Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden episodes of muscle weakness known as cataplexy. It often disrupts daily activities and impacts overall quality of life due to unpredictable sleep attacks and difficulty maintaining regular sleep patterns. Discover more about managing narcolepsy and improving your sleep health in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
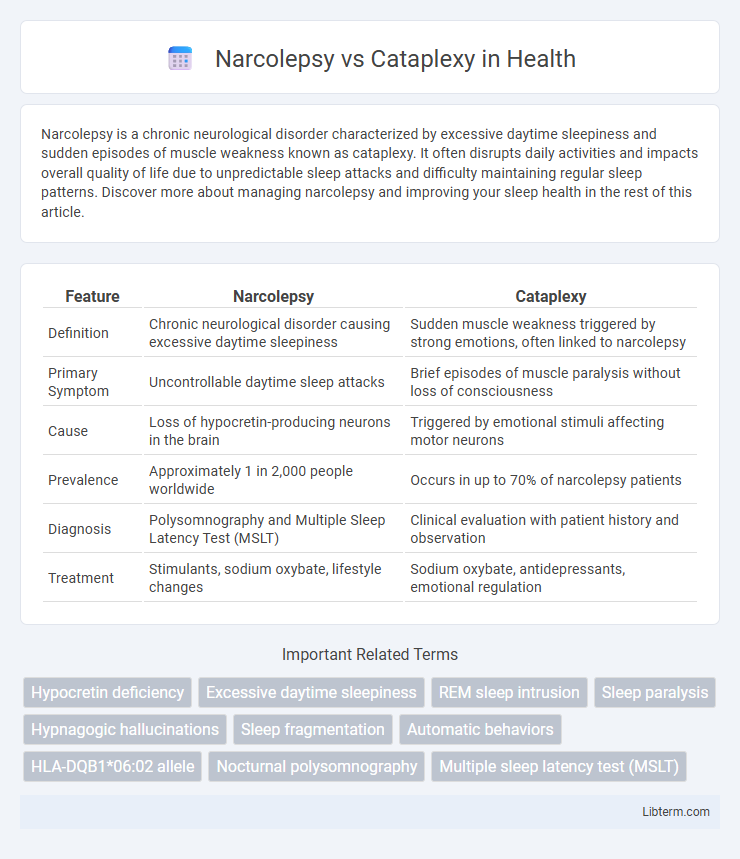
| Feature | Narcolepsy | Cataplexy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Chronic neurological disorder causing excessive daytime sleepiness | Sudden muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions, often linked to narcolepsy |
| Primary Symptom | Uncontrollable daytime sleep attacks | Brief episodes of muscle paralysis without loss of consciousness |
| Cause | Loss of hypocretin-producing neurons in the brain | Triggered by emotional stimuli affecting motor neurons |
| Prevalence | Approximately 1 in 2,000 people worldwide | Occurs in up to 70% of narcolepsy patients |
| Diagnosis | Polysomnography and Multiple Sleep Latency Test (MSLT) | Clinical evaluation with patient history and observation |
| Treatment | Stimulants, sodium oxybate, lifestyle changes | Sodium oxybate, antidepressants, emotional regulation |
Understanding Narcolepsy: Definition and Key Features
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden loss of muscle control, and disrupted nighttime sleep patterns. Cataplexy is a distinct symptom of narcolepsy, involving sudden, brief episodes of muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or anger. Understanding the relationship between narcolepsy and cataplexy is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management of these intertwined sleep disorders.
What Is Cataplexy? Core Symptoms and Triggers
Cataplexy is a sudden, brief loss of voluntary muscle tone triggered by strong emotions like laughter, anger, or surprise, often occurring in individuals with narcolepsy. Core symptoms include muscle weakness, limpness, and collapse without loss of consciousness, typically lasting seconds to minutes. Emotional stressors serve as primary triggers for cataplexy episodes, distinguishing it from other sleep-related disorders.
Narcolepsy vs Cataplexy: Main Differences
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks, whereas cataplexy is a symptom typically associated with narcolepsy involving sudden, temporary muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions. Narcolepsy affects the brain's ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, while cataplexy specifically impacts muscle control without loss of consciousness. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies for patients.
Similarities Between Narcolepsy and Cataplexy
Narcolepsy and cataplexy share key symptoms involving sudden muscle weakness and excessive daytime sleepiness, indicating disruptions in the brain's sleep-wake regulation. Both conditions often result from abnormalities in hypocretin (orexin) neurotransmitter pathways, which are crucial for maintaining wakefulness and muscle tone. Patients with narcolepsy frequently experience cataplexy as a primary symptom, linking the two disorders through overlapping neurological mechanisms.
Causes and Risk Factors: Narcolepsy and Cataplexy
Narcolepsy is primarily caused by the loss of hypocretin-producing neurons in the hypothalamus, often linked to autoimmune mechanisms, while cataplexy is a sudden muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions and is considered a symptom of narcolepsy type 1. Genetic factors, such as the presence of the HLA-DQB1*06:02 allele, significantly increase the risk of narcolepsy with cataplexy, along with environmental triggers like infections or stress. Both disorders are influenced by complex interactions between genetic predisposition and environmental factors, making diagnosis and management challenging.
Recognizing Symptoms: How Narcolepsy and Cataplexy Present
Narcolepsy presents through excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden sleep attacks, and fragmented nighttime sleep, while cataplexy is characterized by sudden muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions like laughter or surprise. Narcolepsy often includes symptoms such as sleep paralysis and hallucinations, whereas cataplexy is specifically a symptom seen in narcolepsy type 1. Recognizing these distinct manifestations is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning.
Diagnostic Methods: Distinguishing Between the Two
Narcolepsy diagnosis relies on polysomnography followed by the multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) to assess sleep onset and REM latency, while cataplexy is primarily identified through detailed clinical history focusing on sudden muscle weakness triggered by emotions. Hypocretin-1 levels in cerebrospinal fluid serve as a biomarker to differentiate narcolepsy with cataplexy (type 1) from narcolepsy without cataplexy (type 2). Genetic testing for HLA-DQB1*06:02 helps support diagnosis but is not definitive alone, emphasizing the importance of combining clinical and laboratory data.
Treatment Options: Narcolepsy Versus Cataplexy
Treatment options for narcolepsy primarily include stimulant medications such as modafinil or armodafinil to improve wakefulness and sodium oxybate to reduce excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy episodes. Cataplexy-specific treatments focus on suppressing sudden muscle weakness using antidepressants like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants, which reduce the frequency and severity of cataplexy attacks. Both conditions benefit from lifestyle modifications, including scheduled naps and sleep hygiene improvements, to manage symptoms effectively.
Living with Narcolepsy or Cataplexy: Coping Strategies
Living with narcolepsy or cataplexy requires tailored coping strategies such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule to manage excessive daytime sleepiness and prevent sudden muscle weakness episodes. Utilizing support networks including healthcare providers, therapy groups, and education about triggers helps patients maintain safety and emotional well-being. Incorporating lifestyle adjustments like scheduled naps, stress reduction techniques, and medication adherence optimizes symptom control and improves quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions: Narcolepsy vs Cataplexy
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks, while cataplexy involves sudden, brief episodes of muscle weakness triggered by strong emotions, often occurring in people with narcolepsy. Key differences include that narcolepsy primarily affects sleep regulation, whereas cataplexy specifically impacts muscle control without loss of consciousness. FAQs often address whether cataplexy can occur independently--rarely--and how both conditions are diagnosed through sleep studies and clinical evaluation.
Narcolepsy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com