Plaque is a sticky, colorless film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth and gums, leading to decay and gum disease if not removed regularly. Effective oral hygiene, including brushing and flossing, is essential to prevent plaque buildup and maintain a healthy smile. Discover how to combat plaque and protect your oral health by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
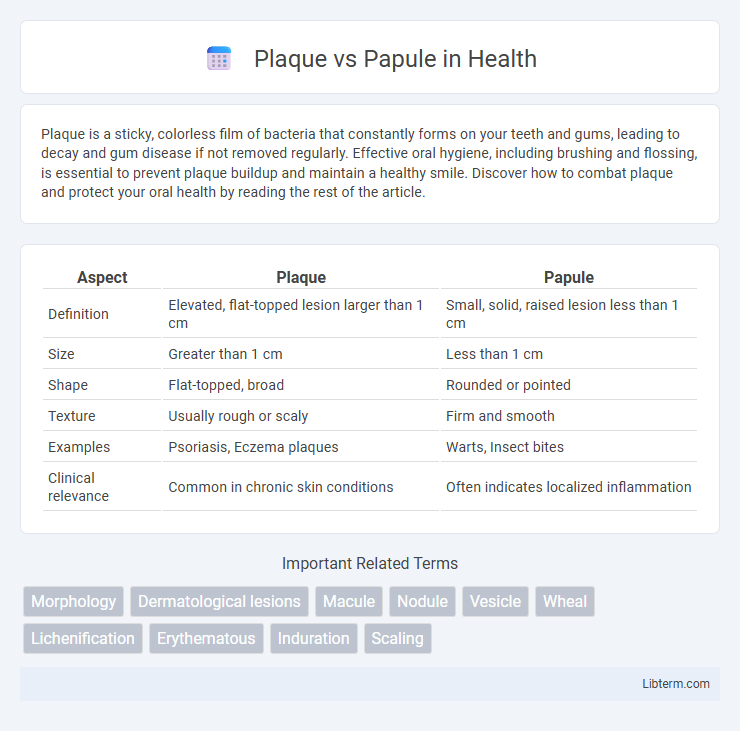
| Aspect | Plaque | Papule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Elevated, flat-topped lesion larger than 1 cm | Small, solid, raised lesion less than 1 cm |
| Size | Greater than 1 cm | Less than 1 cm |
| Shape | Flat-topped, broad | Rounded or pointed |
| Texture | Usually rough or scaly | Firm and smooth |
| Examples | Psoriasis, Eczema plaques | Warts, Insect bites |
| Clinical relevance | Common in chronic skin conditions | Often indicates localized inflammation |
Understanding Plaques and Papules: Key Differences
Plaques are elevated, flat-topped lesions larger than 1 centimeter, commonly seen in conditions such as psoriasis, while papules are smaller, raised, solid bumps under 1 centimeter, often found in acne or dermatitis. The key difference lies in their size and morphology; plaques represent a confluence of papules or scaling skin, whereas papules are distinct, localized elevations. Accurate differentiation of plaques and papules is essential for diagnosing skin diseases and tailoring appropriate dermatologic treatment plans.
What is a Plaque? Definition and Characteristics
A plaque is a raised, flat-topped, and palpable skin lesion typically larger than 1 centimeter in diameter, often formed by the coalescence of papules. It is characterized by its broad, plateau-like surface and can be found in dermatological conditions such as psoriasis and eczema. Plaques represent a thickened, inflamed area of skin resulting from epidermal proliferation or infiltration.
What is a Papule? Definition and Characteristics
A papule is a small, raised, solid bump on the skin typically less than 1 centimeter in diameter, often appearing as a distinct, palpable lesion. Unlike plaques, papules do not form a broad, flat surface but present as localized, dome-shaped elevations due to inflammation or cellular proliferation. Commonly seen in dermatological conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema, papules are key indicators used by clinicians to diagnose and differentiate various skin disorders.
How Plaques Form on the Skin
Plaques form on the skin through the accumulation and thickening of epidermal cells caused by chronic inflammation, often seen in conditions like psoriasis. This process leads to raised, flat-topped lesions larger than 1 centimeter in diameter, distinguishing plaques from smaller papules. In plaque formation, the hyperproliferation of keratinocytes results in scaling and redness that contributes to the characteristic appearance of these lesions.
Common Causes of Papules
Papules are small, raised, solid skin lesions often caused by inflammatory conditions such as acne, eczema, or insect bites. Unlike plaques, which are larger and flat-topped patches of thickened skin seen in psoriasis or chronic dermatitis, papules result from localized cellular infiltration or epidermal hyperplasia. Common causes of papules include viral infections like chickenpox, allergic reactions, and folliculitis, where hair follicles become inflamed.
Visual Differences: Plaque vs Papule
Plaques are elevated, flat-topped lesions larger than 1 centimeter in diameter with a broad surface area, often found in skin conditions like psoriasis. Papules are small, solid, raised lesions under 1 centimeter, typically dome-shaped or pointed and more localized on the skin. Visually, plaques appear as thickened, patchy areas while papules are distinct, well-defined bumps.
Associated Skin Conditions: Plaques
Plaques are elevated, flat-topped lesions commonly associated with chronic skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and lichen planus. These thickened patches result from epidermal hyperplasia and inflammation, often exhibiting scaling and erythema. Plaques can also appear in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and chronic dermatitis, indicating underlying immune dysregulation.
Associated Skin Conditions: Papules
Papules are commonly associated with skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema, presenting as small, raised, solid bumps less than 1 centimeter in diameter. They often indicate inflammatory or infectious processes, including dermatitis and viral infections like molluscum contagiosum. Unlike plaques, papules typically do not have a flat, broad surface but can coalesce to form larger lesions in chronic conditions.
Diagnosis: Identifying Plaques and Papules
Plaques are elevated, flat-topped lesions larger than 1 cm, often seen in conditions like psoriasis, diagnosed through clinical examination and sometimes confirmed by skin biopsy. Papules are small, raised, solid bumps less than 1 cm, frequently observed in acne or dermatitis, identified through visual and tactile assessment. Differentiating plaques from papules is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, relying on lesion size, texture, and distribution patterns.
Treatment Options for Plaques and Papules
Treatment options for plaques primarily include topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and phototherapy, which target inflammation and excessive skin cell growth common in conditions like psoriasis. Papules, often treated with topical retinoids, antibiotics, or corticosteroids, require therapies that reduce inflammation and bacterial presence, especially in acne or dermatitis. For both lesions, targeted treatments depend on the underlying cause, with immunomodulators and systemic medications reserved for severe or resistant cases.
Plaque Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com