Infestation occurs when harmful pests invade your living or working spaces, causing damage to property and potential health risks. Effective pest control strategies are essential to eliminate infestations and prevent future occurrences. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to identify, manage, and protect your environment from infestations.
Table of Comparison
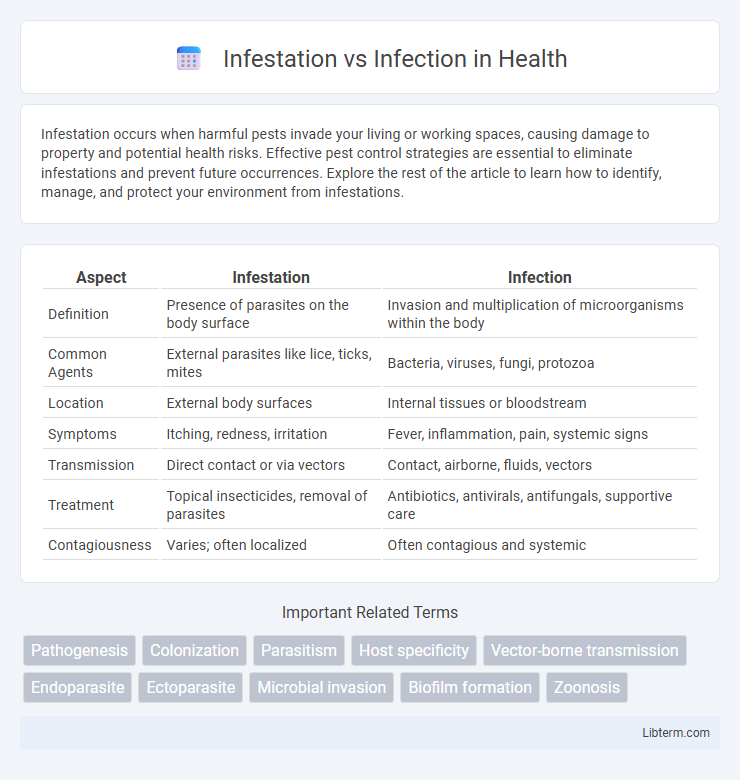
| Aspect | Infestation | Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Presence of parasites on the body surface | Invasion and multiplication of microorganisms within the body |
| Common Agents | External parasites like lice, ticks, mites | Bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa |
| Location | External body surfaces | Internal tissues or bloodstream |
| Symptoms | Itching, redness, irritation | Fever, inflammation, pain, systemic signs |
| Transmission | Direct contact or via vectors | Contact, airborne, fluids, vectors |
| Treatment | Topical insecticides, removal of parasites | Antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, supportive care |
| Contagiousness | Varies; often localized | Often contagious and systemic |
Understanding Infestation and Infection
Infestation refers to the presence of external parasites like lice, ticks, or fleas on the body surface, causing irritation and potential allergic reactions. Infection involves the invasion and multiplication of pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi within body tissues, triggering immune responses and disease symptoms. Distinguishing between infestation and infection is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment strategies in medical practice.
Key Differences Between Infestation and Infection
Infestation involves the presence of external parasites such as lice, ticks, or mites on the body surface, while infection occurs when pathogens like bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade and multiply within body tissues. Infestations typically cause localized irritation or allergic reactions, whereas infections can lead to systemic illness and provoke immune responses. Diagnosis and treatment differ; infestations often require topical agents to eliminate parasites, whereas infections may need systemic antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals depending on the causative microorganism.
Causes of Infestation
Infestation occurs when external parasites like lice, fleas, or ticks attach to the skin or hair, feeding on the host's blood or tissue. Common causes of infestation include poor hygiene, close contact with infested individuals or animals, and exposure to contaminated environments such as bedding or clothing. Unlike infections, infestations do not involve the invasion of body tissues by microorganisms but rely on external organisms that live on the surface of the host.
Causes of Infection
Infections are caused by pathogenic microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites entering the body and multiplying. These pathogens can infiltrate through cuts, respiratory droplets, contaminated food or water, and direct contact with infected individuals. The immune system's ability to recognize and destroy these microorganisms determines the severity and progression of the infection.
Common Organisms Responsible for Infestation
Common organisms responsible for infestation include ectoparasites such as lice, fleas, mites, and ticks, which live on the surface of the host and cause conditions like pediculosis, scabies, and tick-borne diseases. These parasites attach to the skin or hair and feed on blood or skin debris, leading to itching, rashes, and potential secondary infections. Unlike infections caused by bacteria or viruses that invade body tissues, infestations primarily involve external colonization by multicellular organisms.
Common Pathogens Responsible for Infection
Common pathogens responsible for infection include bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, viruses like influenza and HIV, fungi including Candida species, and parasites such as Plasmodium causing malaria. These microorganisms invade body tissues, multiply, and provoke an immune response leading to symptoms. Understanding the specific pathogen involved is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective antimicrobial treatment.
Symptoms of Infestation vs. Infection
Symptoms of infestation often include visible signs of parasites like itching, rash, or the presence of lice or mites on the skin, while infection symptoms typically involve inflammation, fever, swelling, and pain due to bacterial, viral, or fungal agents. Infestations usually manifest with external discomfort and localized irritation, whereas infections can cause systemic symptoms such as fatigue, chills, and elevated white blood cell count. Accurate diagnosis depends on identifying the specific cause, with infestations detected through physical examination and infections confirmed via laboratory tests.
Diagnosis: Infestation vs. Infection
Diagnosis of infestation involves identifying the presence of external parasites such as lice, mites, or ticks on the host through visual inspection, skin scrapings, or microscopic examination. Infection diagnosis often requires laboratory tests, including blood cultures, serology, or molecular assays, to detect pathogenic microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, or fungi within the host tissues or bloodstream. Accurate differentiation relies on clinical signs, sample analysis, and diagnostic imaging to determine whether symptoms result from external parasites or internal pathogens.
Treatment and Prevention Strategies
Treatment for infestation typically involves antiparasitic medications targeting external parasites such as lice or mites, while infection requires antimicrobial agents tailored to bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens. Preventive measures for infestation emphasize personal hygiene, regular cleaning of clothing and bedding, and avoidance of known infested environments. Infection prevention focuses on vaccination, proper handwashing, sterilization of medical equipment, and minimizing contact with contagious individuals.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek medical attention for infestation if persistent itching, skin rashes, or visible parasites (such as lice or scabies mites) appear and do not improve with over-the-counter treatments. Infection requires urgent care when symptoms include spreading redness, swelling, warmth, fever, or pus, indicating potential bacterial involvement. Prompt diagnosis and treatment prevent complications from infestations and infections, ensuring effective resolution and recovery.
Infestation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com