Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions in the body that convert food into energy, enabling cells to perform vital functions. Understanding how your metabolism works can help optimize energy levels and support weight management goals. Explore the full article to learn strategies for boosting your metabolic health effectively.
Table of Comparison
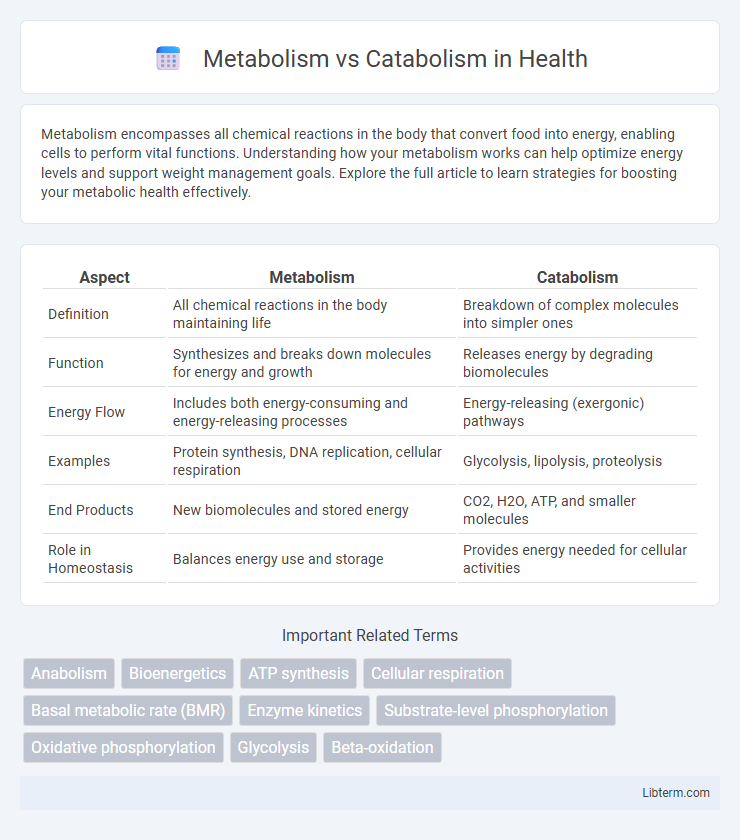
| Aspect | Metabolism | Catabolism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | All chemical reactions in the body maintaining life | Breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones |
| Function | Synthesizes and breaks down molecules for energy and growth | Releases energy by degrading biomolecules |
| Energy Flow | Includes both energy-consuming and energy-releasing processes | Energy-releasing (exergonic) pathways |
| Examples | Protein synthesis, DNA replication, cellular respiration | Glycolysis, lipolysis, proteolysis |
| End Products | New biomolecules and stored energy | CO2, H2O, ATP, and smaller molecules |
| Role in Homeostasis | Balances energy use and storage | Provides energy needed for cellular activities |
Understanding Metabolism: An Overview
Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions in living organisms that convert food into energy, sustaining life processes. Catabolism, a subset of metabolism, involves breaking down complex molecules into simpler ones to release energy. Understanding metabolism requires recognizing its dual role in energy production through catabolism and energy usage in anabolic processes for growth and repair.
What Is Catabolism?
Catabolism is a metabolic process that breaks down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy stored in chemical bonds. It involves reactions such as the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into smaller units like glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids, which cells use to generate ATP. This energy release is essential for fueling various cellular activities and maintaining overall metabolic balance.
Key Differences: Metabolism vs Catabolism
Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions within a cell, including both anabolic and catabolic processes, essential for maintaining life. Catabolism specifically refers to metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units, releasing energy stored in chemical bonds. The key difference lies in metabolism being an umbrella term for all chemical reactions, while catabolism focuses solely on the energy-releasing breakdown of complex molecules.
Role of Catabolic Pathways in the Body
Catabolic pathways play a crucial role in breaking down complex molecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins into simpler molecules like glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids, facilitating energy release. These pathways generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), vital for cellular functions, through processes including glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. By providing energy and essential metabolic intermediates, catabolic pathways support biosynthesis, cellular maintenance, and overall homeostasis within the body.
Anabolic vs Catabolic Processes
Anabolic processes involve the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones, requiring energy input and playing a key role in growth, repair, and storage within metabolism. Catabolic processes break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy that cells use for various functions. Together, anabolic and catabolic pathways maintain metabolic balance, supporting cellular function and energy homeostasis.
How Metabolism Influences Energy Production
Metabolism encompasses all chemical reactions in the body that convert nutrients into energy, with catabolism specifically breaking down molecules to release this energy. During catabolic processes like glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, complex molecules such as carbohydrates and fats are degraded to produce ATP, the primary energy carrier in cells. Efficient metabolism ensures a continuous supply of ATP, driving essential biological functions and maintaining cellular homeostasis.
Enzymes Involved in Catabolic Reactions
Catabolic reactions involve enzymes such as hydrolases, oxidoreductases, and lyases that break down complex molecules into simpler units, releasing energy stored in chemical bonds. Key enzymes include amylase for carbohydrate breakdown, lipase for lipid degradation, and proteases like pepsin and trypsin for protein catabolism. These enzymes facilitate energy production by converting substrates into ATP precursors through pathways like glycolysis and the citric acid cycle.
Factors Affecting Metabolic and Catabolic Rates
Metabolic and catabolic rates are influenced by factors such as age, hormone levels, genetic predisposition, and physical activity. Thyroid hormones play a crucial role in regulating basal metabolic rate, while enzymes determine the efficiency of catabolic reactions. Environmental conditions like temperature and nutrient availability also significantly impact these biological processes.
Metabolic Disorders Linked to Catabolism
Metabolic disorders linked to catabolism involve disruptions in the body's ability to break down complex molecules into simpler ones for energy, leading to conditions such as Maple Syrup Urine Disease or Phenylketonuria. These disorders result from enzymatic deficiencies affecting amino acid or carbohydrate catabolic pathways, causing toxic metabolite accumulation and impaired energy production. Early diagnosis and management are crucial to prevent severe complications including developmental delays, neurological damage, and metabolic crises.
Boosting Metabolic Health: Tips and Strategies
Boosting metabolic health involves enhancing both anabolism and catabolism to maintain efficient energy production and cellular function. Incorporating regular physical activity, balanced nutrition rich in protein and micronutrients, and adequate hydration supports optimal metabolic rate and effective catabolic breakdown of nutrients. Managing stress levels and ensuring quality sleep further regulate hormonal balance, promoting sustained metabolic efficiency and improved metabolic health outcomes.
Metabolism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com