Marble is a durable, natural stone prized for its unique veining and elegant appearance, commonly used in flooring, countertops, and sculptures. Its heat resistance and timeless beauty make it a popular choice for both classic and contemporary interiors. Discover how marble can transform Your space by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
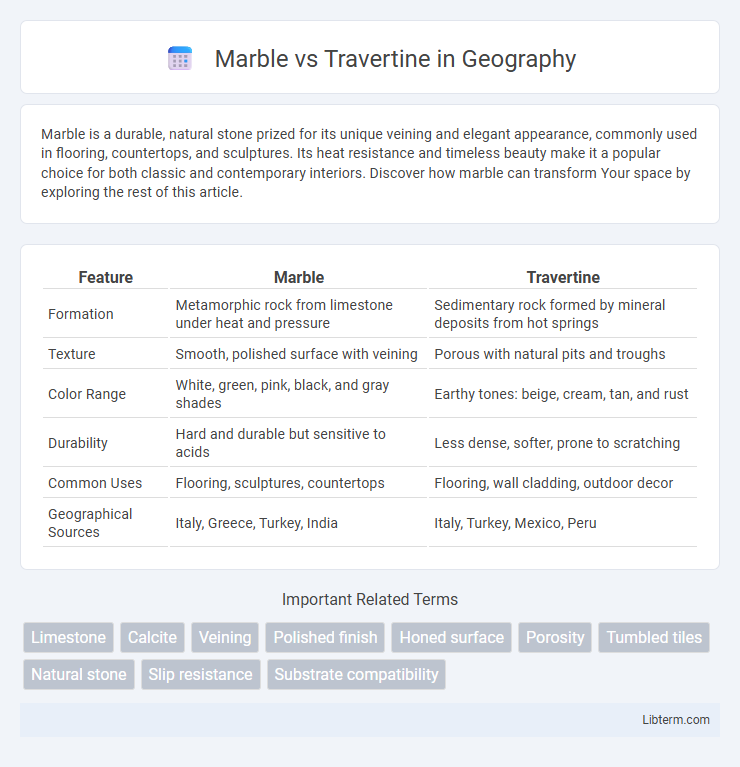
| Feature | Marble | Travertine |
|---|---|---|
| Formation | Metamorphic rock from limestone under heat and pressure | Sedimentary rock formed by mineral deposits from hot springs |
| Texture | Smooth, polished surface with veining | Porous with natural pits and troughs |
| Color Range | White, green, pink, black, and gray shades | Earthy tones: beige, cream, tan, and rust |
| Durability | Hard and durable but sensitive to acids | Less dense, softer, prone to scratching |
| Common Uses | Flooring, sculptures, countertops | Flooring, wall cladding, outdoor decor |
| Geographical Sources | Italy, Greece, Turkey, India | Italy, Turkey, Mexico, Peru |
Introduction to Marble and Travertine
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed primarily of recrystallized carbonate minerals, typically calcite or dolomite, known for its luxurious appearance and wide range of colors and veining patterns. Travertine is a sedimentary limestone formed by mineral deposits from natural springs, characterized by its porous texture and earthy tones, commonly found in beige, cream, and rust shades. Both stones are popular choices for flooring, countertops, and architectural features, with marble prized for its elegance and travertine valued for its rustic, warm aesthetic.
Geological Origins and Formation
Marble originates from the metamorphism of limestone or dolostone, where intense heat and pressure recrystallize the carbonate minerals, creating a dense, crystalline structure. Travertine forms through the precipitation of calcium carbonate from mineral-rich hot springs or limestone caves, resulting in a porous, banded texture characterized by its fibrous or concentric appearance. The distinct geological processes influence their durability, porosity, and aesthetic qualities, making marble smoother and more uniform while travertine exhibits natural cavities and variegated patterns.
Appearance and Color Variations
Marble features a smooth, polished surface with intricate veining patterns in shades of white, gray, black, green, and pink, creating a luxurious and elegant appearance. Travertine displays a more textured, porous surface with natural pits and holes, offering earthy tones such as beige, cream, rust, and gold, giving a warm and rustic charm. The distinct color variations and surface finishes between marble and travertine significantly influence their aesthetic appeal in interior and exterior design.
Durability and Hardness Comparison
Marble features a Mohs hardness rating of 3 to 4, making it softer and more prone to scratches and etching compared to travertine, which typically rates between 4 and 5. Travertine's porous structure requires sealing to enhance durability, but it generally withstands wear and heavy foot traffic better than marble. Both natural stones require maintenance, yet travertine's higher hardness and density offer improved resistance to chips and abrasions in high-use environments.
Common Applications in Home Design
Marble is widely used for countertops, bathroom vanities, and elegant flooring due to its smooth texture and sophisticated appearance. Travertine, favored for its porous surface and natural matte finish, is commonly applied in outdoor patios, backsplashes, and shower walls. Both materials enhance home design aesthetics but serve distinct functional purposes based on durability and maintenance needs.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Marble requires regular sealing and gentle cleaning with pH-neutral cleaners to maintain its polished surface and prevent etching or staining. Travertine, being more porous, demands more frequent sealing and careful cleaning to avoid buildup in its natural pits and crevices. Both stones benefit from prompt spill cleanup and avoiding acidic or abrasive cleaners to prolong their durability and appearance.
Cost and Affordability
Marble typically costs between $40 and $100 per square foot, making it a more expensive option compared to travertine, which ranges from $25 to $60 per square foot. Travertine offers greater affordability while maintaining a luxurious appearance, making it popular for budget-conscious homeowners. Cost variations in both materials depend on factors such as quality, origin, and installation complexity.
Advantages of Marble
Marble offers superior durability and a luxurious appearance with its smooth, polished surface and unique veining patterns, making it a popular choice for high-end interiors. Its resistance to heat and ability to be finely carved allow for intricate designs and long-lasting use in flooring, countertops, and decorative elements. Marble's natural elegance and timeless appeal increase property value and enhance aesthetic appeal in residential and commercial spaces.
Advantages of Travertine
Travertine offers exceptional durability and resistance to weathering, making it ideal for both indoor and outdoor applications such as flooring, patios, and pool surrounds. Its porous texture provides natural slip resistance, enhancing safety in wet areas. Compared to marble, travertine has a unique, earthy appearance with warm tones that add timeless elegance to any space while requiring less maintenance.
Which Stone Is Right for Your Project?
Marble offers a luxurious, polished appearance with unique veining patterns ideal for high-end interior projects requiring elegance and durability. Travertine provides a more rustic, earthy aesthetic with natural porous textures, making it suitable for outdoor spaces and Mediterranean-style designs. Your choice depends on the desired aesthetic, location, and maintenance preferences, as marble demands more care while travertine offers greater slip resistance and natural variation.
Marble Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com