Cataracts cause clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurry vision and difficulty seeing clearly. This common condition often develops with age but can also result from injury, certain medications, or medical diseases. Discover how you can manage symptoms and explore effective treatment options in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
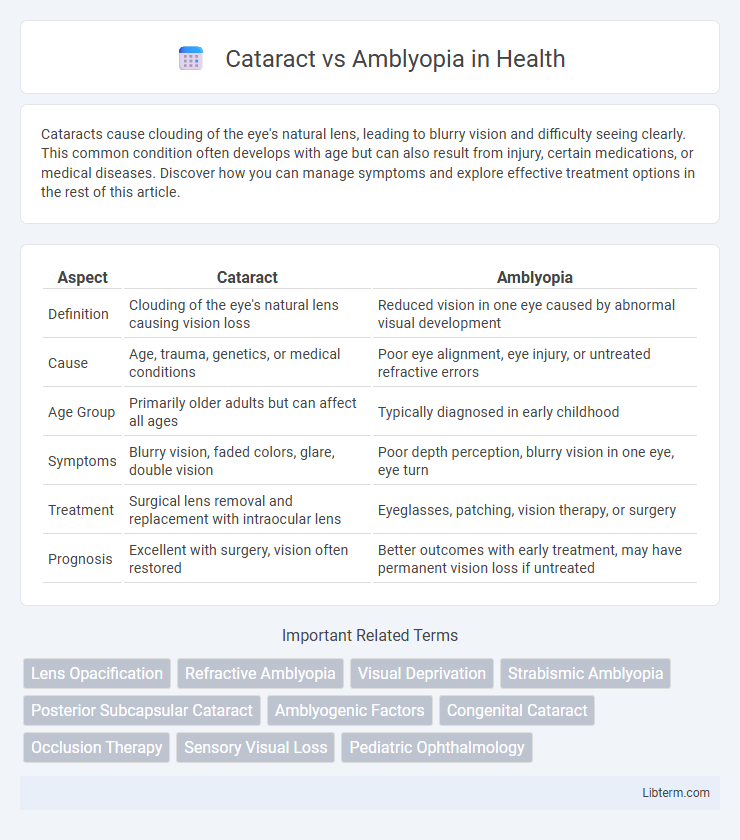
| Aspect | Cataract | Amblyopia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Clouding of the eye's natural lens causing vision loss | Reduced vision in one eye caused by abnormal visual development |
| Cause | Age, trauma, genetics, or medical conditions | Poor eye alignment, eye injury, or untreated refractive errors |
| Age Group | Primarily older adults but can affect all ages | Typically diagnosed in early childhood |
| Symptoms | Blurry vision, faded colors, glare, double vision | Poor depth perception, blurry vision in one eye, eye turn |
| Treatment | Surgical lens removal and replacement with intraocular lens | Eyeglasses, patching, vision therapy, or surgery |
| Prognosis | Excellent with surgery, vision often restored | Better outcomes with early treatment, may have permanent vision loss if untreated |
Understanding Cataract: Definition and Causes
Cataract is a clouding of the eye's natural lens that leads to blurred vision and, if untreated, potential blindness, primarily caused by aging, trauma, or certain medical conditions like diabetes. Unlike amblyopia, which is a developmental vision disorder often referred to as "lazy eye" caused by abnormal visual experience during childhood, cataract develops from protein clumping within the lens. Understanding cataract involves recognizing risk factors such as ultraviolet light exposure, smoking, and prolonged use of corticosteroids, which contribute to lens opacity and visual impairment.
What is Amblyopia? Overview and Origins
Amblyopia, commonly known as "lazy eye," is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by reduced vision in one eye that is not correctable by glasses or contact lenses and is not caused by any eye disease. It originates during early childhood when the brain and the affected eye fail to work together properly, often due to factors like strabismus, refractive errors, or cataracts blocking visual input. This condition disrupts normal visual development, leading to permanent vision impairment if untreated during the critical period of visual maturation.
Key Differences Between Cataract and Amblyopia
Cataract is characterized by clouding of the eye's natural lens, leading to blurred vision and is often age-related, while amblyopia, or "lazy eye," is a neurodevelopmental disorder causing decreased vision in one eye due to abnormal visual experience during childhood. Cataract primarily affects the lens and can often be treated with surgery to restore clarity, whereas amblyopia involves the brain's visual processing pathways and requires early intervention through vision therapy or corrective lenses to improve visual acuity. Unlike cataract, which can develop later in life, amblyopia onset is typically in early childhood and is associated with conditions like strabismus or refractive errors.
Signs and Symptoms: Cataract vs Amblyopia
Cataract symptoms include blurry vision, faded colors, glare sensitivity, and difficulty seeing at night due to clouding of the eye's lens. Amblyopia presents as reduced visual acuity in one eye, poor depth perception, and eye wandering or misalignment, often without visible abnormalities. Unlike cataracts, amblyopia's signs relate to neural development issues rather than lens opacity.
Risk Factors for Cataract and Amblyopia
Cataract risk factors include aging, diabetes, prolonged UV exposure, smoking, and corticosteroid use, which contribute to lens opacity and vision impairment. Amblyopia, often caused by strabismus, refractive errors, or deprivation from cataracts in early childhood, leads to reduced visual acuity in one eye. Early diagnosis and intervention are critical to prevent permanent vision loss in both conditions.
Diagnosis Methods: Cataract and Amblyopia
Cataract diagnosis primarily relies on slit-lamp examination, visual acuity tests, and retro-illumination to detect lens opacities. Amblyopia diagnosis involves assessing visual acuity differences between eyes, refraction tests to identify underlying causes, and eye alignment evaluations to rule out strabismus. Advanced imaging techniques like OCT may assist in differentiating amblyopia from organic causes, while cataract requires clinical slit-lamp confirmation.
Treatment Options for Cataract
Cataract treatment primarily involves surgical removal of the cloudy lens followed by implantation of an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore vision. Phacoemulsification is the most common surgical technique, using ultrasonic waves to break up the cataract for removal through a small incision, promoting rapid recovery. Non-surgical treatments for cataracts are limited and mainly involve prescription glasses or magnifying lenses to temporarily improve vision until surgery is necessary.
Amblyopia Management and Therapies
Amblyopia management primarily involves correcting underlying causes such as refractive errors or cataracts through prescription glasses or surgical intervention. Occlusion therapy using eye patches or pharmacologic penalization helps stimulate the weaker eye to improve visual acuity. Emerging treatments include binocular vision therapy and digital applications designed to enhance neural plasticity and support long-term visual development.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes
Cataract prognosis largely depends on the timing of surgical intervention, with timely removal leading to favorable long-term visual outcomes and minimal risk of permanent vision loss. Amblyopia prognosis is closely tied to early detection and consistent treatment, such as patching or atropine therapy, with delayed therapy often resulting in persistent visual impairment due to neural deficits in the visual cortex. Long-term outcomes for cataract patients typically show significant improvement in visual acuity, while amblyopia patients may experience limited recovery if treatment is initiated after the critical period of visual development.
Prevention and Early Detection Strategies
Cataract prevention focuses on minimizing UV exposure, maintaining a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, and regular eye exams to detect early lens clouding, especially in older adults. Amblyopia prevention emphasizes early vision screening in children to identify and treat conditions like strabismus or refractive errors that impair visual development. Early detection through routine pediatric eye exams and prompt intervention significantly improves outcomes for both cataract and amblyopia, reducing the risk of long-term vision loss.
Cataract Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com