Hemiparesis and monoplegia are neurological conditions characterized by muscle weakness or paralysis affecting specific parts of the body. Hemiparesis typically impacts one entire side, while monoplegia is confined to a single limb, both resulting from brain or spinal cord injuries. Explore the full article to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options tailored for your condition.
Table of Comparison
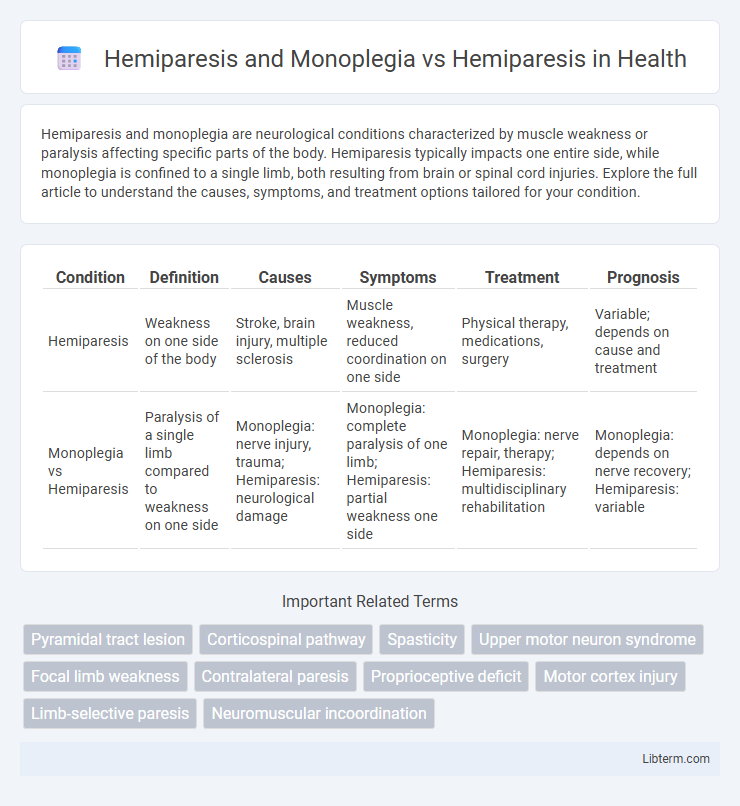
| Condition | Definition | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemiparesis | Weakness on one side of the body | Stroke, brain injury, multiple sclerosis | Muscle weakness, reduced coordination on one side | Physical therapy, medications, surgery | Variable; depends on cause and treatment |
| Monoplegia vs Hemiparesis | Paralysis of a single limb compared to weakness on one side | Monoplegia: nerve injury, trauma; Hemiparesis: neurological damage | Monoplegia: complete paralysis of one limb; Hemiparesis: partial weakness one side | Monoplegia: nerve repair, therapy; Hemiparesis: multidisciplinary rehabilitation | Monoplegia: depends on nerve recovery; Hemiparesis: variable |
Overview of Hemiparesis and Monoplegia
Hemiparesis refers to partial weakness or paralysis affecting one side of the body, commonly resulting from brain injuries such as stroke or traumatic brain injury, while monoplegia involves paralysis confined to a single limb. Both conditions arise from neurological damage disrupting motor pathways, but hemiparesis typically impacts arm, leg, and facial muscles on the affected side. Understanding the distinction aids in targeted rehabilitation strategies tailored to the extent and distribution of muscle weakness.
Defining Hemiparesis: Causes and Symptoms
Hemiparesis is characterized by weakness or partial paralysis on one side of the body, often resulting from brain injuries such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, or neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis. Causes of hemiparesis include ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral palsy, and brain tumors, leading to impaired motor function, muscle weakness, and reduced coordination. Symptoms typically present as diminished strength in the arm, leg, and sometimes the face on one side, along with difficulties in speech, balance, and sensory perception.
Understanding Monoplegia: Key Characteristics
Monoplegia is characterized by paralysis affecting a single limb, differentiating it from hemiparesis, which involves weakness or partial paralysis on one side of the body. Key features of monoplegia include localized muscle weakness, loss of motor function limited to one extremity, and often a clearer prognosis due to the confined nature of the paralysis. Understanding this distinction is crucial for targeted rehabilitation strategies and accurate neurological assessments.
Hemiparesis vs Monoplegia: Clinical Differences
Hemiparesis involves weakness affecting one entire side of the body, usually resulting from strokes or brain injuries, whereas monoplegia refers to paralysis confined to a single limb often due to localized nerve damage or trauma. Clinically, hemiparesis presents with unilateral motor impairment, sensory deficits, and spasticity, while monoplegia typically shows isolated motor loss without widespread neurological symptoms. Diagnostic differentiation relies on neuroimaging and electrophysiological studies to identify lesion location and extent, guiding targeted rehabilitation strategies.
Common Causes of Hemiparesis and Monoplegia
Hemiparesis commonly results from stroke, traumatic brain injury, multiple sclerosis, or brain tumors affecting one side of the brain, leading to weakness on the opposite side of the body. Monoplegia, a paralysis affecting a single limb, often stems from localized nerve injuries, peripheral neuropathies, or brachial plexus lesions. Identifying the precise cause is crucial for targeted treatment and rehabilitation strategies in both hemiparesis and monoplegia cases.
Diagnosis: Evaluating Motor Weakness Patterns
Diagnosis of hemiparesis and monoplegia versus hemiparesis alone involves detailed evaluation of motor weakness patterns and neurological assessments. Hemiparesis typically presents as weakness affecting one side of the body, while monoplegia involves paralysis limited to a single limb. Advanced imaging techniques such as MRI and electromyography (EMG) help differentiate these conditions by identifying lesion locations and nerve involvement.
Treatment Approaches for Hemiparesis and Monoplegia
Treatment approaches for hemiparesis and monoplegia primarily focus on physical and occupational therapies to improve muscle strength, coordination, and motor function. Hemiparesis rehabilitation often involves neuroplasticity-based interventions, such as constraint-induced movement therapy and task-specific training, while monoplegia treatment emphasizes targeted exercises to restore function in the affected limb. Both conditions may benefit from adjunctive therapies including electrical stimulation, pharmacologic management for spasticity, and assistive devices to enhance independence and quality of life.
Rehabilitation Strategies: Tailored Interventions
Rehabilitation strategies for hemiparesis and monoplegia differ due to the extent of motor impairment; hemiparesis involves weakness on one side of the body, requiring comprehensive interventions targeting both upper and lower limbs, while monoplegia affects a single limb, allowing for more focused therapy. Tailored interventions for hemiparesis emphasize bilateral coordination, neuroplasticity through constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT), and functional electrical stimulation to enhance motor recovery. Monoplegia rehabilitation prioritizes repetitive task training and strength conditioning of the affected limb to restore independent motor function efficiently.
Prognosis: Recovery Outcomes and Expectations
Hemiparesis, characterized by weakness on one side of the body, generally has a more favorable prognosis compared to monoplegia, which involves paralysis of a single limb with a more localized recovery potential. Recovery outcomes in hemiparesis often include significant functional improvement due to neuroplasticity and intensive rehabilitation, whereas monoplegia recovery may be limited by the damage extent and specific nerve involvement. Expectations for both conditions depend heavily on the underlying cause, time to intervention, and individualized therapy, with hemiparesis showing broader chances for regaining motor skills and independence.
Living with Hemiparesis or Monoplegia: Patient Perspectives
Living with hemiparesis or monoplegia involves significant adjustments in mobility and daily activities, as patients often experience partial weakness affecting one side of the body or a single limb, respectively. Rehabilitation strategies emphasize physical therapy, adaptive devices, and personalized support to enhance independence and quality of life. Patient perspectives highlight the importance of consistent medical care, emotional resilience, and community support in managing challenges associated with hemiparesis and monoplegia.
Hemiparesis and Monoplegia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com