Cellulite is a common skin condition characterized by dimpled, lumpy flesh, often appearing on the thighs, hips, and buttocks due to fat deposits pushing through connective tissue. Its occurrence can be influenced by factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and diet, making it a persistent concern for many seeking smoother skin. Discover effective treatments and lifestyle tips in the rest of this article to help reduce your cellulite's appearance.
Table of Comparison
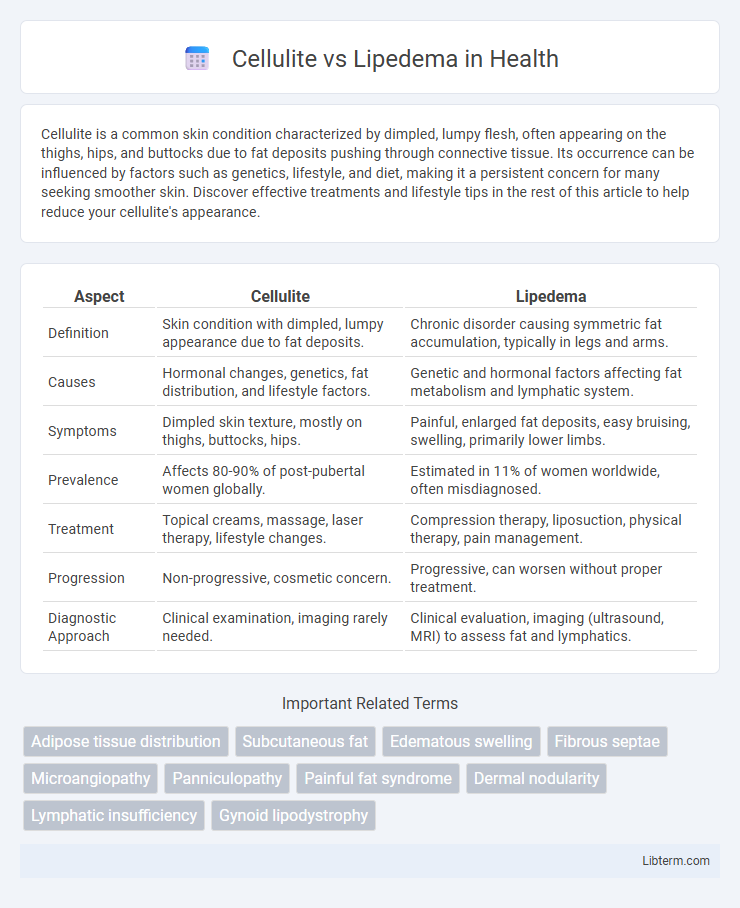
| Aspect | Cellulite | Lipedema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Skin condition with dimpled, lumpy appearance due to fat deposits. | Chronic disorder causing symmetric fat accumulation, typically in legs and arms. |
| Causes | Hormonal changes, genetics, fat distribution, and lifestyle factors. | Genetic and hormonal factors affecting fat metabolism and lymphatic system. |
| Symptoms | Dimpled skin texture, mostly on thighs, buttocks, hips. | Painful, enlarged fat deposits, easy bruising, swelling, primarily lower limbs. |
| Prevalence | Affects 80-90% of post-pubertal women globally. | Estimated in 11% of women worldwide, often misdiagnosed. |
| Treatment | Topical creams, massage, laser therapy, lifestyle changes. | Compression therapy, liposuction, physical therapy, pain management. |
| Progression | Non-progressive, cosmetic concern. | Progressive, can worsen without proper treatment. |
| Diagnostic Approach | Clinical examination, imaging rarely needed. | Clinical evaluation, imaging (ultrasound, MRI) to assess fat and lymphatics. |
Understanding Cellulite: Causes and Characteristics
Cellulite is characterized by the dimpled, lumpy appearance of skin commonly found on the thighs, buttocks, and hips, caused by fat deposits pushing through connective tissue beneath the skin. Factors contributing to cellulite include genetics, hormonal changes, poor circulation, and lifestyle habits such as sedentary behavior and diet. Unlike lipedema, which involves abnormal fat accumulation primarily in the legs and is often painful, cellulite is generally not associated with pain or significant swelling.
What Is Lipedema? Key Features and Symptoms
Lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by symmetrical fat accumulation, primarily affecting the legs and sometimes the arms, distinguishable from cellulite by its nodular, painful texture and resistance to diet and exercise. Key features include disproportionate fat deposits, easy bruising, swelling, and sensitivity to touch, often worsening with hormonal changes such as puberty or pregnancy. Unlike cellulite, lipedema involves inflammation and can lead to mobility issues if untreated, requiring specific medical diagnosis and treatment.
Cellulite and Lipedema: Quick Comparison
Cellulite is a common cosmetic condition characterized by dimpled, uneven skin caused by fat deposits pushing through connective tissue, predominantly affecting thighs and buttocks. Lipedema is a chronic medical disorder involving symmetrical fat accumulation, primarily in the legs and arms, often accompanied by pain and easy bruising. Unlike cellulite, lipedema requires medical diagnosis and treatment due to its progressive nature and impact on mobility.
Risk Factors Associated with Cellulite and Lipedema
Cellulite primarily affects women and is linked to factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, poor circulation, and a sedentary lifestyle, often appearing during puberty, pregnancy, or weight fluctuations. Lipedema is a chronic condition mostly seen in women, with risk factors including family history, hormonal imbalances, and obesity, leading to symmetrical fat accumulation in the lower body. Both conditions are exacerbated by weight gain, yet lipedema involves a pathological fat distribution and pain, whereas cellulite is mainly a cosmetic concern driven by skin and connective tissue structure.
How to Distinguish Between Cellulite and Lipedema
Cellulite presents as dimpled, uneven skin primarily caused by fat pushing through connective tissue, while lipedema is a chronic disorder characterized by symmetrical fat accumulation, often in the legs and arms, that is painful and resistant to diet and exercise. Cellulite typically affects surface skin texture without significant swelling, whereas lipedema leads to swelling, tenderness, and easy bruising due to abnormal fat deposits and fluid retention. Medical diagnosis of lipedema may involve ultrasound or MRI imaging to differentiate it from cellulite and lymphedema, emphasizing the importance of professional evaluation for accurate treatment.
Diagnosis: Identifying Cellulite and Lipedema Correctly
Accurate diagnosis of cellulite and lipedema involves differentiating their distinct clinical features; cellulite presents as dimpled skin primarily on thighs and buttocks, whereas lipedema is characterized by symmetrical fat accumulation and tenderness, often extending to the legs. Diagnostic methods include physical examination, patient history, and imaging techniques like ultrasound or MRI to assess tissue structure and inflammation. Early and precise identification is essential for effective treatment planning and to prevent disease progression or mismanagement.
Treatment Options for Cellulite
Cellulite treatment options primarily focus on improving skin texture and reducing the appearance of dimples through methods like topical creams containing retinol or caffeine, laser therapy, and radiofrequency treatments that stimulate collagen production. Mechanical treatments such as massage, subcision, or acoustic wave therapy can also enhance lymphatic drainage and break down fat deposits. Lifestyle changes, including regular exercise, a healthy diet, and hydration, complement medical procedures by promoting overall skin health and reducing fat accumulation.
Effective Management and Treatment for Lipedema
Effective management of lipedema requires specialized treatments distinct from those used for cellulite, as lipedema is a chronic adipose tissue disorder characterized by symmetrical fat layer deposition and pain. Compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and liposuction tailored for lipedema are the most effective interventions for reducing symptoms and improving mobility. Early diagnosis and a multidisciplinary approach involving nutrition, physical therapy, and psychological support enhance long-term outcomes for lipedema patients.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Tips
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids supports skin health and reduces inflammation linked to both cellulite and lipedema. Regular low-impact exercise such as walking or swimming enhances lymphatic circulation, preventing fluid buildup and fat deposits characteristic of these conditions. Consistent hydration and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing help minimize tissue swelling and promote overall vascular function.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cellulite vs Lipedema
Cellulite and lipedema are often confused due to their similar appearance, but cellulite is caused by fat deposits pushing through connective tissue, resulting in a dimpled skin texture, whereas lipedema is a chronic condition characterized by abnormal fat accumulation and swelling primarily in the legs and arms. Common questions include how to differentiate between the two, with lipedema typically causing pain, easy bruising, and resistance to diet or exercise, unlike cellulite which is mostly cosmetic. Treatments vary significantly: lipedema may require specialized therapy such as compression garments and lymphatic drainage, while cellulite is often addressed through topical creams, laser treatments, or lifestyle changes.
Cellulite Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com