Nonmaleficence is a foundational ethical principle in healthcare, emphasizing the obligation to avoid causing harm to patients through actions or omissions. It guides medical professionals to carefully weigh risks and benefits before intervening, ensuring patient safety and well-being are prioritized. Discover how this crucial principle shapes clinical decisions and impacts your healthcare experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
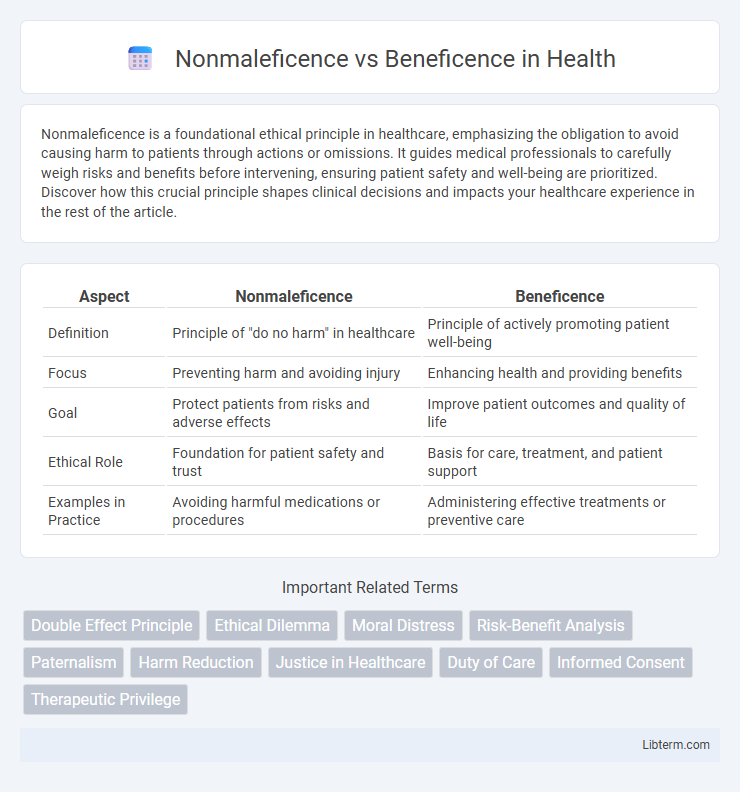
| Aspect | Nonmaleficence | Beneficence |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Principle of "do no harm" in healthcare | Principle of actively promoting patient well-being |
| Focus | Preventing harm and avoiding injury | Enhancing health and providing benefits |
| Goal | Protect patients from risks and adverse effects | Improve patient outcomes and quality of life |
| Ethical Role | Foundation for patient safety and trust | Basis for care, treatment, and patient support |
| Examples in Practice | Avoiding harmful medications or procedures | Administering effective treatments or preventive care |
Understanding Nonmaleficence: Definition and Principles
Nonmaleficence, a foundational ethical principle in healthcare, emphasizes the obligation to avoid causing harm to patients, guiding medical professionals to prioritize patient safety above all. It mandates minimizing risks and preventing harm through careful clinical judgment and evidence-based practices, ensuring that interventions do not worsen a patient's condition. This principle operates alongside beneficence, but while beneficence involves actively promoting good, nonmaleficence strictly focuses on the commitment to refrain from harmful actions.
The Essence of Beneficence in Healthcare
The essence of beneficence in healthcare lies in the commitment to promote patient well-being through actions that prevent harm and contribute positively to health outcomes. This principle requires healthcare professionals to actively improve patients' health by providing effective treatments and compassionate care, balancing potential benefits against risks. Beneficence drives ethical decision-making that ensures interventions serve the best interests of patients, enhancing their quality of life.
Historical Roots of Medical Ethics
Nonmaleficence and beneficence are foundational principles in medical ethics with deep historical roots traced back to the Hippocratic Oath, which emphasizes the duty of physicians to avoid harm and promote the well-being of patients. These ethical imperatives have evolved through centuries of philosophical discourse, particularly influenced by Judeo-Christian morality and Enlightenment thought, shaping modern biomedical ethics frameworks such as principlism. The balance between preventing harm (nonmaleficence) and actively contributing to patient welfare (beneficence) remains central to clinical decision-making and ethical medical practice.
Key Differences Between Nonmaleficence and Beneficence
Nonmaleficence emphasizes the ethical duty to avoid causing harm, prioritizing safety and prevention of injury or suffering, while beneficence involves actively promoting the well-being and welfare of others through positive actions. The key difference lies in nonmaleficence's focus on restraint from harmful conduct versus beneficence's encouragement of proactive good deeds. Healthcare ethics rely on balancing these principles to ensure patient care minimizes risks while maximizing benefits.
Real-World Examples: Nonmaleficence in Practice
Nonmaleficence in healthcare is exemplified by strict protocols ensuring surgical precision to avoid patient harm during operations. Medication management systems prevent adverse drug interactions, upholding the principle of "do no harm" by minimizing risks to patients. These practices contrast with beneficence, which actively promotes patient well-being beyond merely avoiding harm.
Beneficence in Clinical Decision-Making
Beneficence in clinical decision-making emphasizes actions that promote patient well-being and positive health outcomes. It requires healthcare professionals to actively contribute to the welfare of patients by recommending treatments that maximize benefits and minimize harm. Integrating beneficence ensures ethical responsibility prioritizes patient interests alongside clinical efficacy.
Ethical Dilemmas: When Principles Conflict
Nonmaleficence and beneficence often create ethical dilemmas when healthcare providers must balance the duty to avoid harm with the obligation to promote patient well-being. In clinical decision-making, conflicts arise such as choosing between a treatment that may cause side effects (nonmaleficence) and the potential benefits it offers (beneficence). Effective resolution requires careful evaluation of risks, benefits, patient values, and the context of care to uphold ethical standards in practice.
Balancing Patient Harm and Benefit
Balancing patient harm and benefit requires careful evaluation of nonmaleficence, the duty to avoid causing harm, against beneficence, the obligation to promote patient well-being. Medical decisions prioritize minimizing risks while maximizing therapeutic outcomes, often necessitating ethical deliberation to ensure interventions provide more benefit than harm. Clinicians employ evidence-based guidelines and patient preferences to navigate this balance, ensuring ethically sound and effective care.
Nonmaleficence vs Beneficence: Legal Perspectives
Nonmaleficence and beneficence represent core ethical principles in healthcare, with nonmaleficence emphasizing the duty to avoid harm and beneficence focusing on promoting patient well-being. Legally, nonmaleficence often underpins malpractice claims, as healthcare providers are held accountable for actions causing harm or injury, whereas beneficence supports positive obligations to act in patients' best interests, which can influence standards of care and informed consent laws. Courts frequently balance these principles when adjudicating cases, ensuring that medical interventions neither cause unnecessary harm nor fail to provide beneficial treatment, shaping regulatory frameworks and professional guidelines.
The Future of Ethical Practice in Medicine
The future of ethical practice in medicine hinges on balancing nonmaleficence, the commitment to avoid harm, with beneficence, the obligation to actively promote patient well-being. Advances in precision medicine and AI-driven diagnostics demand rigorous ethical frameworks ensuring treatments maximize benefits without unintended harm. Integrating patient-centered care models with these ethical principles will shape sustainable, trustworthy healthcare delivery.
Nonmaleficence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com