation Techniques for Topographic Contours
Topographic contour interpretation techniques involve analyzing contour spacing, shape, and elevation intervals to understand terrain features such as slopes, ridges, and valleys. Closely spaced contours indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced contours signify gentle slopes or flat areas. Recognizing contour patterns enables accurate identification of landforms and assists in applications like watershed management, construction planning, and navigation.
Applications of Topographic Contours in Land Surveying
Topographic contours provide precise elevation data essential for land surveying, enabling surveyors to create accurate land models and assess terrain characteristics. These contours assist in boundary delineation, construction planning, and drainage analysis by representing the three-dimensional landscape on two-dimensional maps. Effective use of topographic contours ensures enhanced decision-making in land development and resource management.
Common Challenges in Reading Topographic Contours
Reading topographic contours involves interpreting lines that represent elevation on a map, which can be challenging due to closely spaced lines indicating steep slopes and widely spaced lines suggesting gentle gradients. Common difficulties include distinguishing between contour lines and index contours, misreading elevation changes, and understanding the terrain's three-dimensional features from a two-dimensional representation. Adequate practice with contour intervals, recognizing contour patterns, and using supplementary tools like digital elevation models enhance accuracy in terrain analysis.
Future Trends in Topographic Contour Mapping
Future trends in topographic contour mapping emphasize increased integration of AI-driven algorithms and high-resolution LiDAR data to enhance accuracy and real-time updates. Advances in drone-based photogrammetry enable more precise and rapid terrain analysis, revolutionizing traditional contour mapping approaches. Enhanced 3D visualization tools and cloud-based GIS platforms are set to transform data accessibility and collaborative mapping efforts for topographic contours.
Topographic Contour Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com