Geography explores the relationship between people, places, and environments, examining physical landscapes and human activities shaping the world. Understanding geographic patterns reveals insights into climate, resources, culture, and urban development affecting daily life. Discover how geography influences your surroundings and global connections by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
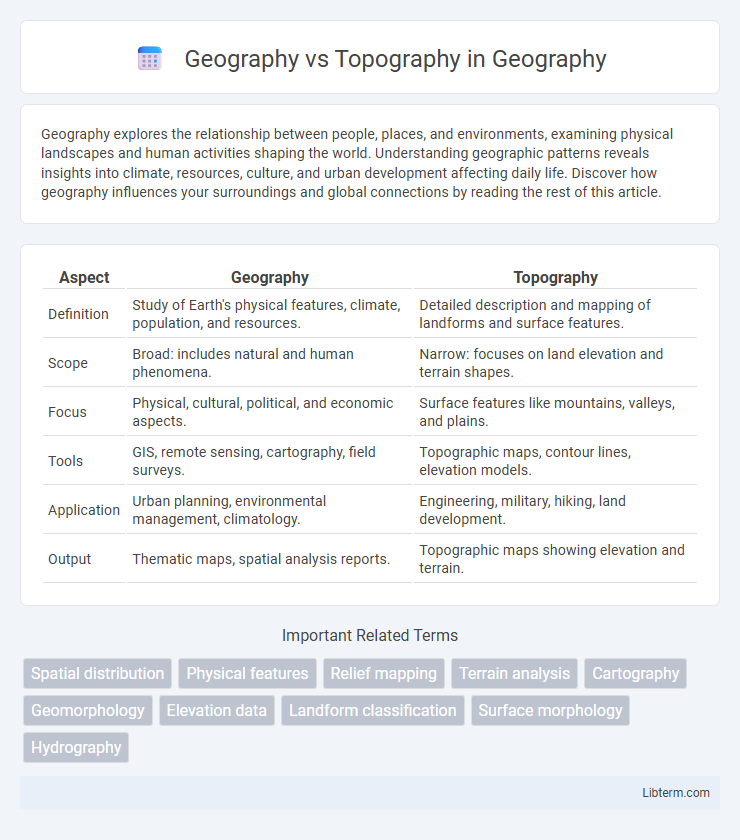
| Aspect | Geography | Topography |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of Earth's physical features, climate, population, and resources. | Detailed description and mapping of landforms and surface features. |
| Scope | Broad: includes natural and human phenomena. | Narrow: focuses on land elevation and terrain shapes. |
| Focus | Physical, cultural, political, and economic aspects. | Surface features like mountains, valleys, and plains. |
| Tools | GIS, remote sensing, cartography, field surveys. | Topographic maps, contour lines, elevation models. |
| Application | Urban planning, environmental management, climatology. | Engineering, military, hiking, land development. |
| Output | Thematic maps, spatial analysis reports. | Topographic maps showing elevation and terrain. |
Introduction to Geography and Topography
Geography studies the Earth's physical features, climate, population, and human activities, providing a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships and environments. Topography specifically focuses on the detailed mapping and description of Earth's surface features, including mountains, valleys, and plains. Mastery of both geography and topography is essential for fields like urban planning, environmental science, and geological research.
Defining Geography: Scope and Significance
Geography encompasses the study of Earth's physical features, human societies, and the interactions between them across spatial and temporal scales. It integrates natural science elements such as climate, landforms, and ecosystems with social science aspects like population distribution, urban development, and cultural landscapes. Understanding geography is essential for addressing environmental challenges, resource management, and sustainable development.
Understanding Topography: Meaning and Elements
Topography refers to the detailed mapping and description of the physical features of a terrain, including its elevation, slope, and landforms such as hills, valleys, and rivers. Key elements of topography include contour lines representing elevation changes, landforms shaping the surface, and natural as well as artificial features that define the landscape. Understanding topography is essential for applications in geography, environmental studies, urban planning, and civil engineering, providing insights into terrain structure and spatial relationships.
Key Differences Between Geography and Topography
Geography studies Earth's physical features, climate, populations, and human-environment interactions, offering a broad understanding of spatial patterns and processes. Topography specifically examines the surface shapes and features of the land, such as elevation, slope, and terrain relief, often represented through maps and topographic surveys. The key difference lies in geography's holistic scope versus topography's detailed focus on landform structure and physical landscape characteristics.
How Geography Encompasses Topographical Studies
Geography encompasses topographical studies by integrating the detailed analysis of Earth's physical features such as mountains, valleys, and plains within broader spatial contexts including climatic, ecological, and human factors. Topography specifically maps and measures surface configurations, while geography synthesizes this information to understand environmental patterns, land use, and regional development. This interdisciplinary approach enhances geographic information systems (GIS), spatial planning, and natural resource management by providing comprehensive spatial data.
Tools and Techniques in Geography vs. Topography
Geography employs tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS), remote sensing, and spatial analysis to study Earth's physical features and human-environment interactions at macro and micro scales. Topography focuses on detailed measurement and representation of surface features using instruments such as theodolites, total stations, and digital elevation models (DEMs) to create precise maps of elevation and land contours. Both fields utilize satellite imagery and GPS technology, but topography emphasizes elevation data accuracy and terrain modeling, while geography integrates broader spatial data for environmental and socio-economic analysis.
Practical Applications of Geography
Geography involves the study of Earth's landscapes, environments, and human interactions, providing essential insights for urban planning, environmental management, and disaster risk reduction. Topography focuses on the detailed mapping and analysis of landforms and terrain features, which aids in construction projects, military operations, and infrastructure development. Practical applications of geography integrate spatial data with social, economic, and environmental factors to optimize resource allocation and policy-making.
The Role of Topography in Environmental Analysis
Topography plays a crucial role in environmental analysis by providing detailed information about the Earth's surface features, such as elevation, slope, and landforms, which directly influence climate patterns, water flow, and vegetation distribution. Unlike geography, which encompasses broader spatial relationships and human-environment interactions, topography focuses specifically on the physical configuration of terrain, essential for flood risk assessment, habitat mapping, and land use planning. Integrating topographic data through Geographic Information Systems (GIS) enhances precision in modeling environmental processes and managing natural resources effectively.
Interdependence Between Geography and Topography
Geography and topography are interdependent disciplines that together provide a comprehensive understanding of Earth's physical features and spatial relationships. Topography, which maps the detailed surface features such as elevation, landforms, and terrain, supplies essential data for geographic analysis, influencing climate patterns, human settlement, and natural resource distribution within geographical regions. Geographic studies utilize topographic information to interpret environmental processes, plan land use, and manage ecosystems, highlighting the critical linkage between Earth's physical shape and its broader spatial dynamics.
Conclusion: Integrating Geographic and Topographic Insights
Integrating geographic and topographic insights enhances spatial analysis by combining broad environmental context with detailed landform data, supporting more accurate mapping and planning. Geographic information systems (GIS) leverage both disciplines to improve decision-making in urban development, natural resource management, and disaster response. This comprehensive approach fosters a deeper understanding of terrain and spatial relationships essential for effective environmental and infrastructural strategies.
Geography Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com