Unani medicine, an ancient holistic healing system, integrates natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments to enhance your overall well-being. Rooted in the principles of balance among bodily humors, it offers personalized treatments for various ailments using herbs, diet, and therapies. Discover how Unani can transform your health by exploring the details in the full article.
Table of Comparison
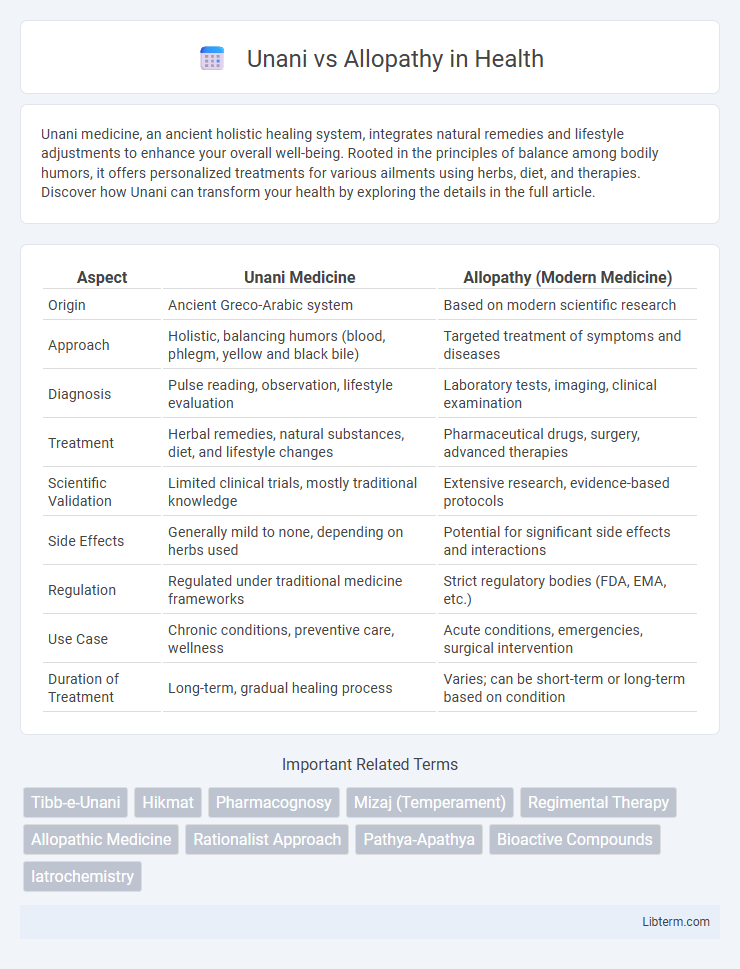
| Aspect | Unani Medicine | Allopathy (Modern Medicine) |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Ancient Greco-Arabic system | Based on modern scientific research |
| Approach | Holistic, balancing humors (blood, phlegm, yellow and black bile) | Targeted treatment of symptoms and diseases |
| Diagnosis | Pulse reading, observation, lifestyle evaluation | Laboratory tests, imaging, clinical examination |
| Treatment | Herbal remedies, natural substances, diet, and lifestyle changes | Pharmaceutical drugs, surgery, advanced therapies |
| Scientific Validation | Limited clinical trials, mostly traditional knowledge | Extensive research, evidence-based protocols |
| Side Effects | Generally mild to none, depending on herbs used | Potential for significant side effects and interactions |
| Regulation | Regulated under traditional medicine frameworks | Strict regulatory bodies (FDA, EMA, etc.) |
| Use Case | Chronic conditions, preventive care, wellness | Acute conditions, emergencies, surgical intervention |
| Duration of Treatment | Long-term, gradual healing process | Varies; can be short-term or long-term based on condition |
Introduction to Unani and Allopathy
Unani medicine is a traditional system rooted in Greco-Arabic principles, emphasizing balance of the four humors--blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile--for health and disease management. Allopathy, also known as modern Western medicine, relies on evidence-based practices, diagnostics, and pharmaceutical interventions to treat symptoms and underlying causes of diseases. Both systems approach health holistically, but Unani integrates natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments, while Allopathy prioritizes technologically advanced treatments and surgical procedures.
Historical Origins of Unani and Allopathic Medicine
Unani medicine traces its origins to ancient Greek and Arab scholars like Hippocrates and Ibn Sina, emphasizing a holistic approach based on the balance of bodily humors. Allopathic medicine, also known as modern Western medicine, developed through scientific advancements since the 19th century, emphasizing evidence-based practices and biochemical mechanisms. Both systems have distinct historical foundations that shape their diagnostic and therapeutic methodologies today.
Core Philosophies and Principles
Unani medicine is based on the balance of the four humors--blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile--emphasizing holistic healing and natural remedies to restore equilibrium in the body. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, relies on evidence-based practices, targeting specific pathogens or physiological dysfunctions with pharmaceuticals and surgical interventions. The core philosophy of Unani centers on promoting wellness through lifestyle, diet, and herbal treatments, while allopathy focuses on diagnosing and treating diseases primarily through measurable clinical outcomes.
Diagnostic Techniques in Unani vs Allopathy
Unani diagnostic techniques emphasize detailed pulse examination (Nabz), urine analysis (Bail), and observation of physical signs to assess imbalances in the four humors, focusing on holistic body assessment. Allopathy relies heavily on advanced laboratory tests, imaging technologies like MRI and CT scans, and biochemical analyses to identify specific pathogens or abnormalities at a molecular and systemic level. While Unani diagnostics prioritize natural symptom observation and humoral theory, Allopathy utilizes evidence-based, technology-driven approaches for precise diagnosis.
Treatment Modalities and Approaches
Unani medicine relies on natural remedies, herbal formulations, and holistic approaches aimed at balancing the body's humors (blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile) to restore health. Allopathy, or modern conventional medicine, utilizes pharmaceutical drugs, surgical interventions, and advanced diagnostic technologies targeting specific diseases and symptoms. While Unani emphasizes personalized treatment and preventive care through lifestyle modifications, Allopathy focuses on evidence-based clinical trials and standardized protocols for rapid symptom relief and disease management.
Safety, Efficacy, and Side Effects
Unani medicine emphasizes natural herbs and holistic balance, offering treatments with fewer side effects but variable scientific validation on efficacy compared to allopathy. Allopathy provides evidence-based interventions with proven efficacy for acute and chronic conditions but carries a higher risk of side effects due to synthetic drugs and invasive procedures. Safety profiles differ as Unani treatments are generally safer for long-term use, while allopathic methods are critical for emergency and severe disease management.
Integration and Acceptance in Modern Healthcare
Unani medicine, rooted in ancient Greco-Arabic traditions, is increasingly integrated into modern healthcare systems through evidence-based practices and collaborative treatment approaches alongside allopathy. Hospitals and research institutions worldwide recognize the benefits of combining Unani's holistic principles with allopathy's targeted interventions to enhance patient outcomes, especially in chronic disease management. Growing acceptance is evident in policy frameworks and healthcare programs that encourage complementary use, promoting a synergy between traditional and modern therapeutic methods.
Popularity and Global Reach
Unani medicine, originating from ancient Greek and Islamic traditions, remains popular primarily in South Asia and the Middle East, with significant use in countries such as India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. Allopathy, or modern Western medicine, dominates global healthcare systems due to its evidence-based approach, extensive research, and widespread institutional support across North America, Europe, and many parts of Asia. Worldwide, allopathy maintains higher popularity and global reach, supported by advanced technology, pharmaceutical advancements, and universal accessibility in both urban and rural areas.
Common Misconceptions and Myths
Unani medicine is often misunderstood as unscientific despite its rich history of herbal and holistic treatments supported by clinical practice, while allopathy is sometimes wrongly perceived as free from side effects due to its reliance on modern pharmaceuticals. A common misconception is that Unani lacks efficacy, whereas scientific studies increasingly validate its role in managing chronic diseases through personalized care. Conversely, allopathy is frequently seen as the only evidence-based system, ignoring ongoing research into integrative approaches that combine both practices for comprehensive health benefits.
Future Prospects and Comparative Outlook
Unani medicine, rooted in ancient Greco-Arabic principles, shows promising growth due to its holistic approach and minimal side effects, gaining increased acceptance in integrative healthcare systems worldwide. Allopathy remains dominant, driven by advanced biomedical research, rapid technological innovations, and evidence-based treatment protocols, ensuring its critical role in managing acute and complex health conditions. Future prospects highlight a potential synergy where Unani complements allopathic care, promoting personalized medicine and expanding therapeutic options for chronic illness management.
Unani Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com